1️⃣ Ministry of Electronics & Information Technology (MeitY):
• Semiconductor Manufacturing: Approval of four semiconductor manufacturing units under the Semicon India Programme.
• Artificial Intelligence Leadership: Hosted the 6th meeting of the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Ministerial Council in New Delhi; set to be the outgoing chair in 2025.
• Skill Development: Trained 6.39 crore individuals under the Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (PMGDISHA), exceeding the target of 6 crore.
• Language Accessibility: BHASHINI initiative bridged language barriers for accessible digital services, offering translation services in 22 scheduled Indian languages.
• Supercomputing Infrastructure: Launched three PARAM Rudra supercomputers to strengthen research and innovation in India.
• Semiconductor Manufacturing: Approval of four semiconductor manufacturing units under the Semicon India Programme.
• Artificial Intelligence Leadership: Hosted the 6th meeting of the Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI) Ministerial Council in New Delhi; set to be the outgoing chair in 2025.
• Skill Development: Trained 6.39 crore individuals under the Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (PMGDISHA), exceeding the target of 6 crore.
• Language Accessibility: BHASHINI initiative bridged language barriers for accessible digital services, offering translation services in 22 scheduled Indian languages.
• Supercomputing Infrastructure: Launched three PARAM Rudra supercomputers to strengthen research and innovation in India.
2️⃣ Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change:
• Afforestation Efforts: Achieved the milestone of planting 102 crore trees under the 'Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam' campaign, aiming for 140 crore by March 2025.
• Eco-Mark Rules: Notified the Eco-mark Rules on 26th September 2024 to promote environmentally friendly products.
• Air Quality Improvement: Under the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP), achieved a 40% reduction in particulate matter in 23 cities; allocated ₹11,200 crore for pollution control; launched the PRANA Portal for real-time air quality monitoring.
• Mangrove Restoration: Launched MISHTI on World Environment Day 2024 to restore mangroves and boost coastal sustainability.
• Biodiversity Conservation: Notified the Biological Diversity Rules, 2024, and increased the number of tiger reserves in India to 57 with the addition of two new reserves.
• Afforestation Efforts: Achieved the milestone of planting 102 crore trees under the 'Ek Ped Maa Ke Naam' campaign, aiming for 140 crore by March 2025.
• Eco-Mark Rules: Notified the Eco-mark Rules on 26th September 2024 to promote environmentally friendly products.
• Air Quality Improvement: Under the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP), achieved a 40% reduction in particulate matter in 23 cities; allocated ₹11,200 crore for pollution control; launched the PRANA Portal for real-time air quality monitoring.
• Mangrove Restoration: Launched MISHTI on World Environment Day 2024 to restore mangroves and boost coastal sustainability.
• Biodiversity Conservation: Notified the Biological Diversity Rules, 2024, and increased the number of tiger reserves in India to 57 with the addition of two new reserves.
3️⃣ Ministry of Home Affairs:
• Criminal Law Reforms: Enacted three new criminal laws—Bharatiya Nyay Sanhita, Bharatiya Nagrik Suraksha Sanhita, and Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam—to ensure justice-oriented and victim-centric legal processes.
• Disaster Management: Passed the Disaster Management (Amendment) Bill to empower response forces for more effective disaster management.
• Counter-Terrorism Efforts: Strengthened measures to create a terror-free Jammu and Kashmir through a multi-pronged approach.
• Naxalism Reduction: Achieved significant success in curbing left-wing extremism, eliminating 287 Naxalites and arresting 992 individuals.
• Drug Abuse Helpline: Launched MANAS with a toll-free number 1933, a web portal, and mobile app to provide support for de-addiction and rehabilitation.
• Peace Accords: Signed a tripartite agreement to end conflicts in the Northeast by fulfilling long-pending demands.
• Women's Safety: Approved the establishment of the first all-women battalion of CISF and continued the 'Safety of Women' scheme with a total outlay of ₹1,179.72 crore.
• Criminal Law Reforms: Enacted three new criminal laws—Bharatiya Nyay Sanhita, Bharatiya Nagrik Suraksha Sanhita, and Bharatiya Sakshya Adhiniyam—to ensure justice-oriented and victim-centric legal processes.
• Disaster Management: Passed the Disaster Management (Amendment) Bill to empower response forces for more effective disaster management.
• Counter-Terrorism Efforts: Strengthened measures to create a terror-free Jammu and Kashmir through a multi-pronged approach.
• Naxalism Reduction: Achieved significant success in curbing left-wing extremism, eliminating 287 Naxalites and arresting 992 individuals.
• Drug Abuse Helpline: Launched MANAS with a toll-free number 1933, a web portal, and mobile app to provide support for de-addiction and rehabilitation.
• Peace Accords: Signed a tripartite agreement to end conflicts in the Northeast by fulfilling long-pending demands.
• Women's Safety: Approved the establishment of the first all-women battalion of CISF and continued the 'Safety of Women' scheme with a total outlay of ₹1,179.72 crore.
4️⃣ Ministry of Commerce and Industry:
• Trade Agreements: Signed the Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement with the European Free Trade Association; re-launched negotiations for the India-European Union Free Trade Agreement.
• Bharat Mart: Launched a global trade hub for Indian exporters in Dubai to enhance international trade opportunities.
• Trade Connect e-Platform: Introduced a single-window initiative to assist exporters and MSMEs in accessing new markets.
• Trade Agreements: Signed the Trade and Economic Partnership Agreement with the European Free Trade Association; re-launched negotiations for the India-European Union Free Trade Agreement.
• Bharat Mart: Launched a global trade hub for Indian exporters in Dubai to enhance international trade opportunities.
• Trade Connect e-Platform: Introduced a single-window initiative to assist exporters and MSMEs in accessing new markets.
5️⃣ Ministry of Railways:
• Track Renewal and Speed Enhancement: Completed 6,450 km of track renewal, 8,550 turnout renewals, and increased speeds to 130 kmph over 2,000 km.
• Electrification: Electrified 3,210 Route kilometers (Rkm), extending the electrified Broad Gauge network to 97% with renewable energy capacity reaching 2,014 MW.
• Introduction of New Trains: Introduced a record 136 Vande Bharat trains and the first Namo Bharat Rapid Rail.
• Freight Loading: Achieved 1,473 million tonnes (MT) of freight loading, marking a 3.86% growth.
• Station Development: Commenced work on 1,198 stations under the Amrit Bharat Station Scheme.
• Safety Technology: Equipped 10,000 locomotives with Kavach safety technology and trained 9,000 technicians.
• Heritage Digitization: Digitized heritage sites, including 80 stations and 78 structures, to boost tourism.
• Track Renewal and Speed Enhancement: Completed 6,450 km of track renewal, 8,550 turnout renewals, and increased speeds to 130 kmph over 2,000 km.
• Electrification: Electrified 3,210 Route kilometers (Rkm), extending the electrified Broad Gauge network to 97% with renewable energy capacity reaching 2,014 MW.
• Introduction of New Trains: Introduced a record 136 Vande Bharat trains and the first Namo Bharat Rapid Rail.
• Freight Loading: Achieved 1,473 million tonnes (MT) of freight loading, marking a 3.86% growth.
• Station Development: Commenced work on 1,198 stations under the Amrit Bharat Station Scheme.
• Safety Technology: Equipped 10,000 locomotives with Kavach safety technology and trained 9,000 technicians.
• Heritage Digitization: Digitized heritage sites, including 80 stations and 78 structures, to boost tourism.
6️⃣ Ministry of Food Processing Industries:
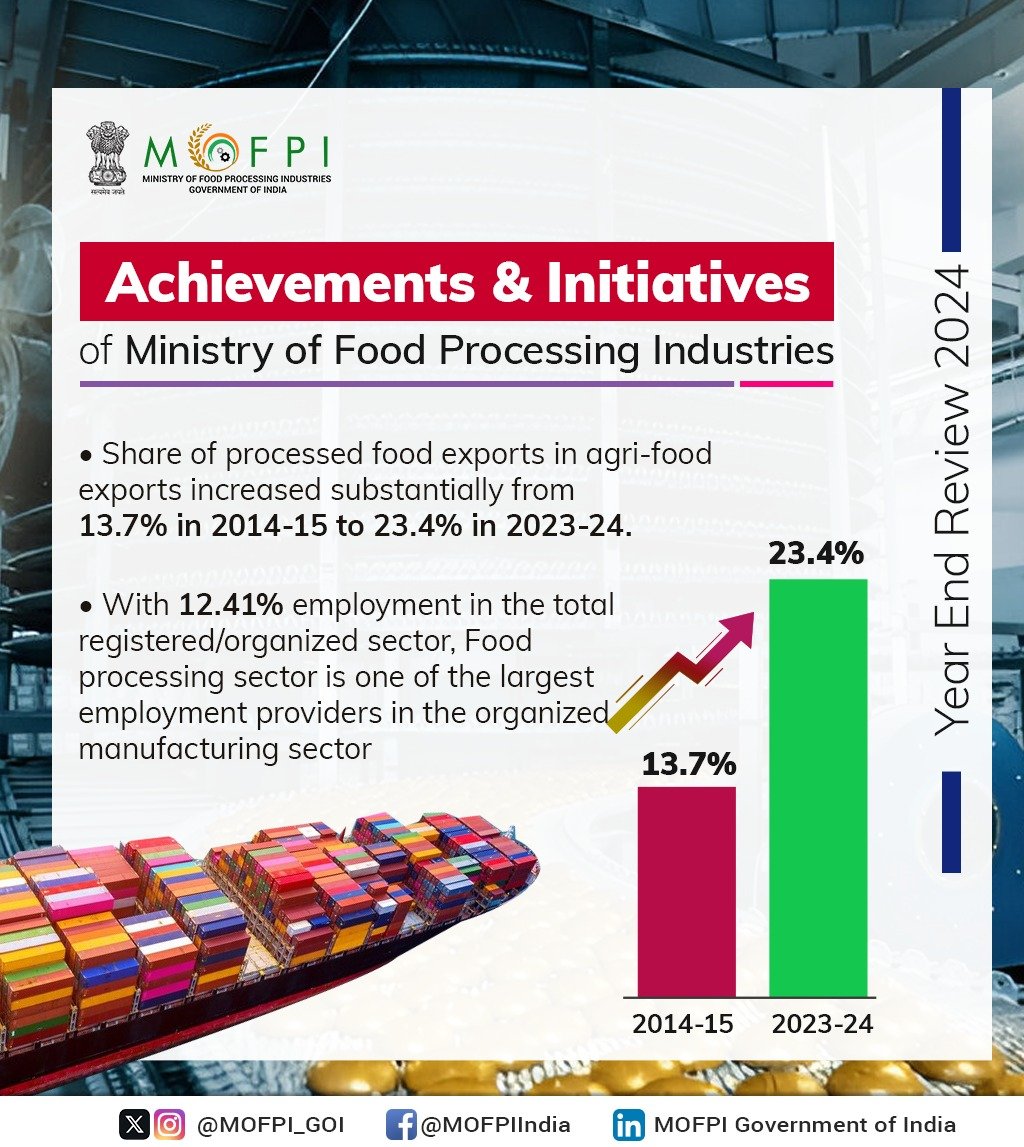
• Processed Food Exports: Increased the share of processed food exports in agri-food exports from 13.7% in 2014-15 to 23.4% in 2023-24.
• Employment Generation: Recognized as one of the largest employment providers in the organized manufacturing sector, contributing 12.41% to total registered sector employment.
• Credit Support: Sanctioned 46,643 loans under the credit-linked subsidy component of the PM Formalization of Micro Food Processing Enterprises (PMFME) scheme since January 2024.
• Processed Food Exports: Increased the share of processed food exports in agri-food exports from 13.7% in 2014-15 to 23.4% in 2023-24.
• Employment Generation: Recognized as one of the largest employment providers in the organized manufacturing sector, contributing 12.41% to total registered sector employment.
• Credit Support: Sanctioned 46,643 loans under the credit-linked subsidy component of the PM Formalization of Micro Food Processing Enterprises (PMFME) scheme since January 2024.
7️⃣ Ministry of Tourism:
• International Tourist Arrivals: Recorded 18.89 million international tourist arrivals in 2023.
• Foreign Exchange Earnings: Achieved foreign exchange earnings of ₹2,31,927 crore through tourism during 2023.
• Domestic Tourism: Registered 2,509 million domestic tourist visits during 2023.
• Development Projects: Approved 40 projects worth
• International Tourist Arrivals: Recorded 18.89 million international tourist arrivals in 2023.
• Foreign Exchange Earnings: Achieved foreign exchange earnings of ₹2,31,927 crore through tourism during 2023.
• Domestic Tourism: Registered 2,509 million domestic tourist visits during 2023.
• Development Projects: Approved 40 projects worth
8️⃣ Ministry of Health & Family Welfare:
• Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (AAM): As of November 30, 2024, 1,75,338 AAMs have been operationalized, offering an expanded package of 12 services and tele-consultation facilities, with a footfall of 360 crore and 30.75 crore tele-consultations.
• Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY): Currently, 55 crore individuals corresponding to 12.37 crore families are covered under the scheme. Several States/UTs have expanded the beneficiary base at their own cost.
• Strengthening Surveillance of Infectious Diseases: Implemented by the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC); 26 NCDC State branches, 5 NCDC Regional branches, 10 Biosafety Level-3 laboratories, and 20 Metropolitan Surveillance Units are in various stages of establishment.
• U-WIN Platform: As of December 15, 2024, 7.90 crore beneficiaries have been registered, 1.32 crore vaccination sessions held, and 29.22 crore administered vaccine doses recorded on U-WIN.
• Ayush-ICMR Advanced Centres for Integrated Health Research: Launched six centers in four AIIMS (Delhi, Jodhpur, Nagpur, Rishikesh) to promote integrated health research.
• Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (AAM): As of November 30, 2024, 1,75,338 AAMs have been operationalized, offering an expanded package of 12 services and tele-consultation facilities, with a footfall of 360 crore and 30.75 crore tele-consultations.
• Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY): Currently, 55 crore individuals corresponding to 12.37 crore families are covered under the scheme. Several States/UTs have expanded the beneficiary base at their own cost.
• Strengthening Surveillance of Infectious Diseases: Implemented by the National Centre for Disease Control (NCDC); 26 NCDC State branches, 5 NCDC Regional branches, 10 Biosafety Level-3 laboratories, and 20 Metropolitan Surveillance Units are in various stages of establishment.
• U-WIN Platform: As of December 15, 2024, 7.90 crore beneficiaries have been registered, 1.32 crore vaccination sessions held, and 29.22 crore administered vaccine doses recorded on U-WIN.
• Ayush-ICMR Advanced Centres for Integrated Health Research: Launched six centers in four AIIMS (Delhi, Jodhpur, Nagpur, Rishikesh) to promote integrated health research.
9️⃣ Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs:
• Urban Housing and PMAY 2.0: Introduced a new Rental Housing Vertical under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) 2.0, benefiting migrant populations, working women, industrial workers, homeless individuals, students, and other beneficiaries.
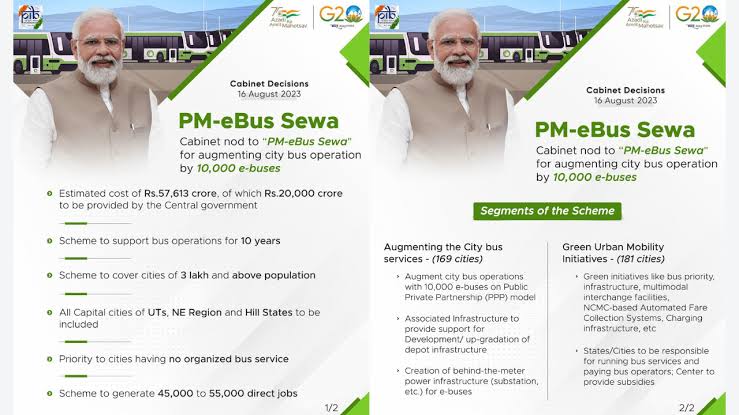
• PM-e-Bus Sewa: Launched on August 16, 2023, aiming to augment urban bus operations with Central Assistance of ₹20,000 crore for deploying 10,000 fully air-conditioned electric buses under the Gross Cost Contract (GCC) model.
• Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban (SBM-U): The government released over ₹1,123 crore for projects in nine states—Assam, Bihar, Delhi, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Mizoram, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal—for Solid Waste and Used Water Management, Information, Education, and Communication (IEC), and Capacity Building Projects.
• Capital Expenditure (Capex) Targets: The Ministry has been urged to ensure efficient utilization of the ₹28,628 crore budget allocated for the financial year 2024-25 to meet urban development goals.
• Urban Housing and PMAY 2.0: Introduced a new Rental Housing Vertical under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) 2.0, benefiting migrant populations, working women, industrial workers, homeless individuals, students, and other beneficiaries.
• PM-e-Bus Sewa: Launched on August 16, 2023, aiming to augment urban bus operations with Central Assistance of ₹20,000 crore for deploying 10,000 fully air-conditioned electric buses under the Gross Cost Contract (GCC) model.
• Swachh Bharat Mission-Urban (SBM-U): The government released over ₹1,123 crore for projects in nine states—Assam, Bihar, Delhi, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Mizoram, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal—for Solid Waste and Used Water Management, Information, Education, and Communication (IEC), and Capacity Building Projects.
• Capital Expenditure (Capex) Targets: The Ministry has been urged to ensure efficient utilization of the ₹28,628 crore budget allocated for the financial year 2024-25 to meet urban development goals.
🔟 Ministry of Defence:
• Indigenization Efforts: The Ministry notified the fifth Positive Indigenisation List, comprising 346 items, to boost self-reliance in defence production.
• Defence Production: Achieved a record-high defence production figure of ₹1,26,887 crore, reflecting a growth of 16.7% over the previous financial year.
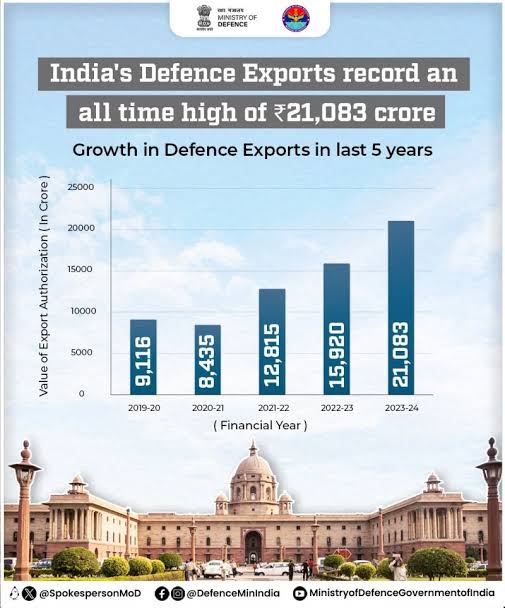
• Defence Exports: Defence exports reached ₹21,083 crore (approximately US$2.63 billion), marking a growth of 32.5% over the previous fiscal year.
• Indigenization Efforts: The Ministry notified the fifth Positive Indigenisation List, comprising 346 items, to boost self-reliance in defence production.
• Defence Production: Achieved a record-high defence production figure of ₹1,26,887 crore, reflecting a growth of 16.7% over the previous financial year.
• Defence Exports: Defence exports reached ₹21,083 crore (approximately US$2.63 billion), marking a growth of 32.5% over the previous fiscal year.
Loading suggestions...