India mourns the loss of former Prime Minister Manmohan Singh.
🧵 A Visionary Leader and Architect of Modern India.
Here are his major contributions to India... x.com
🧵 A Visionary Leader and Architect of Modern India.
Here are his major contributions to India... x.com
As FINANCE MINISTER (1991-1996):
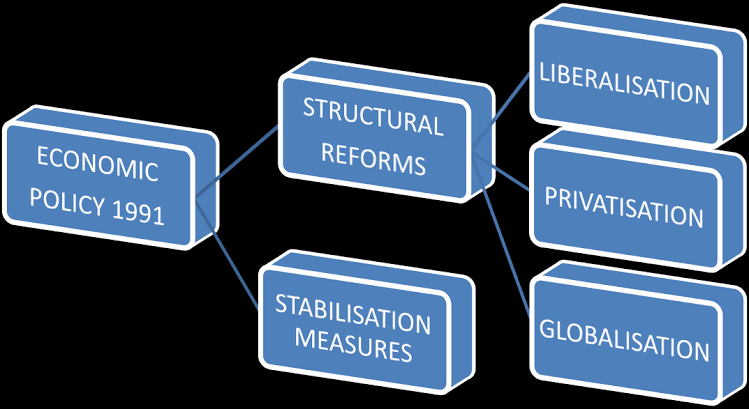
1991 Economic Reforms:
Singh is widely credited with initiating and overseeing the liberalization of the Indian economy. Facing a severe balance of payments crisis, he introduced a series of reforms that included:
1️⃣ Devaluation of the Rupee: This aimed to make exports more competitive and imports more expensive, thereby addressing the trade imbalance.
2️⃣ Fiscal Correction: Measures were taken to reduce the fiscal deficit, a key element in stabilizing the economy.
3️⃣ Tax Reforms: Gradual reduction of import duties, income tax, and corporate tax aimed at simplifying the tax structure and promoting investment.
4️⃣ Deregulation and Liberalization: The reforms dismantled the "License Raj," a complex system of licenses and permits required to operate businesses. This move encouraged private sector participation and competition.
1991 Economic Reforms:
Singh is widely credited with initiating and overseeing the liberalization of the Indian economy. Facing a severe balance of payments crisis, he introduced a series of reforms that included:
1️⃣ Devaluation of the Rupee: This aimed to make exports more competitive and imports more expensive, thereby addressing the trade imbalance.
2️⃣ Fiscal Correction: Measures were taken to reduce the fiscal deficit, a key element in stabilizing the economy.
3️⃣ Tax Reforms: Gradual reduction of import duties, income tax, and corporate tax aimed at simplifying the tax structure and promoting investment.
4️⃣ Deregulation and Liberalization: The reforms dismantled the "License Raj," a complex system of licenses and permits required to operate businesses. This move encouraged private sector participation and competition.
As PRIME MINISTER (2004-2014):
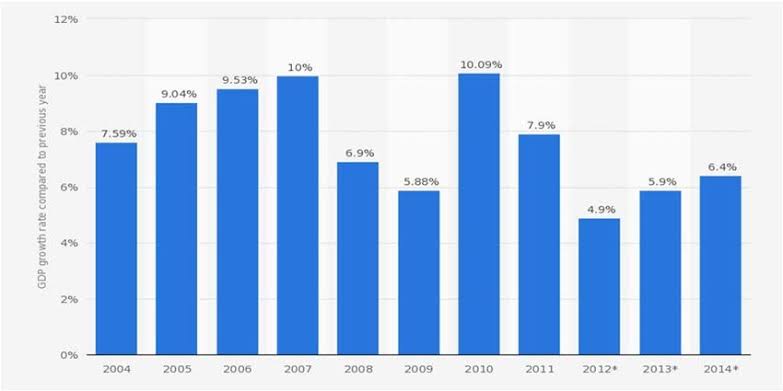
1️⃣ Economic Growth:
• India experienced a period of significant economic growth during Singh's tenure as Prime Minister.
• This was partly driven by the continuation of economic reforms and liberalization policies. x.com
1️⃣ Economic Growth:
• India experienced a period of significant economic growth during Singh's tenure as Prime Minister.
• This was partly driven by the continuation of economic reforms and liberalization policies. x.com
2️⃣ National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (NREGA):
• This flagship program aimed to provide guaranteed employment to rural households, contributing to poverty reduction and rural development. x.com
• This flagship program aimed to provide guaranteed employment to rural households, contributing to poverty reduction and rural development. x.com
3️⃣ Right to Information Act (RTI): The RTI Act, passed during Singh's government, empowered citizens to access information from government bodies, promoting transparency and accountability. x.com
4️⃣ National Food Security Act (NFSA):
• The NFSA aimed to provide subsidized food grains to a large portion of the population, addressing food security concerns. x.com
• The NFSA aimed to provide subsidized food grains to a large portion of the population, addressing food security concerns. x.com
5️⃣ Value Added Tax (VAT)
• Implementation: Building on earlier reforms, the introduction of VAT in 2005 streamlined the indirect tax system.
• VAT was replaced by Goods and Services Tax (GST), all over India from 1 July 2017.
• Implementation: Building on earlier reforms, the introduction of VAT in 2005 streamlined the indirect tax system.
• VAT was replaced by Goods and Services Tax (GST), all over India from 1 July 2017.
6️⃣ Strengthened Foreign Relations:
Singh's government pursued stronger ties with various countries.
1. The Indo-US Civilian Nuclear Agreement was a significant development during his tenure.
2. Strengthened Relations with the US: Singh prioritised building a stronger strategic partnership with the United States, encompassing cooperation in defense, trade, and technology.
3. Look East Policy: He further developed the "Look East Policy," initiated by his predecessor, to deepen engagement with Southeast Asian countries, fostering economic and strategic ties.
4. Improved Relations with China: Despite existing border disputes, Singh's government worked towards managing differences and expanding economic cooperation with China.
5. Engagement with Pakistan: Singh continued efforts to improve relations with Pakistan through dialogue and confidence-building measures, although progress remained challenging.
6. Focus on Multilateral Forums: He actively participated in and strengthened India's role in multilateral forums like the G20, BRICS, and the East Asia Summit, advocating for India's interests on global issues.
Singh's government pursued stronger ties with various countries.
1. The Indo-US Civilian Nuclear Agreement was a significant development during his tenure.
2. Strengthened Relations with the US: Singh prioritised building a stronger strategic partnership with the United States, encompassing cooperation in defense, trade, and technology.
3. Look East Policy: He further developed the "Look East Policy," initiated by his predecessor, to deepen engagement with Southeast Asian countries, fostering economic and strategic ties.
4. Improved Relations with China: Despite existing border disputes, Singh's government worked towards managing differences and expanding economic cooperation with China.
5. Engagement with Pakistan: Singh continued efforts to improve relations with Pakistan through dialogue and confidence-building measures, although progress remained challenging.
6. Focus on Multilateral Forums: He actively participated in and strengthened India's role in multilateral forums like the G20, BRICS, and the East Asia Summit, advocating for India's interests on global issues.
Loading suggestions...