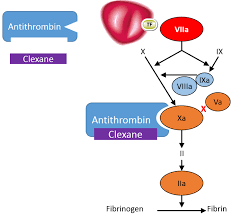
Lets learn about the most given anticoagulation in hospitals , clexane/ enoxaparin.
Easy peasy. Some important information what everyone should know.
#MedTwitter
Easy peasy. Some important information what everyone should know.
#MedTwitter
This results in anticoagulation.
Usual prophylactic dose in hospital settings to prevent DVT is 40mg sc once a day and therapeutic dose is either 1mg/kg bid or 1.5mg/kg once a day.
Usual prophylactic dose in hospital settings to prevent DVT is 40mg sc once a day and therapeutic dose is either 1mg/kg bid or 1.5mg/kg once a day.
Half life is approximately 12 hours compared to unfractionated heparin, which last only 4 hours. So if you plan to do any surgery or procedure, it better should be stopped atleast 12 hours before.
Creatinine clearance <30ml/s, is a contraindication of using enoxaparin. Other option is unfractionated heparin which can easily be given in renal failure patients.
One con is that you cannot measure the anticoagulant effect by measuring PT/INR, PTT. So how do you know in such a patient if adequate anticoagulation is achieved?
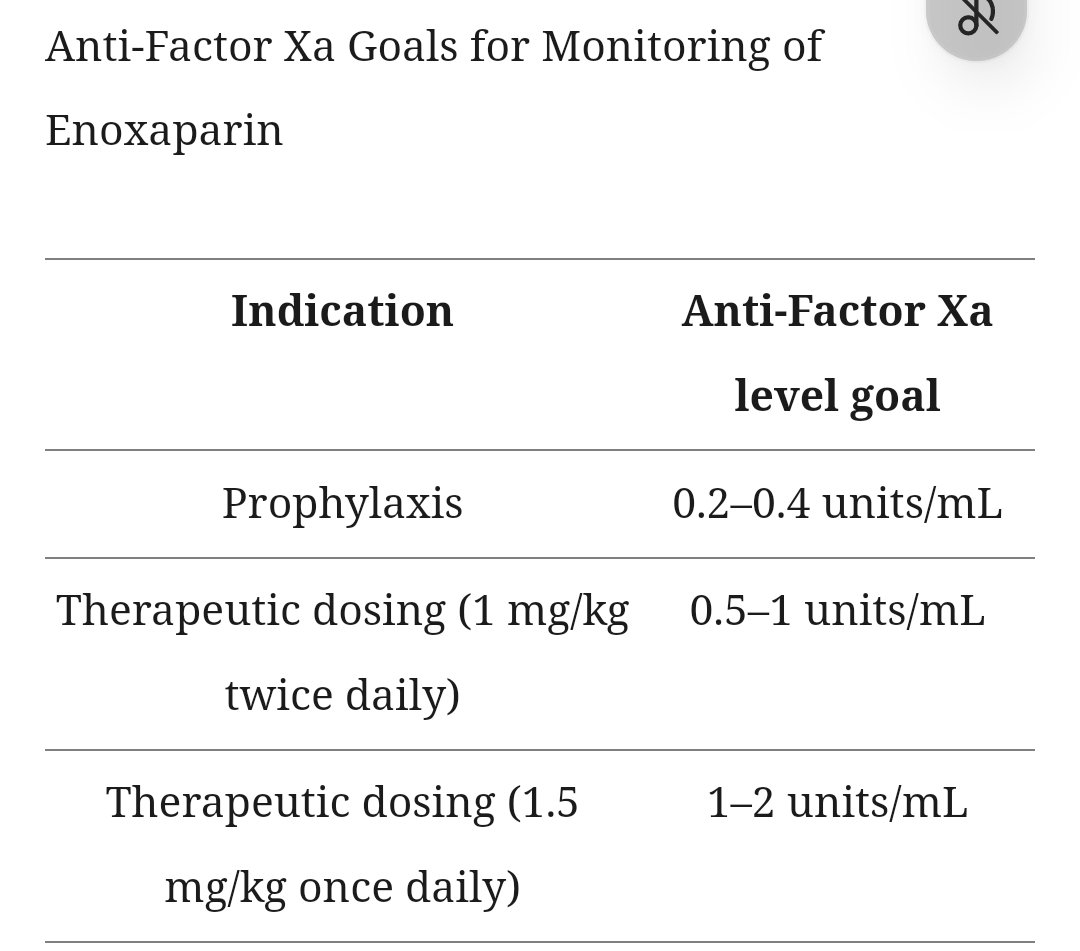
So you send anti factor 10A levels. The mechanism of action of LMWH makes the anti-factor Xa level a useful measurement for its efficacy. The anti-factor Xa level should be drawn as a peak, 3–5 hours after the third dose of enoxaparin, which should reflect the steady state.
Three populations, obese patients, renal failure patients and pregnant patients may be candidates for testing anti factor 10 A levels specially. Generally unless the patient is critically relying on anticoagulation, generally monitoring levels in not really practical and cost effective. In real life, most hospitals specially in the third world countries, the levels are not available.
From hematology point of view, I would advise doing any procedure that has risk of bleeding within 12 hours of enoxaparin injection.
Heparin is reversed by protamine sulphate. Whats the antidote of enoxaparin?
So protamine will partially reverse enoxaparin, lets say 60%. Other options are Andexanet alfa, which works against factor 10A inhibitors.
So protamine will partially reverse enoxaparin, lets say 60%. Other options are Andexanet alfa, which works against factor 10A inhibitors.
To neutralise consider half life of enoxaparin. If adminstered <8 hours prior, give 1mg protamine sulphate for every 1mg of enoxaparin. If >8hours, give 0.5mg of protamine for every 1mg of enoxaparin.
Dosage in very obese patient like >100kg, there are two opinions. One is to give them 1mg/kg bid dose as it is, other opinion is to cap at 100kg. There is no clear guideline, however generally we should prescribe dose/kg atleast till 125kg of body weight.
Hope it all makes sense. Would love to answer your questions. Take care and bye.
Loading suggestions...