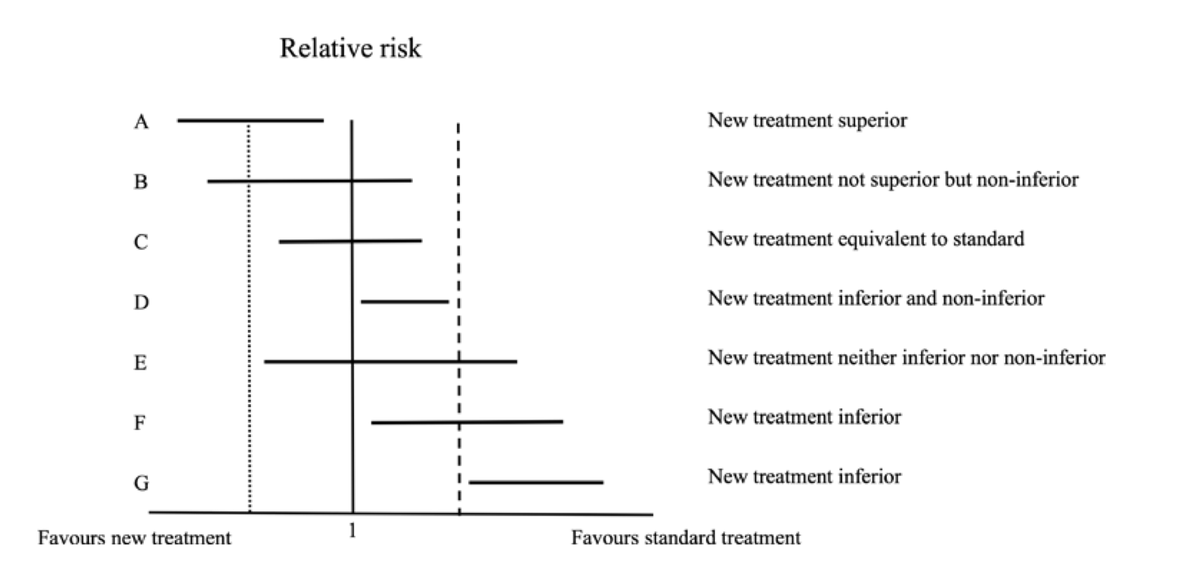
Non- inferiority trials in cardiology: what clinicians need to know: @Heart_BMJ
🥸 In light of many non-inferiority trials from #ESCCongress, here are 20 facts about superiority vs. non-inferiority trials...
😱 Happy Sunday
👇👇👇
🥸 In light of many non-inferiority trials from #ESCCongress, here are 20 facts about superiority vs. non-inferiority trials...
😱 Happy Sunday
👇👇👇
🥸 1️⃣ Clinical trials are critical to advancing medical practice by rigorously testing new treatments and forming the foundation for clinical guidelines that impact patient care across all subspecialties.
🥸 2️⃣ Superiority trials aim to show that a new treatment is better than the current standard of care or placebo, often leading to changes in clinical practice guidelines if proven effective.
🥸 3️⃣ Landmark superiority trials like SPAF (Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation) showed that warfarin was significantly better than placebo at preventing strokes in atrial fibrillation.
🥸 4️⃣ Similarly, the GUSTO trial demonstrated that accelerated TPA improved survival in AMI patients compared to standard treatment; same with PCI trials a decade later - this influenced clinical practice guidelines and standards of are.
🥸 5️⃣ The null hypothesis in superiority trials assumes the new treatment offers no benefit over the standard; rejecting this hypothesis is key to proving the new treatment's effectiveness.
🥸 6️⃣ If the trial results are statistically significant, the null hypothesis is rejected, meaning the new treatment is proven to be superior, as seen in trials like the CURE trial, where clopidogrel and aspirin outperformed aspirin alone in preventing cardiovascular events.
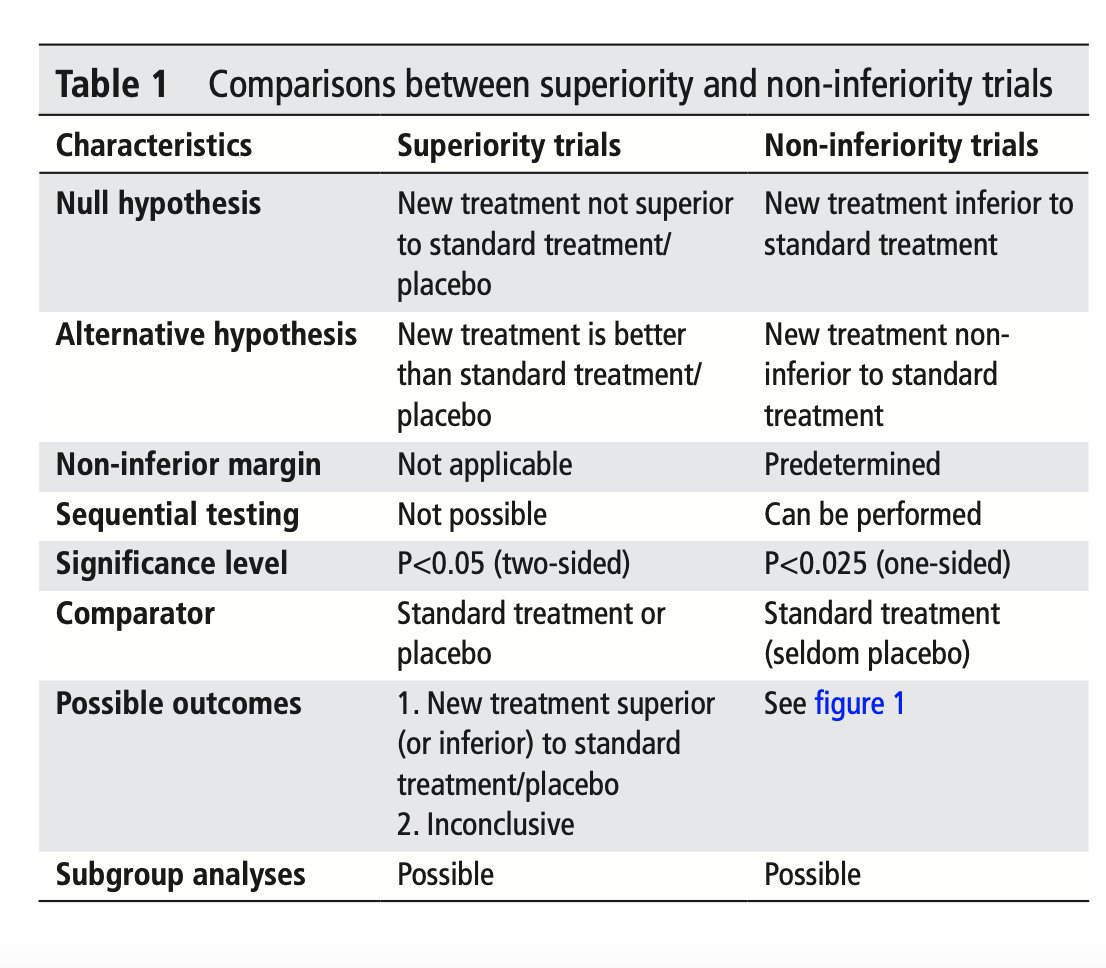
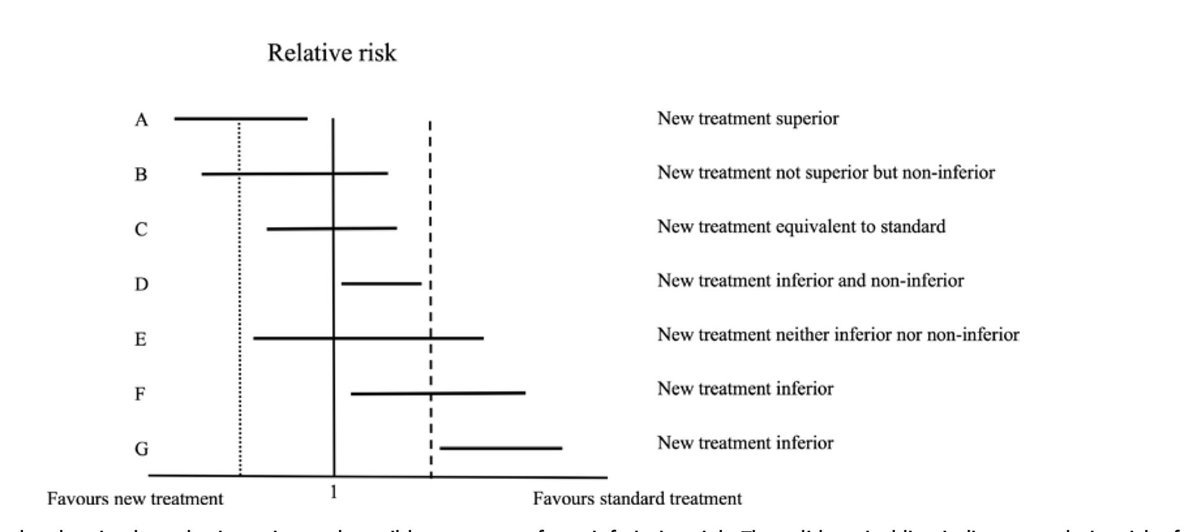
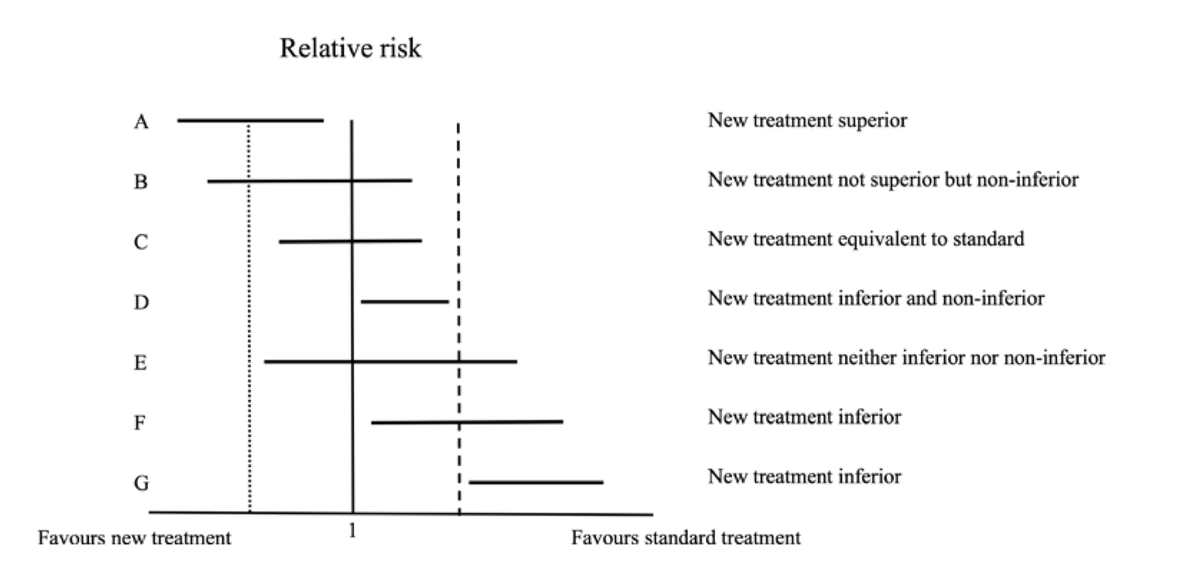
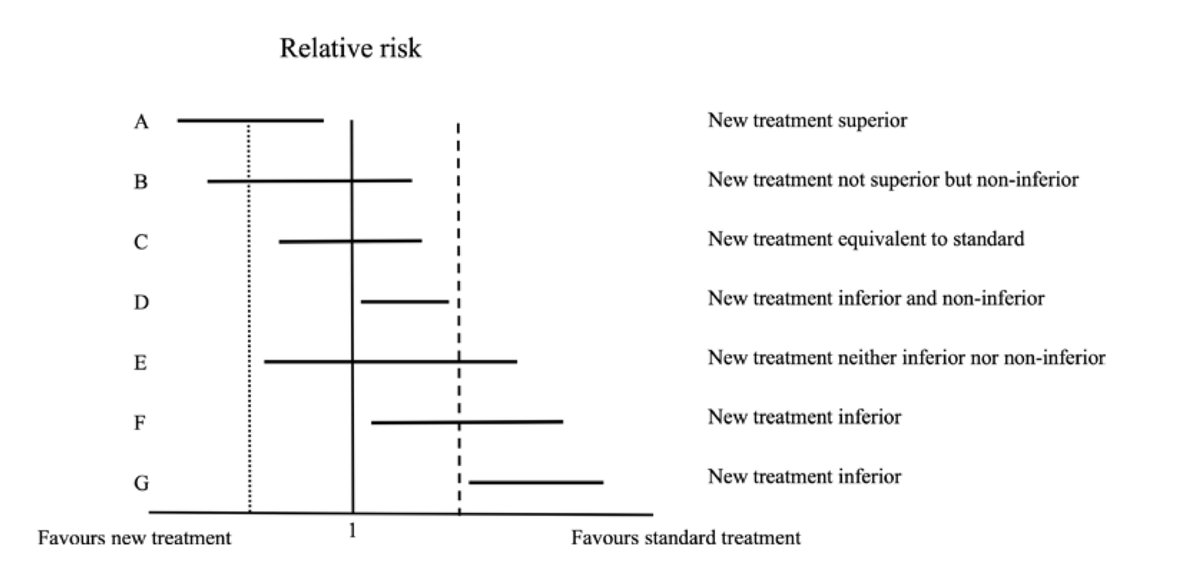
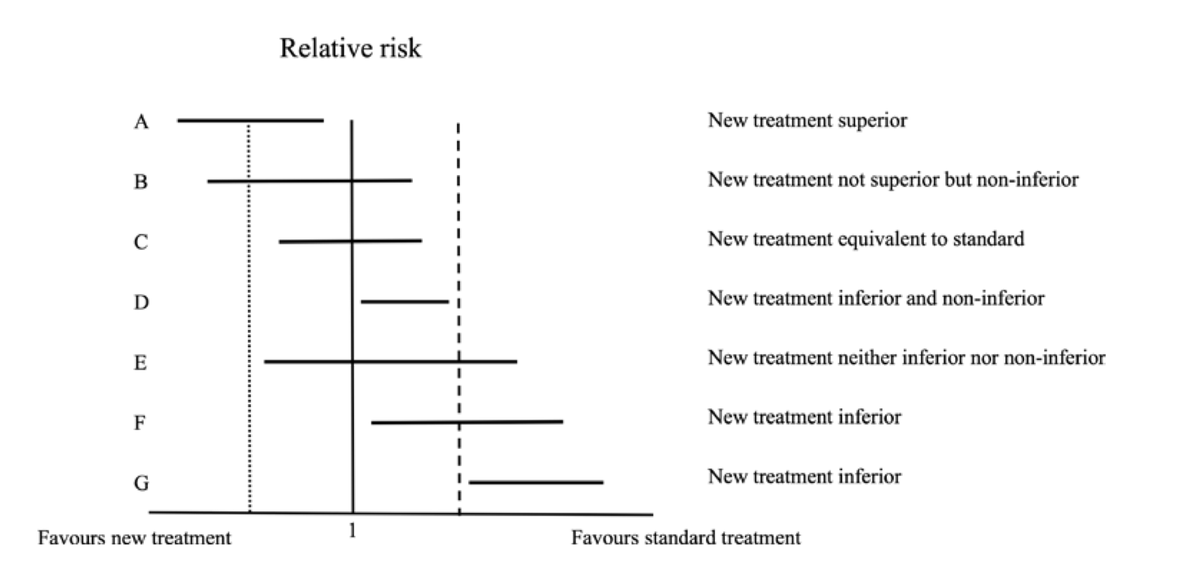
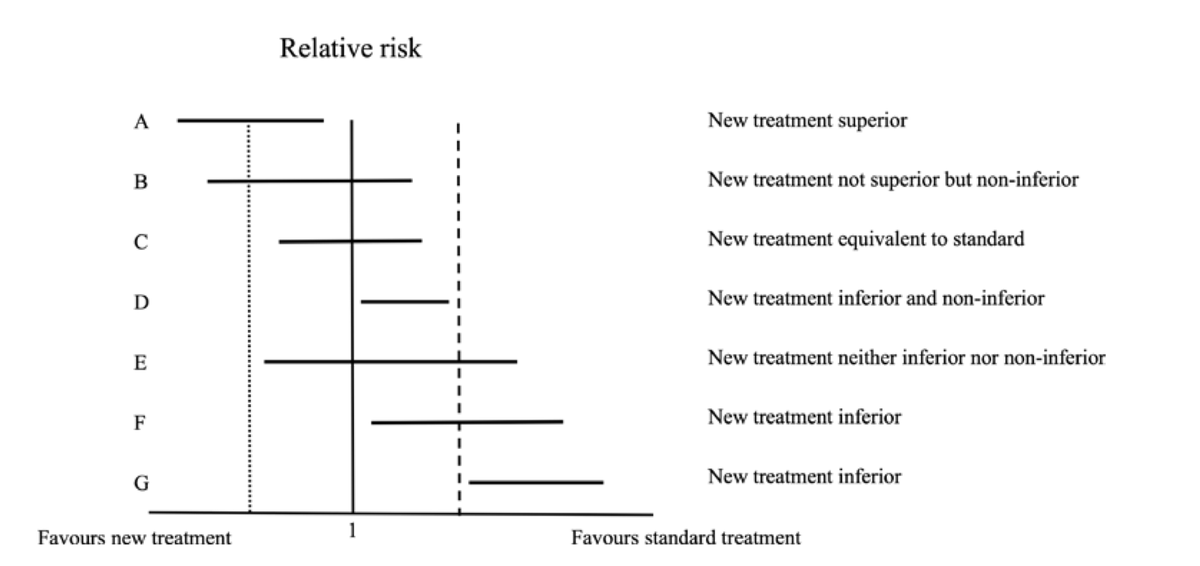
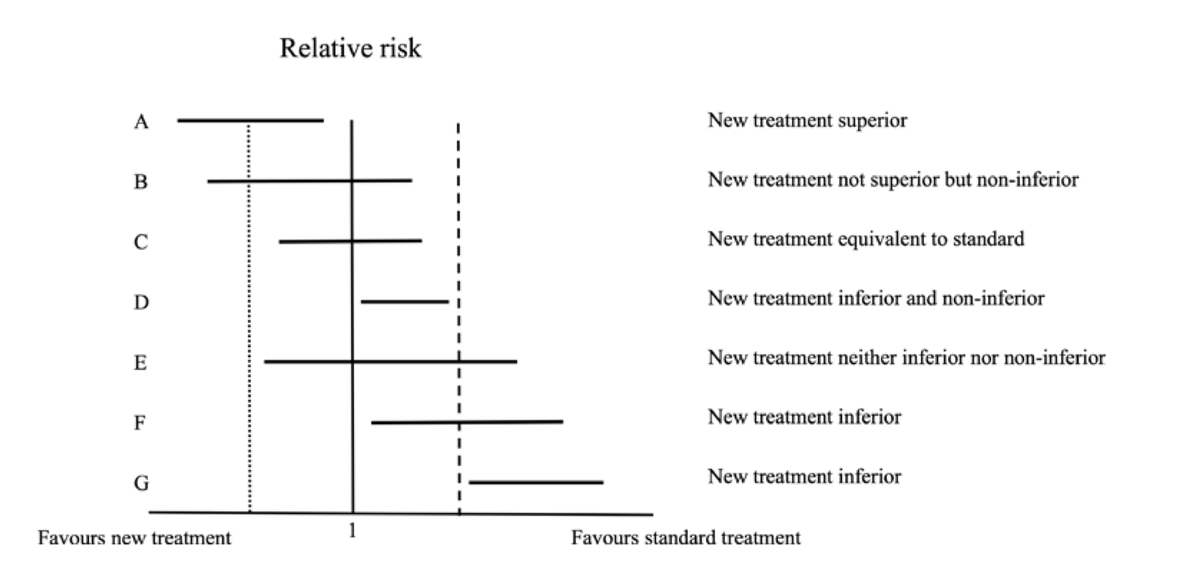
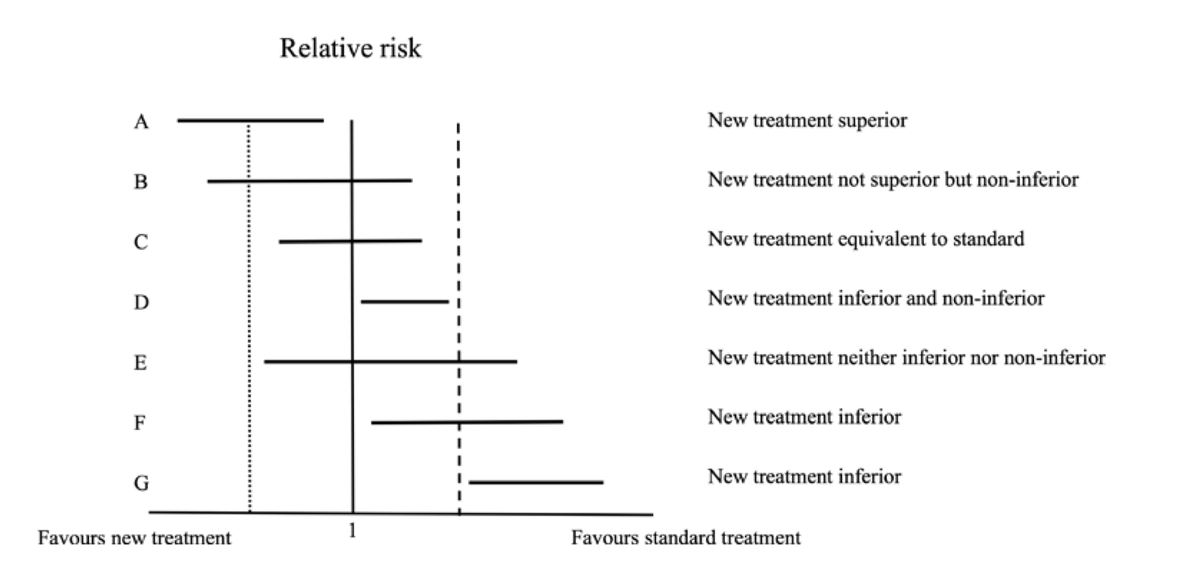
🥸 7️⃣ Non-inferiority trials, on the other hand, test whether a new treatment is "not worse" than the standard of care; it is used when there is a new therapy with fewer side effects or easier to use while maintaining similar efficacy.
🥸 8️⃣ A key example is the ROCKET AF trial, which showed that the novel anticoagulant rivaroxaban was non-inferior to warfarin for preventing strokes in atrial fibrillation; which initially offered an alternative therapy that did not need a regular blood monitoring for PT/INR.
🥸 🔟 Non-inferiority margins are pre-set thresholds in these trials that define how much worse the new treatment can be while still being clinically acceptable; this margin balances the loss in efficacy with other benefits like convenience.
🥸 1️⃣2️⃣ In ROCKET AF, the margin was carefully defined so that rivaroxaban had to be close enough in efficacy to warfarin, but the real benefit came in easier use and fewer drug interactions.
🥸 1️⃣3️⃣ Sequential testing is often used in non-inferiority trials: first testing if the new treatment is not worse than the standard, and if that passes, testing if it might actually be superior.
🥸 1️⃣4️⃣ High-quality non-inferiority trials must include both intention-to-treat and per-protocol analyses to ensure that the results are reliable and applicable to real-world practice.
🥸 1️⃣5️⃣ Clinicians must be careful when interpreting non-inferiority trials; this requires examining whether the study population, event rates, and endpoints are appropriate and whether the trial design is rigorous enough to avoid bias.
🥸 1️⃣6️⃣ Non-inferiority trials allow the introduction of newer treatments that may not be significantly better in terms of efficacy but offer important advantages, such as fewer side effects, lower costs, or easier administration, which can improve patient outcomes and adherence.
🥸 1️⃣8️⃣ However, it’s important to remember that "non-inferior" does not mean "equivalent" or "equal." It means that the new treatment isn’t unacceptably worse than the standard of care, and clinicians must weigh this carefully when applying trial results to patient care.
🥸 1️⃣9️⃣ Clinicians should also consider how close the study results are to the non-inferiority margin, as a small difference may still be clinically meaningful, especially in high-risk populations or in conditions where treatment options are limited.
🥸 2️⃣0️⃣ As the use of non-inferiority trials continues to grow, clinicians need to be able to interpret these studies, and understand the full context before deciding to adopt a new treatment into practice.
🥸 - Addendum is over :)
😱Have a nice weekend everyone - hope this is helpful.
😱Have a nice weekend everyone - hope this is helpful.
Loading suggestions...