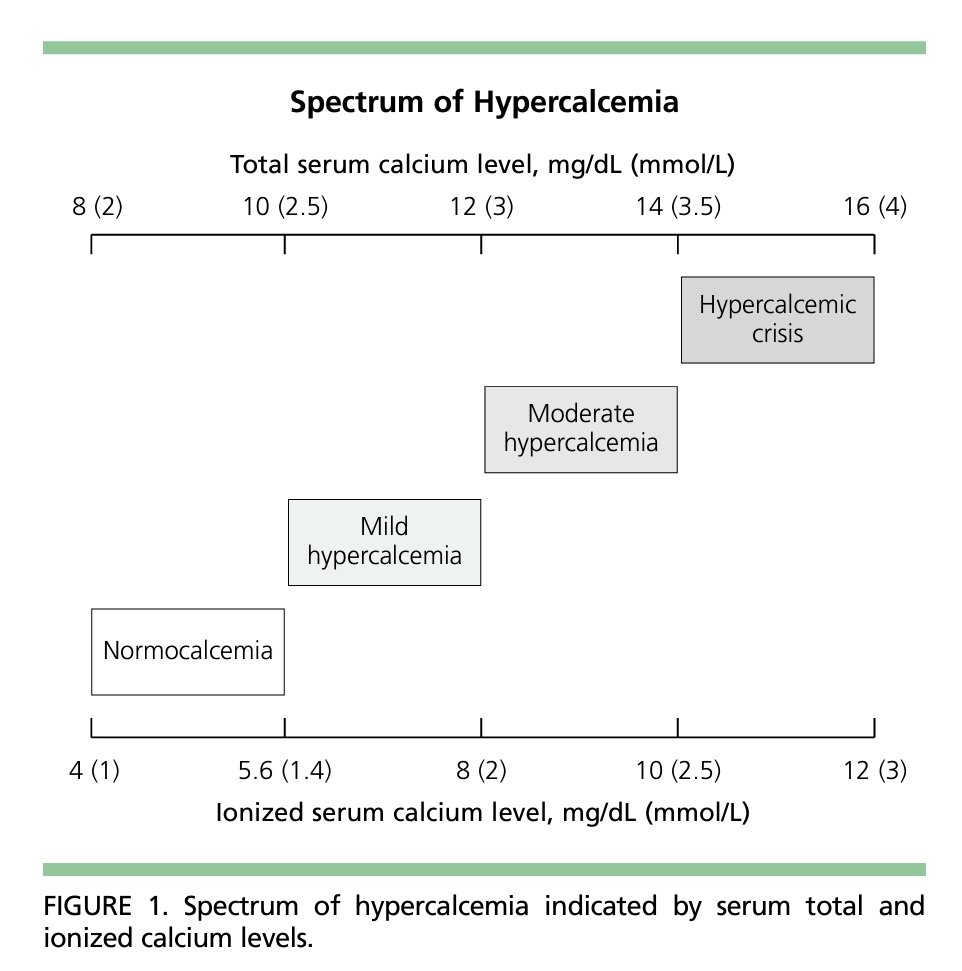
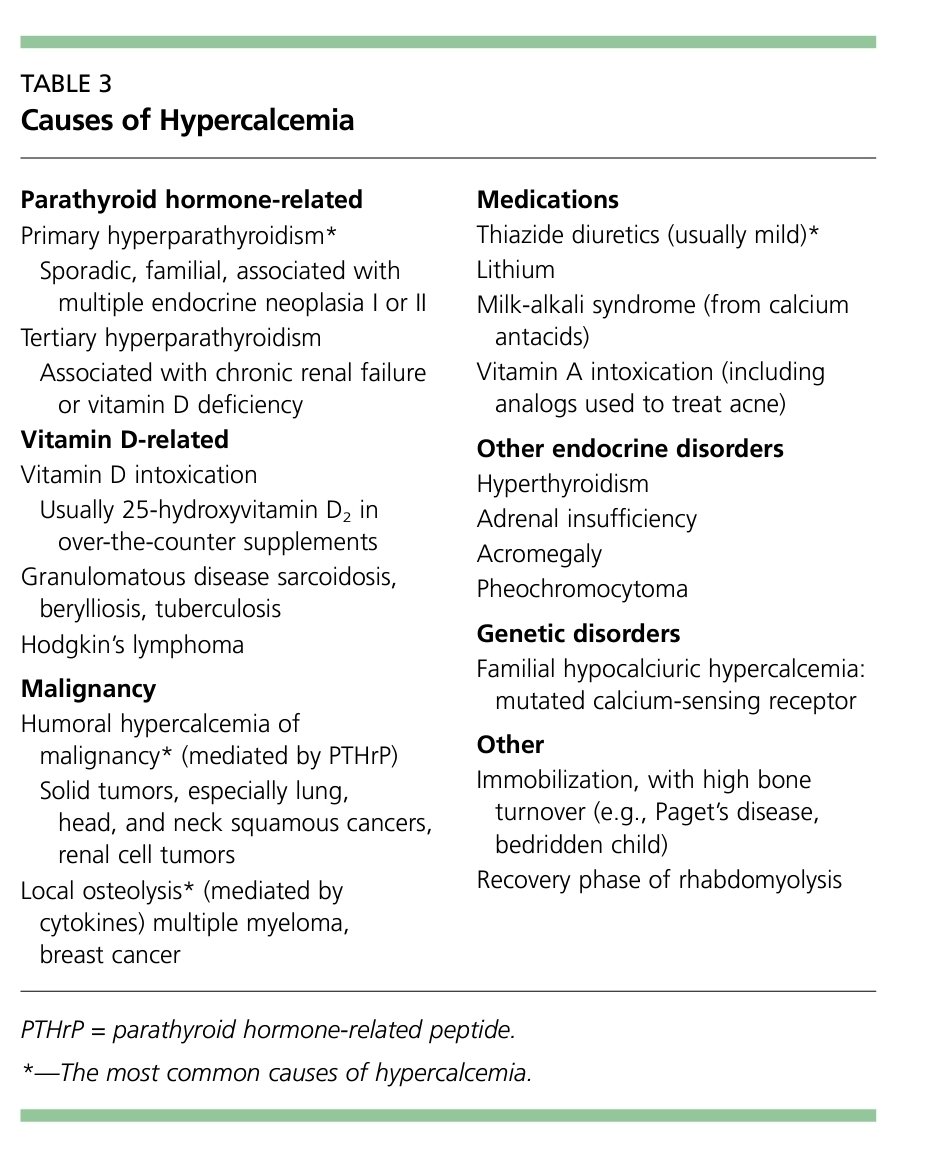
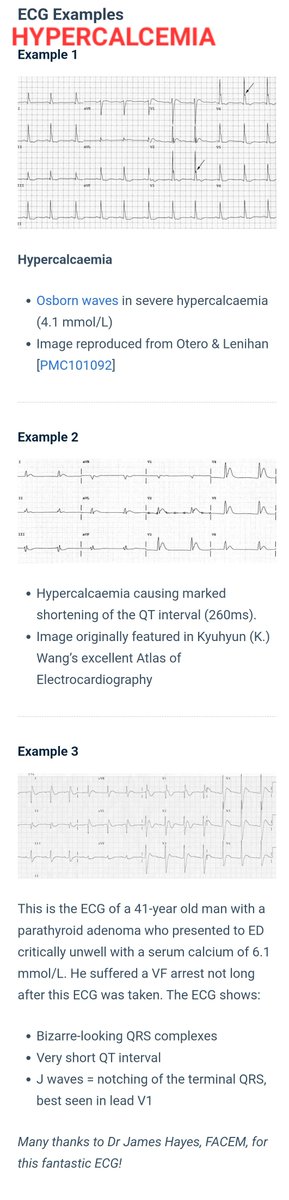
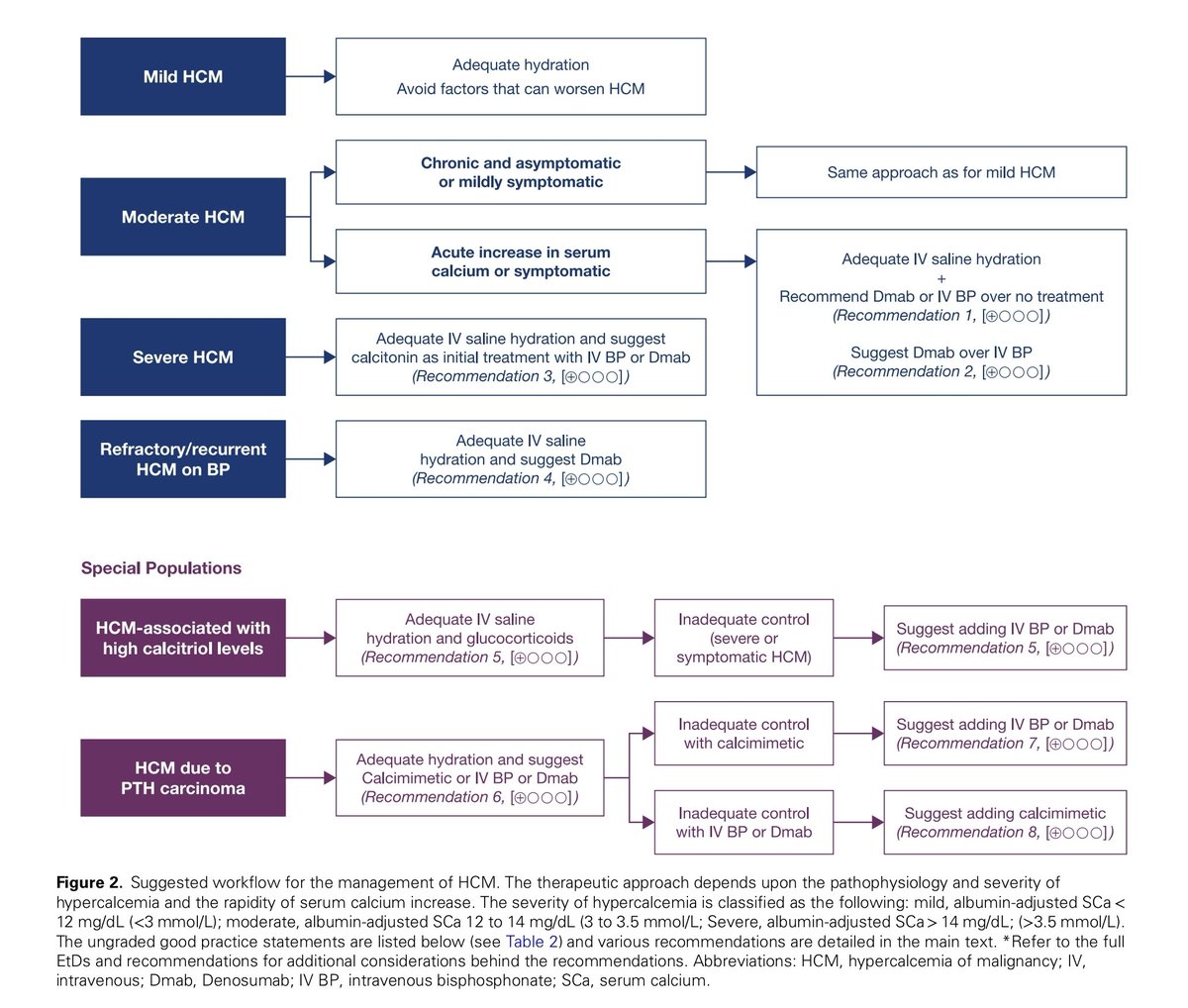
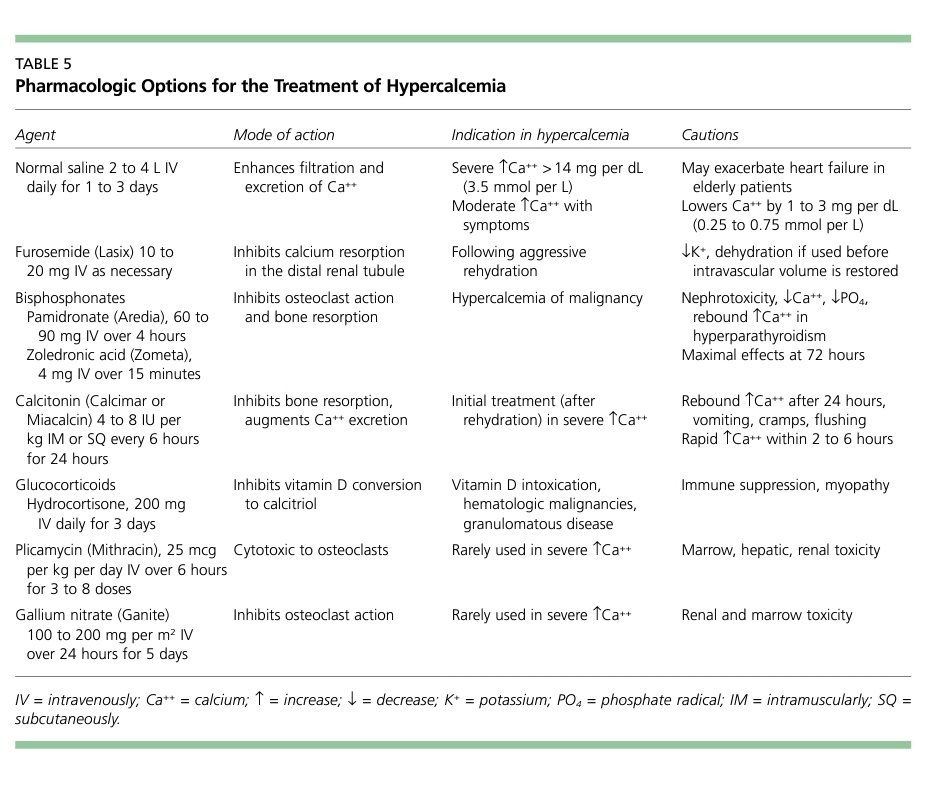
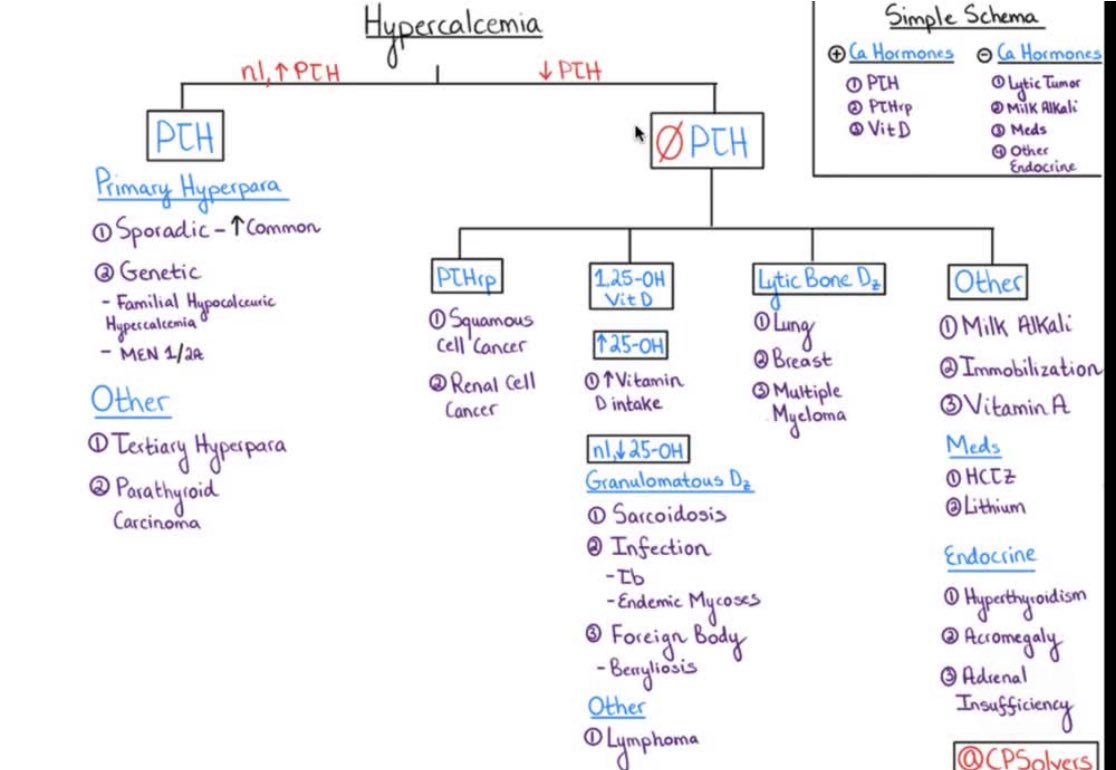
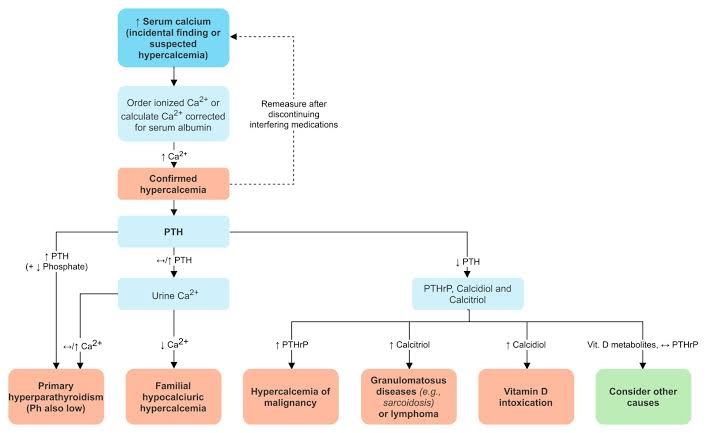
Hypercalcemia can result in significant electrocardiographic changes, including bradycardia, atrioventricular (AV) block, and short QT interval.
These can lead to fatal arrhythmias.
Changes in serum calcium can be monitored by following the QT interval.
From @LITFLblog
These can lead to fatal arrhythmias.
Changes in serum calcium can be monitored by following the QT interval.
From @LITFLblog
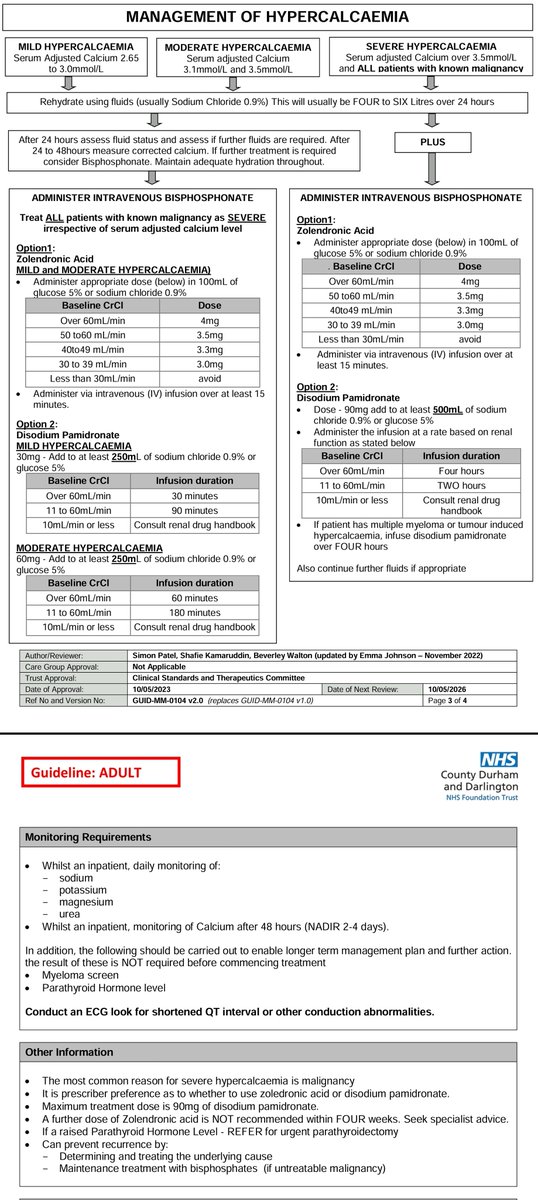
Symptomatic hypercalcemia is an emergency.
The diagnosis is often picked up in the ER by ABG showing hypercalcemia and ECG showing short QTc in a background of suggestive history.
The diagnosis is often picked up in the ER by ABG showing hypercalcemia and ECG showing short QTc in a background of suggestive history.
References
1. Harrison's Principles of Internal
Medicine, 21ed
2. Treatment of Hypercalcemia of
Malignancy in Adults: An
Endocrine Society Clinical Practice
Guideline
doi.org
3. NHS , Guideline for the
management of
HYPERCALCAEMIA in adults
1. Harrison's Principles of Internal
Medicine, 21ed
2. Treatment of Hypercalcemia of
Malignancy in Adults: An
Endocrine Society Clinical Practice
Guideline
doi.org
3. NHS , Guideline for the
management of
HYPERCALCAEMIA in adults
4. A Practical Approach to
Hypercalcemia
aafp.org
5. Treatment of hypercalcaemia of
malignancy in adults
sciencedirect.com
Hypercalcemia
aafp.org
5. Treatment of hypercalcaemia of
malignancy in adults
sciencedirect.com
Loading suggestions...