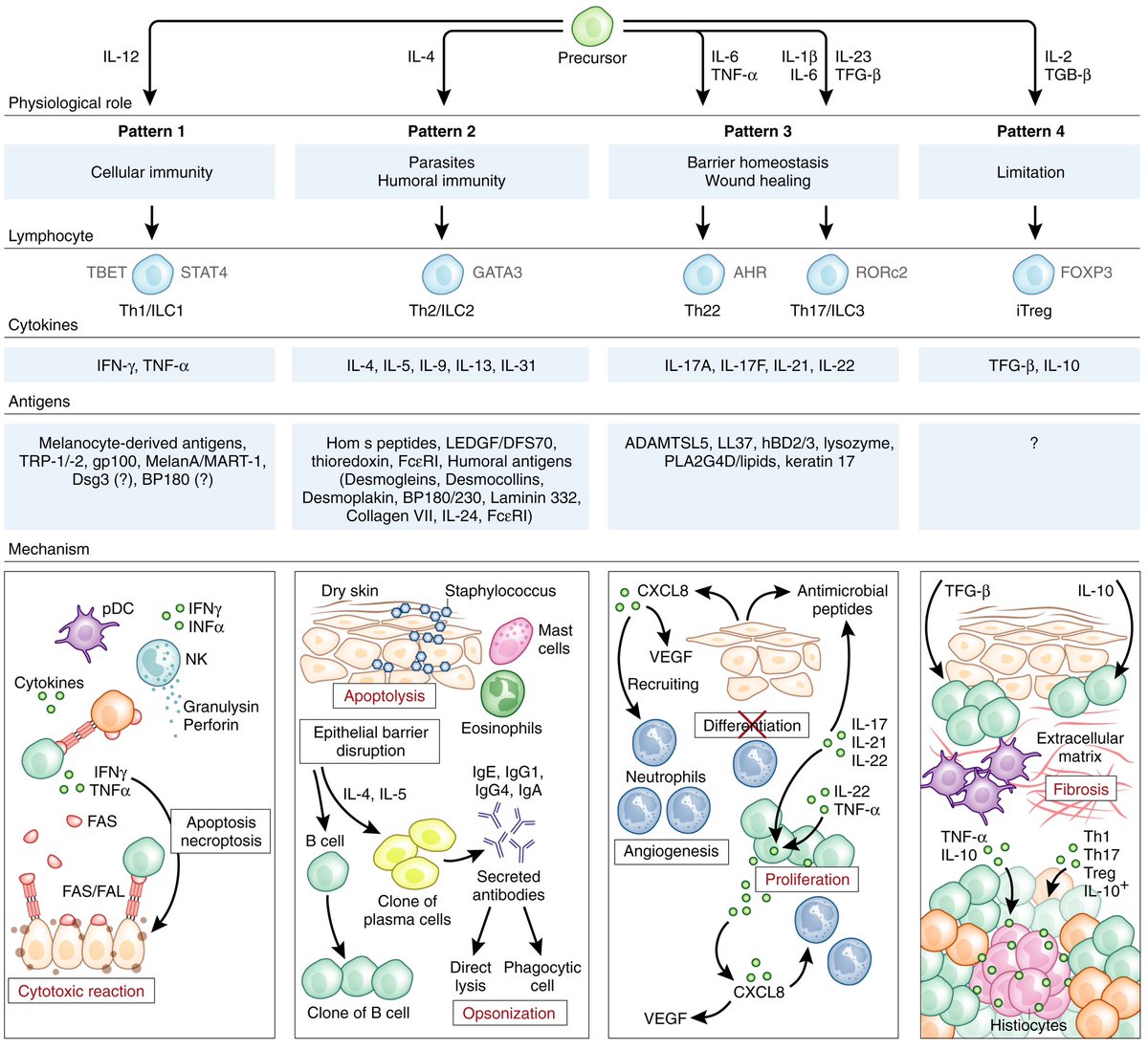
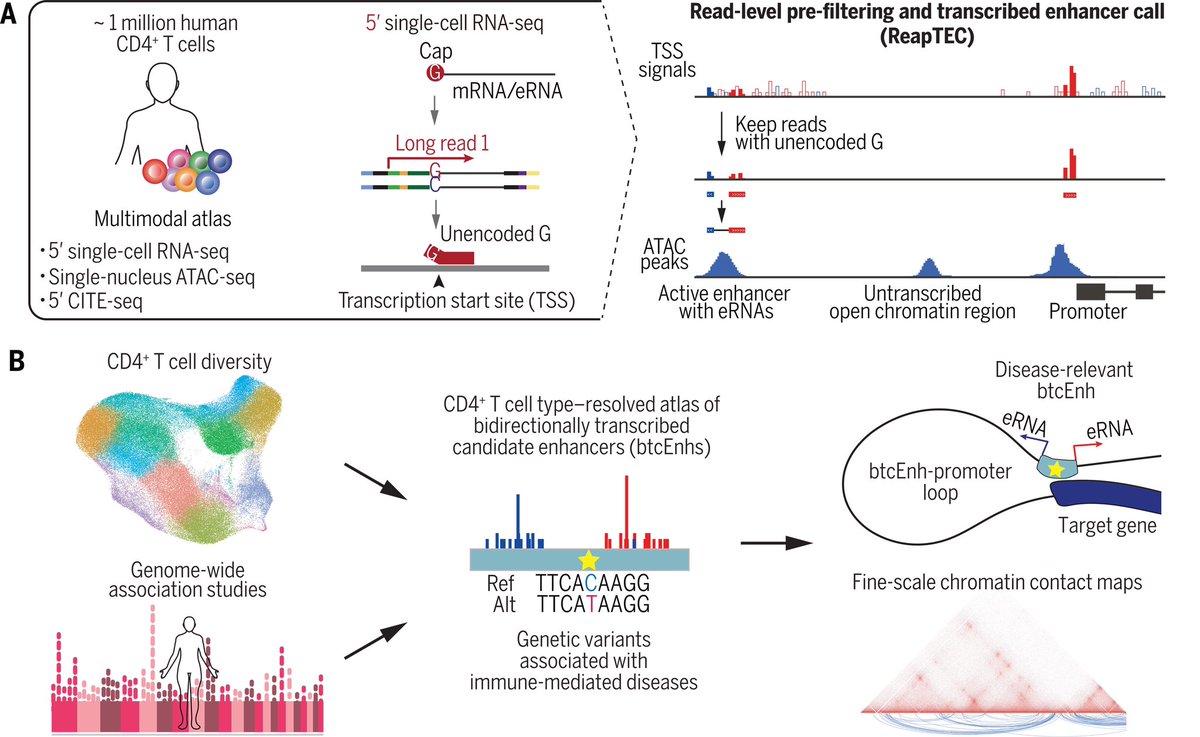
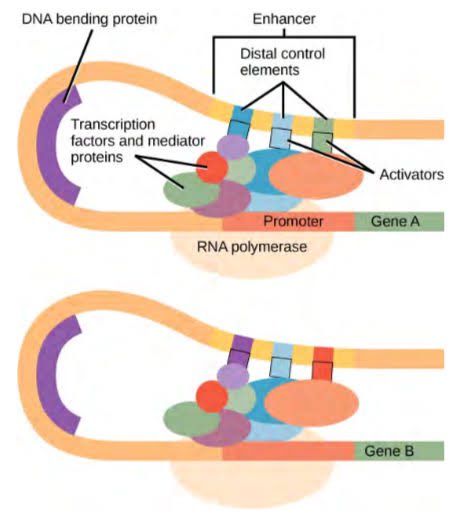
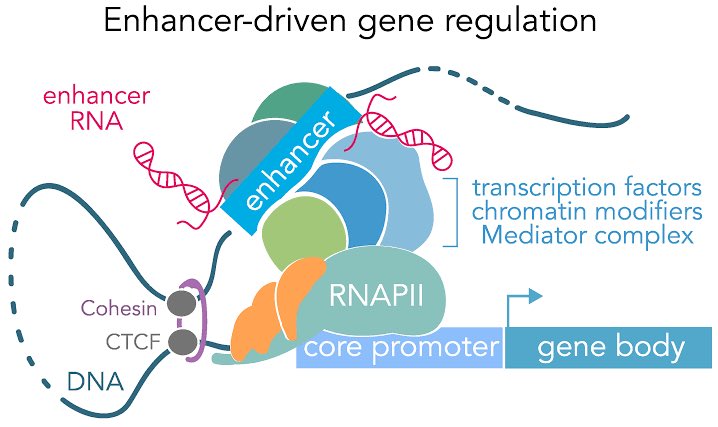
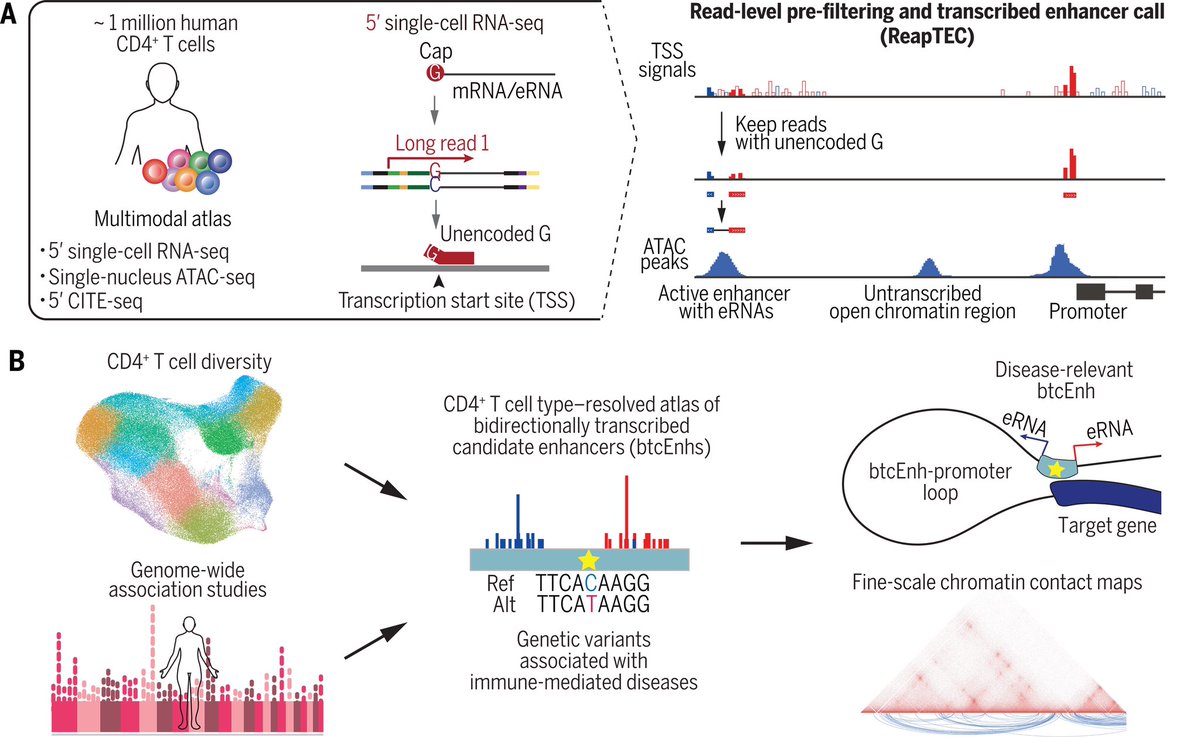
This is made possible by a newly developed technology—#ReapTEC, which identified genetic enhancers in rare T cell subtypes that are linked to specific immune disorders. The new T cell atlas should help in the development of new drug therapies for immune-mediated diseases. 2/
The researchers develop the new ReapTEC technology and look for connections between bidirectional T cell enhancers and immune diseases. 7/
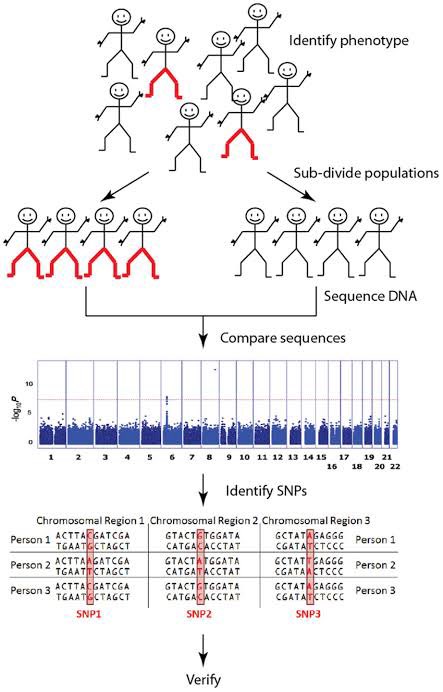
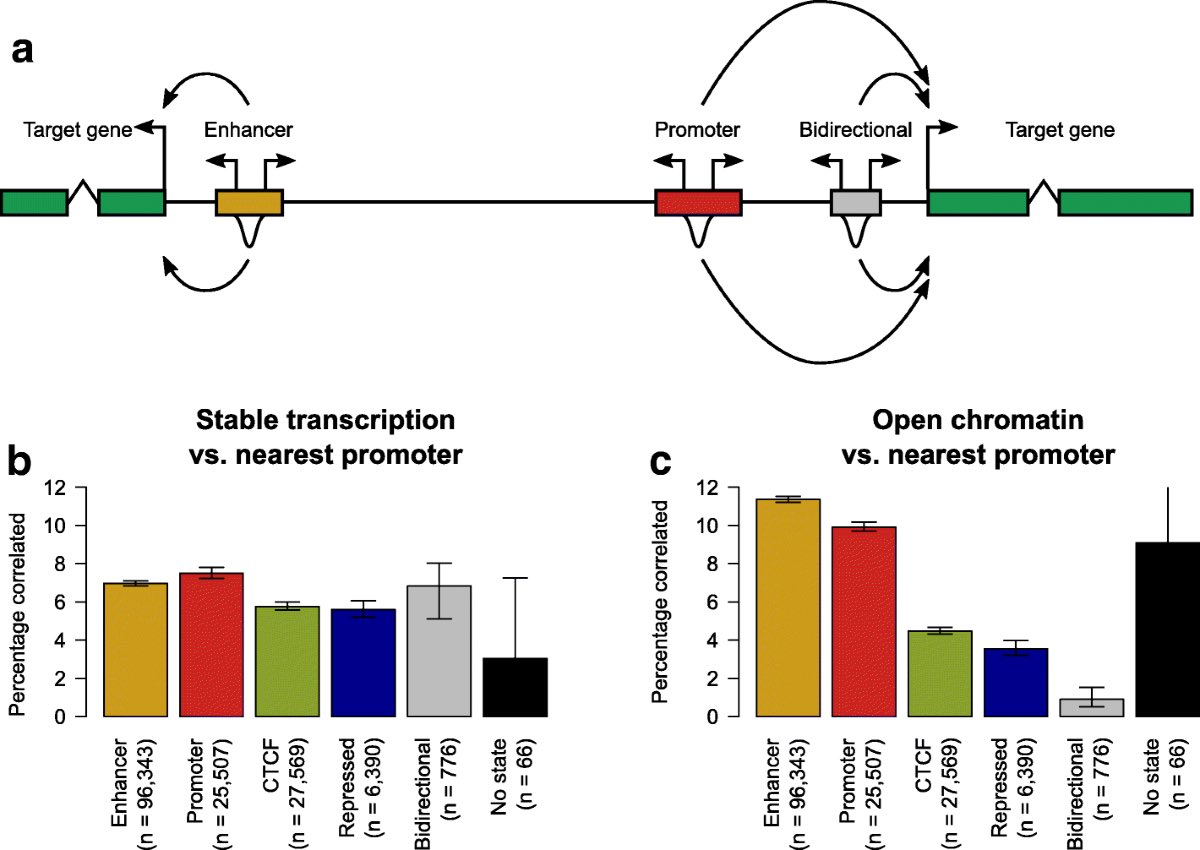
When the researchers combined the GWAS data with the results of their ReapTEC analysis, they found that genetic variants for immune-mediated diseases were often located within the bidirectional enhancer DNA of the rare T cells that they had identified. 10/
In contrast, genetic variants for neurological diseases did not show a similar pattern, meaning that the bidirectional enhancers in these rare T cells are related specifically to immune-mediated diseases. 11/
Going even deeper into the data, the researchers were able to show that individual enhancers in certain rare T cells are related to specific immune diseases. 12/
They were able to identify some genes that are the targets of these disease-related enhancers. Such as, when they activated an enhancer that contained a genetic variant related to inflammatory bowel disease, the resulting enhancer RNA triggered upregulation of the IL7R gene 14/
They hope that this knowledge will lead to a better understanding of the genetic mechanisms underlying human immune-mediated diseases. 16/
In the long-term, the researchers believe follow-up experiments will be able to identify new molecules that can be used to treat immune-mediated diseases. 17/17
science.org
science.org
Loading suggestions...