♻️ Recycling - Plastic, e-waste and Battery 🚀🚀
A thread 🧵 👇
• Recycling is process of recovery by which waste materials are processed to base materials to be used for manufacturing of original or any other product.
Follow, like and repost for more 🔥
(1/n)
#recycling
A thread 🧵 👇
• Recycling is process of recovery by which waste materials are processed to base materials to be used for manufacturing of original or any other product.
Follow, like and repost for more 🔥
(1/n)
#recycling
This post covers the following.
1. Recycled items
2. Plastic Recycling
• Process and Market Opportunity
• Growth drivers and challenges
• EPR guidelines
3. E-waste recycling
• Process & mkt Opportunity
• Growth Drivers and challenges
• Govt policy
4. Companies
(2/n)
1. Recycled items
2. Plastic Recycling
• Process and Market Opportunity
• Growth drivers and challenges
• EPR guidelines
3. E-waste recycling
• Process & mkt Opportunity
• Growth Drivers and challenges
• Govt policy
4. Companies
(2/n)
♻️ Plastic Recyc.
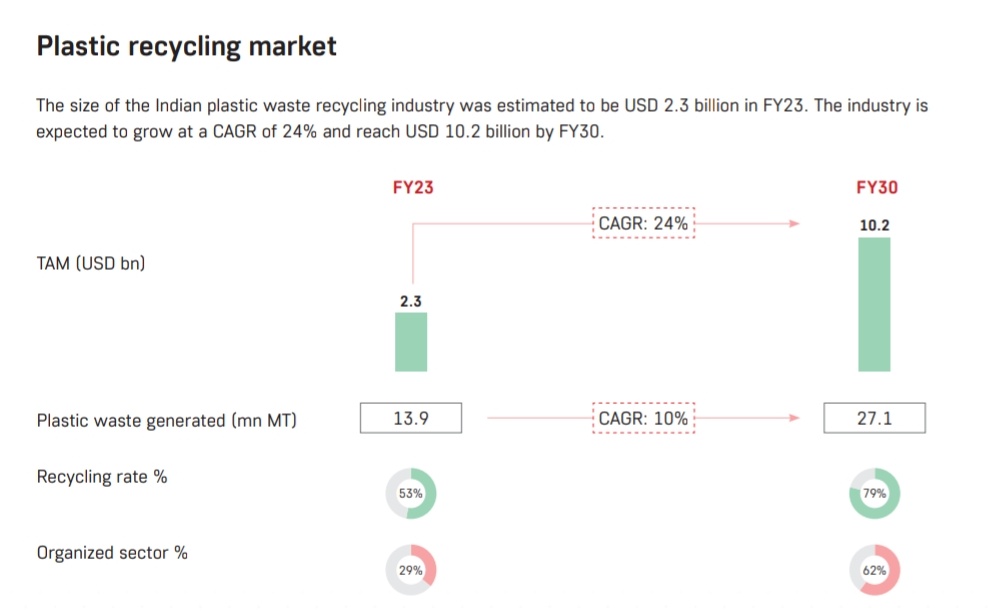
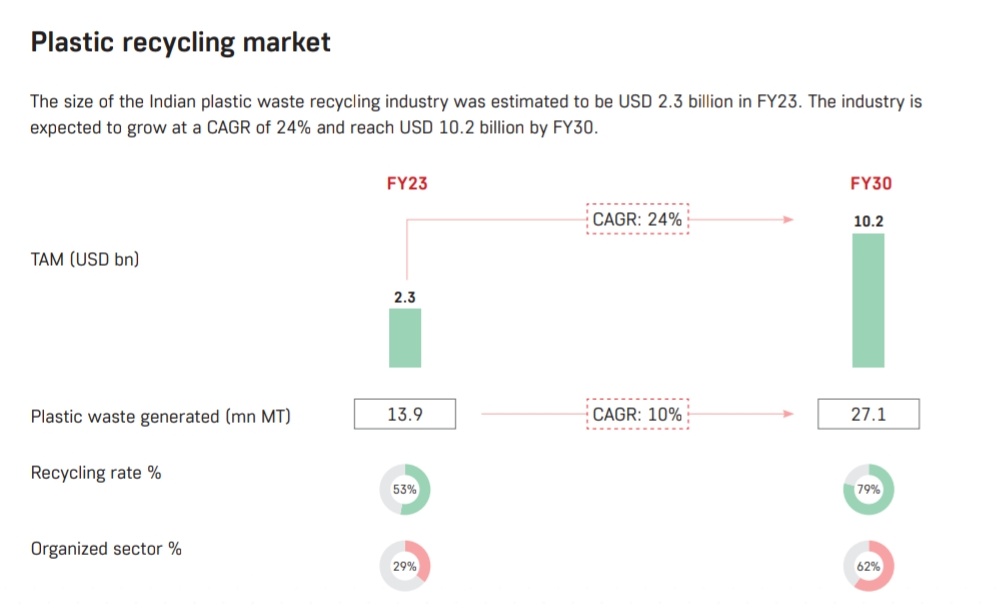
Globally, 400 Mn tons of plastic waste is generated each year with less than 10% being recycled. While in India 13 Mn tons is generated with 60% being recycled.
The plastics such as PET, HDPE are easily recyclable and form 30% of total usage of plastics
(4/n)
Globally, 400 Mn tons of plastic waste is generated each year with less than 10% being recycled. While in India 13 Mn tons is generated with 60% being recycled.
The plastics such as PET, HDPE are easily recyclable and form 30% of total usage of plastics
(4/n)
🎯 Growth Drivers of Plastic Recycling
1. Rising awareness of environmental depletion
2. New start-ups coming up
3. Use of disruptive tech
4. Increase in demand from ecommerce
5. Increase in use of plastic due to light weight nature
(7/n)
1. Rising awareness of environmental depletion
2. New start-ups coming up
3. Use of disruptive tech
4. Increase in demand from ecommerce
5. Increase in use of plastic due to light weight nature
(7/n)
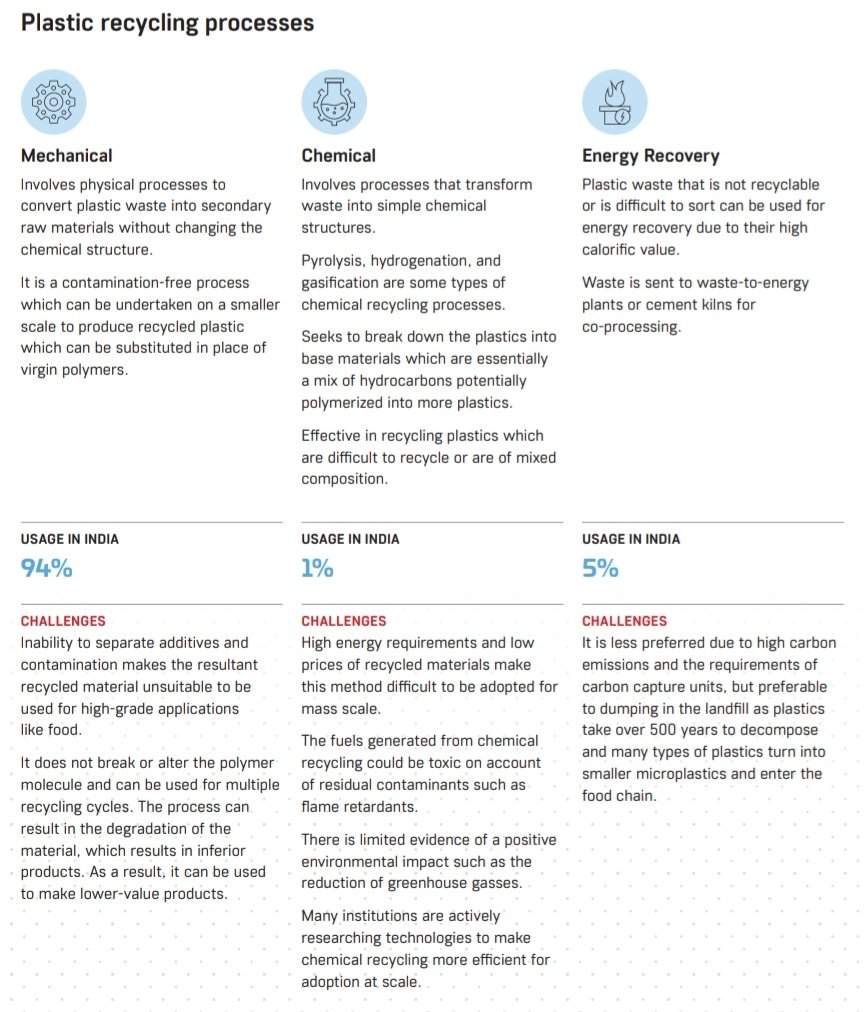
🎯 Challenges in Plastic Recycling
1. Different types of plastics
2. Largely informal sector
3. Ineffective policy implementation
4. Low demand of recycled content
5. Degradation of plastic due to Recycling
6. Multi layered and laminated plastics
(8/n)
1. Different types of plastics
2. Largely informal sector
3. Ineffective policy implementation
4. Low demand of recycled content
5. Degradation of plastic due to Recycling
6. Multi layered and laminated plastics
(8/n)
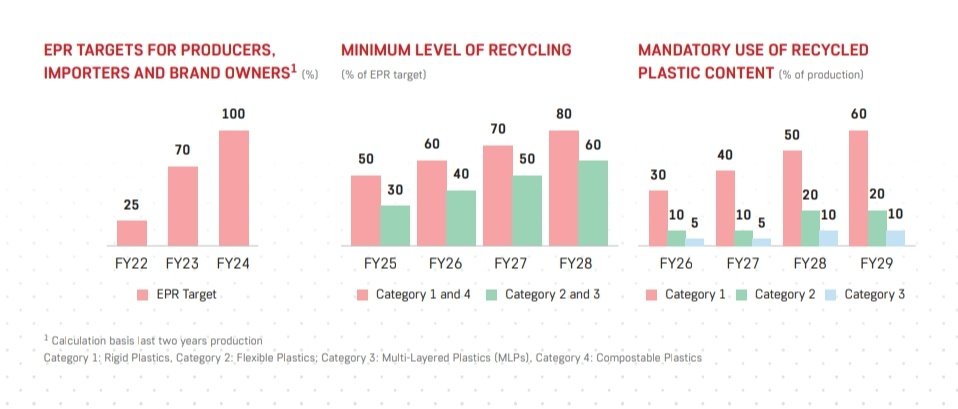
🎯 EPR Guidelines
Classification of plastics
Cat. 1: Rigid packing
Cat. 2: Flexible packing with a single layer or multilayer (>1 layer with diff. types of plastic)
Cat. 3: Multilayer packaging (at least one layer of plastic and at least one layer of other material)
(9/n)
Classification of plastics
Cat. 1: Rigid packing
Cat. 2: Flexible packing with a single layer or multilayer (>1 layer with diff. types of plastic)
Cat. 3: Multilayer packaging (at least one layer of plastic and at least one layer of other material)
(9/n)
♻️ E-waste recycling
The rapid growth of technology has resulted in electronics being a very essential part of our daily lives.
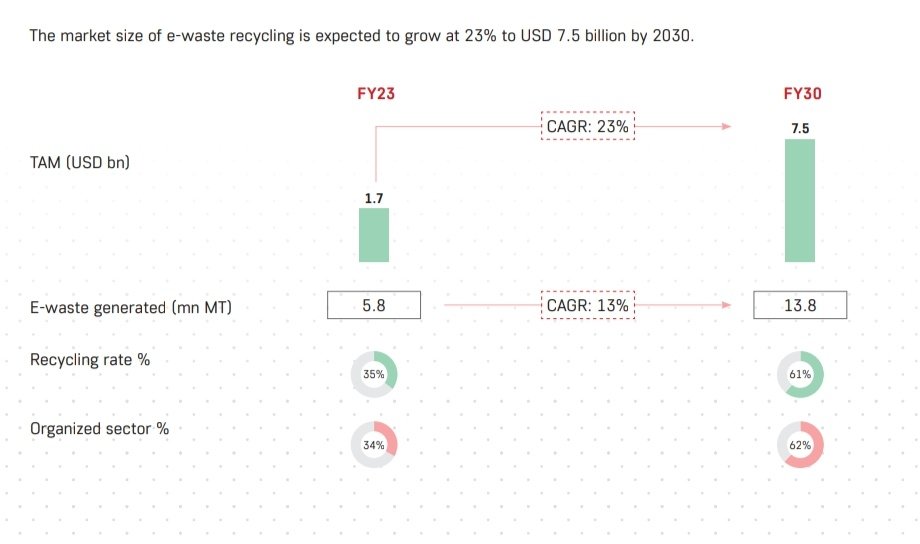
India is 3rd largest generator of e-waste, after USA & China, & only a small portion of the e-waste generated is recycled formally (<10%).
(11/n)
The rapid growth of technology has resulted in electronics being a very essential part of our daily lives.
India is 3rd largest generator of e-waste, after USA & China, & only a small portion of the e-waste generated is recycled formally (<10%).
(11/n)
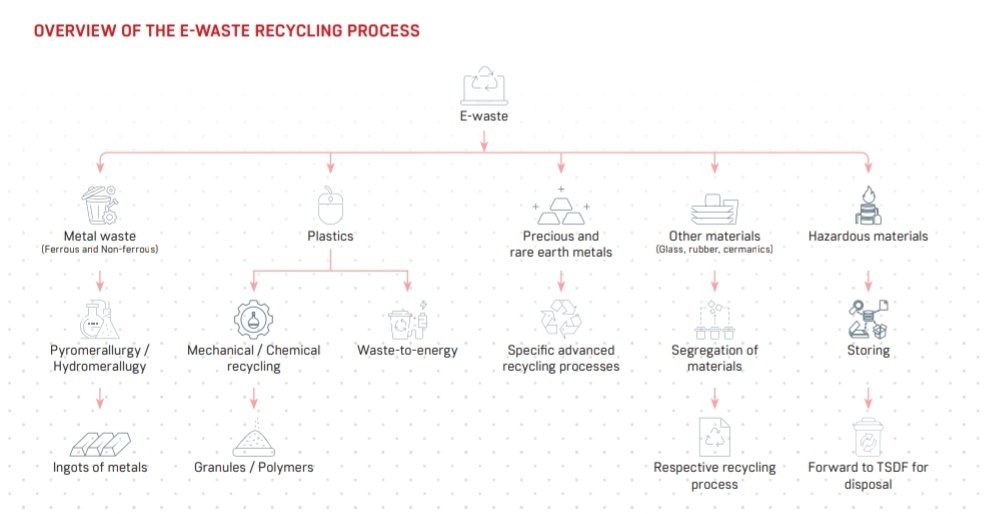
🎯 Constituents of e-waste
1. Ferrous metals such as Iron & Steel (35%)
2. Non-ferrous metals such as Copper and Aluminum (20%)
3. Plastics (35%)
4. Precious metals (<5%)
5. Other materials such as glass, rubber, ceramic (<5%)
6. Hazardous substances (<1%)
(12/n)
1. Ferrous metals such as Iron & Steel (35%)
2. Non-ferrous metals such as Copper and Aluminum (20%)
3. Plastics (35%)
4. Precious metals (<5%)
5. Other materials such as glass, rubber, ceramic (<5%)
6. Hazardous substances (<1%)
(12/n)
🎯 Growth Drivers of e-waste recycling
1. Growing demand of elec. gadgets
2. Urban mining
3. Growth in IT services
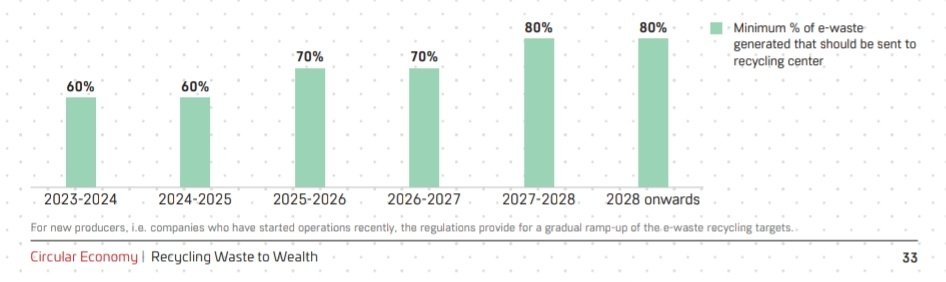
4. Increasing scope of e-waste regulations
5. EMS boost in India will lead to increasing waste
(15/n)
1. Growing demand of elec. gadgets
2. Urban mining
3. Growth in IT services
4. Increasing scope of e-waste regulations
5. EMS boost in India will lead to increasing waste
(15/n)
🎯 Challenges in e-waste recycling
1. Low efficiency and low penetration of formal sector
2. Lower regulatory compliance
3. Low consumer awareness
4. Lack of planning at designing phase
(16/n)
1. Low efficiency and low penetration of formal sector
2. Lower regulatory compliance
3. Low consumer awareness
4. Lack of planning at designing phase
(16/n)
🎯 Companies present in the plastic and e-waste recycling industry.
Plastic
1. Ganesha Ecosphere
2. Gravita
3. Polygenta Tech
E-waste
1. Eco recycling
2. Attero recycling
3. Exigo
4. 3R Recyling
Do comment listed companies in these sectors 😀
(18/n)
Plastic
1. Ganesha Ecosphere
2. Gravita
3. Polygenta Tech
E-waste
1. Eco recycling
2. Attero recycling
3. Exigo
4. 3R Recyling
Do comment listed companies in these sectors 😀
(18/n)
Follow, like and repost for more content 🔥🔥🔥🔥
Source: Avendus
Do read my research on other sectors too 😀.
#recycling
#wasterecycling
#plasticwaste
#ewaste
#gravita #ecoreco #ganeshaeco
Source: Avendus
Do read my research on other sectors too 😀.
#recycling
#wasterecycling
#plasticwaste
#ewaste
#gravita #ecoreco #ganeshaeco
Loading suggestions...