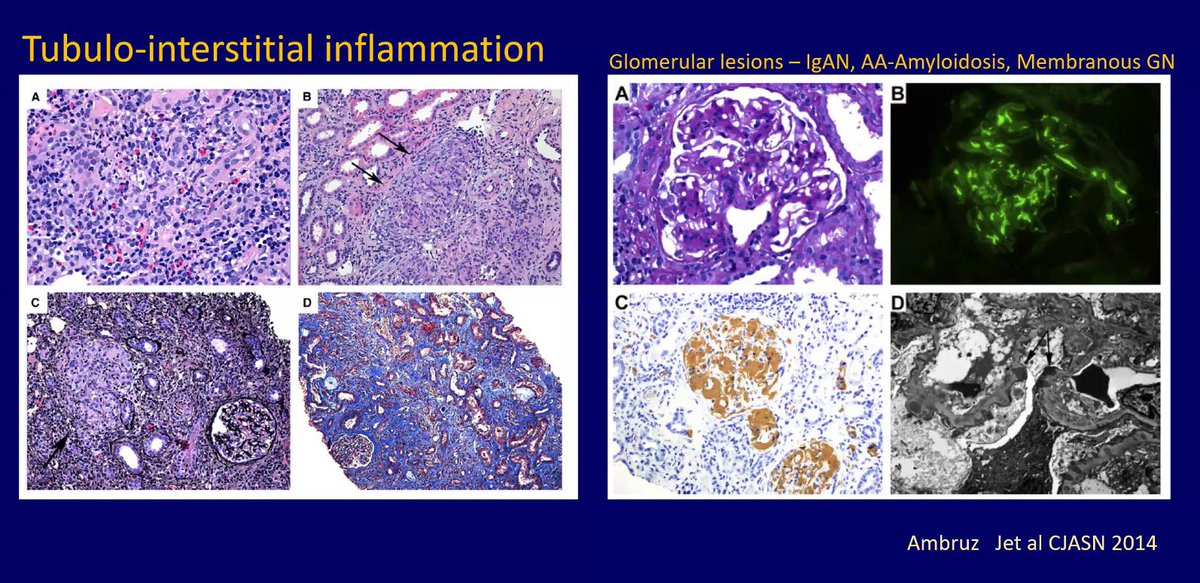
But first, do you think AIN is often underdiagnosed? 🤔
1/14
📍Interstitial nephritis:
kidney inflammation in tubules/interstitium.🔬
📍Also called tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN).
📍Acute (AIN) often from drug hypersensitivity, reversible if drug D/C.
📍Chronic (CIN) involves scarring.
📜 First described in 1898, linked to Strep infections.
👇In this post I'll focus on Non–Drug-Related Interstitial Nephritis
📍Interstitial nephritis:
kidney inflammation in tubules/interstitium.🔬
📍Also called tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN).
📍Acute (AIN) often from drug hypersensitivity, reversible if drug D/C.
📍Chronic (CIN) involves scarring.
📜 First described in 1898, linked to Strep infections.
👇In this post I'll focus on Non–Drug-Related Interstitial Nephritis
2/14
1️⃣Infection-Associated AIN:
(Bacteria viral and fungi)
🔘Bacterial AIN:
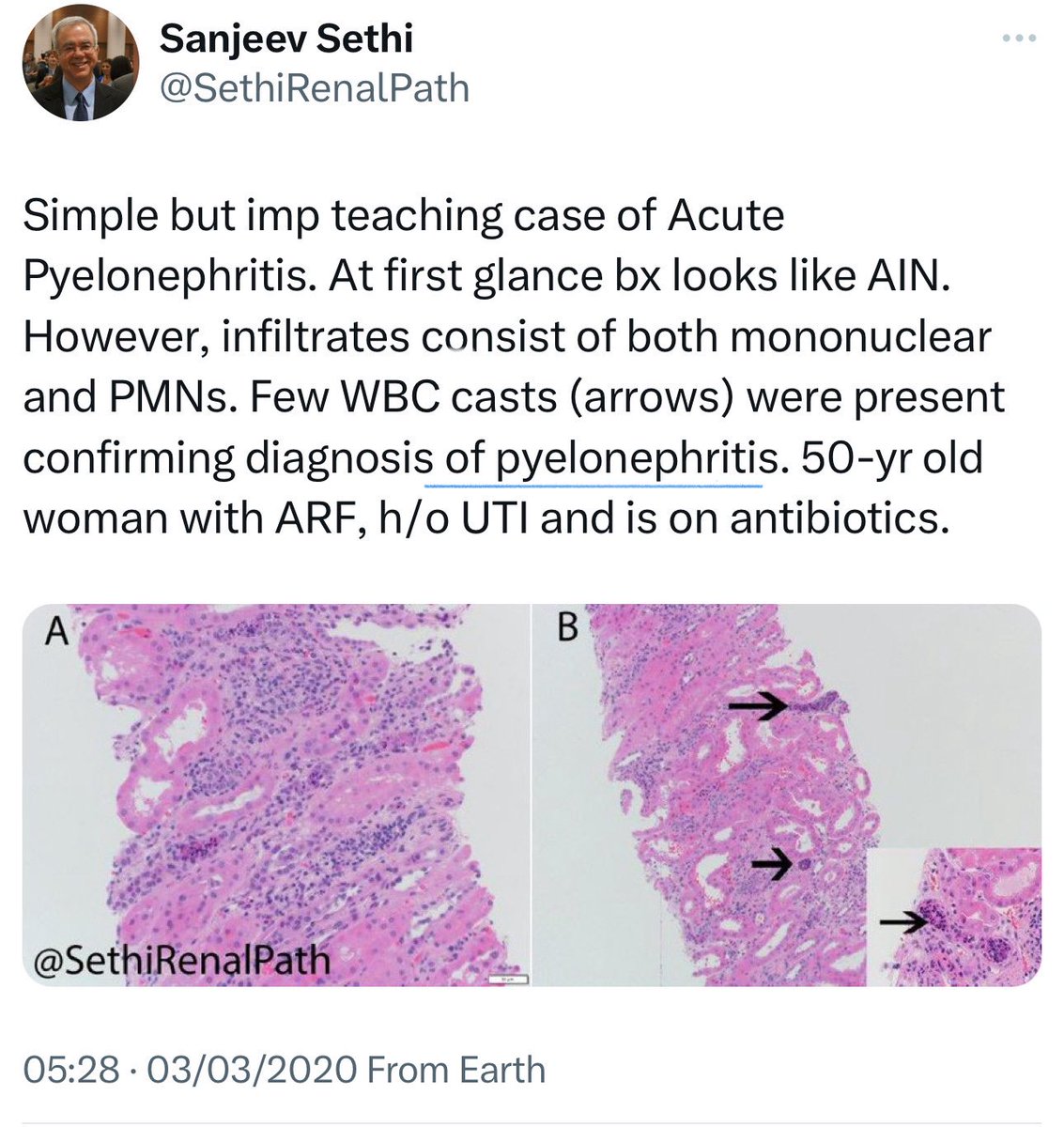
🔹pyelonephritis:
➖Recent cases link acute pyelonephritis (E. coli, S. aureus) to AIN.
➖Symptoms: impaired urinary concentrating ability, ↑K, and salt wasting.
➖Urine may show lymphocytes/WBC casts.
➖Chronic pyelonephritis (vesicoureteral reflux, obstructive stones) lead to xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis, causing renal ischemia, granulomas, and CKD
🔹Salmonella and Campylobacter:
➖AIN reported with typhoid fever and Campylobacter enteritis.
➖Renal injury linked to volume loss.
➖Suspect AIN if renal function doesn't improve after resuscitation.
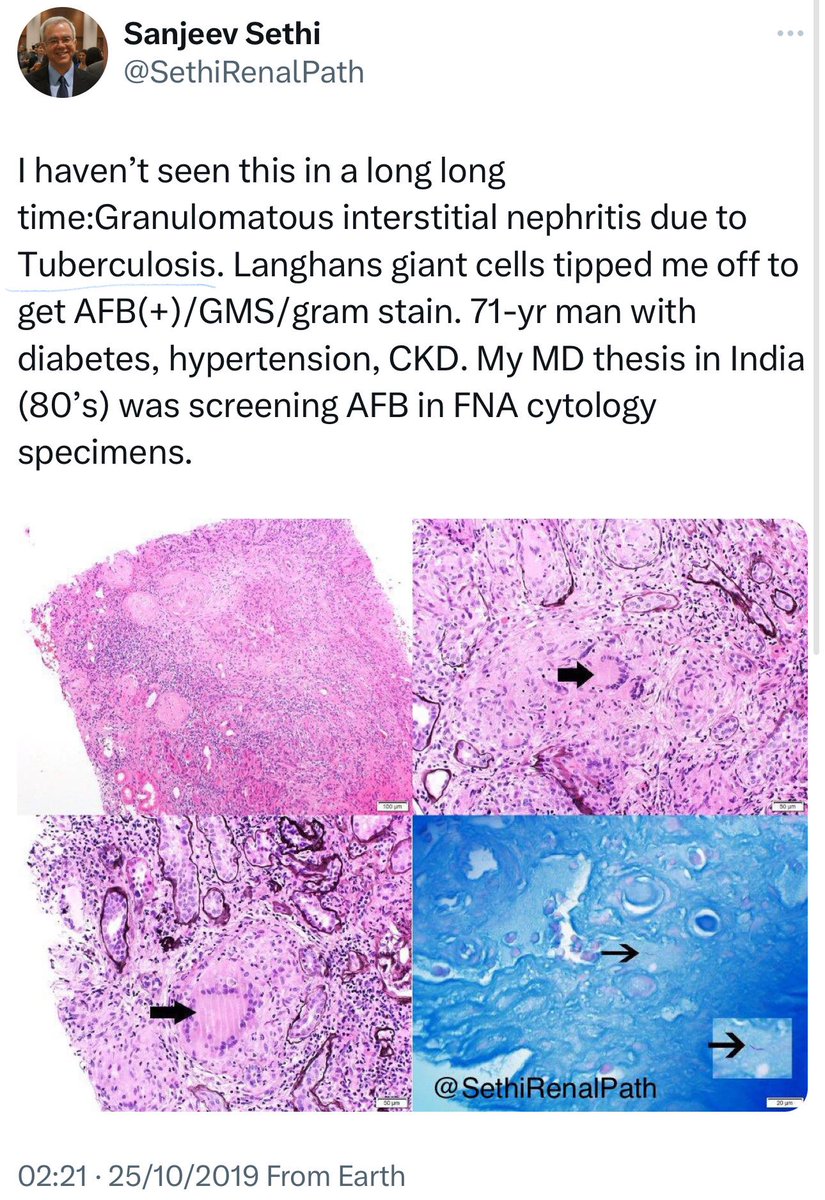
🔹Mycobacterium Tuberculosis:
➖15-20% of extrapulmonary TB cases affect the genitourinary tract causing sterile pyuria and scarring.
➖Biopsy is crucial, especially for ↑-risk groups
➖ Renal biopsy: Chronic granulomatous nephritis
➖Early diagnosis and treatment with (anti-TB drugs + steroids) can preserve renal function.
👇This is a post from @SethiRenalPath regarding a cases of pyelonephritis & TB
1️⃣Infection-Associated AIN:
(Bacteria viral and fungi)
🔘Bacterial AIN:
🔹pyelonephritis:
➖Recent cases link acute pyelonephritis (E. coli, S. aureus) to AIN.
➖Symptoms: impaired urinary concentrating ability, ↑K, and salt wasting.
➖Urine may show lymphocytes/WBC casts.
➖Chronic pyelonephritis (vesicoureteral reflux, obstructive stones) lead to xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis, causing renal ischemia, granulomas, and CKD
🔹Salmonella and Campylobacter:
➖AIN reported with typhoid fever and Campylobacter enteritis.
➖Renal injury linked to volume loss.
➖Suspect AIN if renal function doesn't improve after resuscitation.
🔹Mycobacterium Tuberculosis:
➖15-20% of extrapulmonary TB cases affect the genitourinary tract causing sterile pyuria and scarring.
➖Biopsy is crucial, especially for ↑-risk groups
➖ Renal biopsy: Chronic granulomatous nephritis
➖Early diagnosis and treatment with (anti-TB drugs + steroids) can preserve renal function.
👇This is a post from @SethiRenalPath regarding a cases of pyelonephritis & TB
3/14
⏩️ continue
1️⃣Infection-Associated AIN:
🔘virus AIN
🔹Adenovirus and AIN:
➖ can cause severe illness in immunosuppressed patients
➖Biopsy: lymphocyte, plasma cell & macrophage infiltrate
➖Treatment: IVIG + modifying Immunosupp.
🔹Other Viruses and AIN:
➖Influenza and COVID-19 have also been reported to cause AIN.
➖COVID-19 related AKI can result from direct viral invasion or an immunologic response.
🔹HIV and Renal Disease:
➖ HIV can cause HIVAN, FSGS, MCD, and AIN
➖ AIN often results from meds, coinfections, or autoimmune syndromes.
➖ Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome can cause AKI after starting ART in HIV-TB coinfected patients.
➖Biopsies: granulomatous interstitial nephritis.
➖Treatment: ART+ steroids can restore kidney function.
🔹Cytomegalovirus and AIN:
➖In kidney transplant recipients, CMV can cause interstitial nephritis.
➖Treatment: ganciclovir or valganciclovir + adjusting immunosupp.
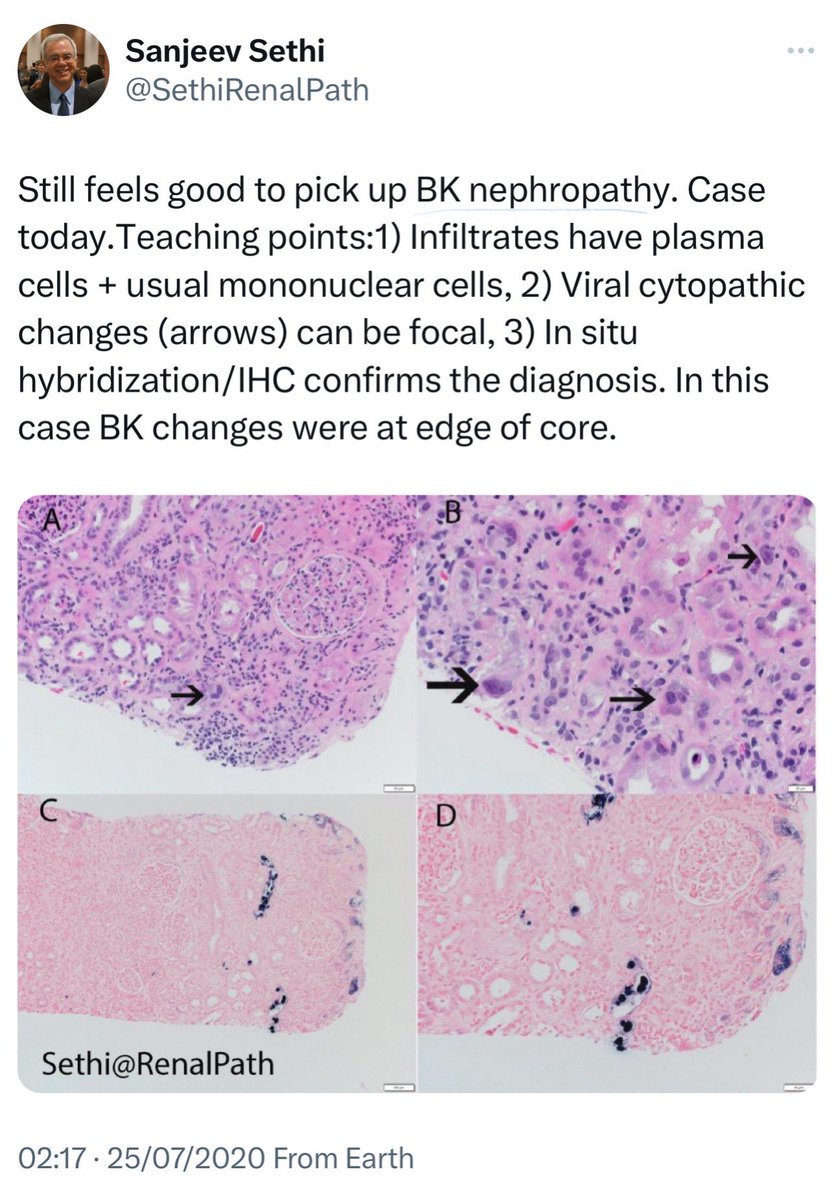
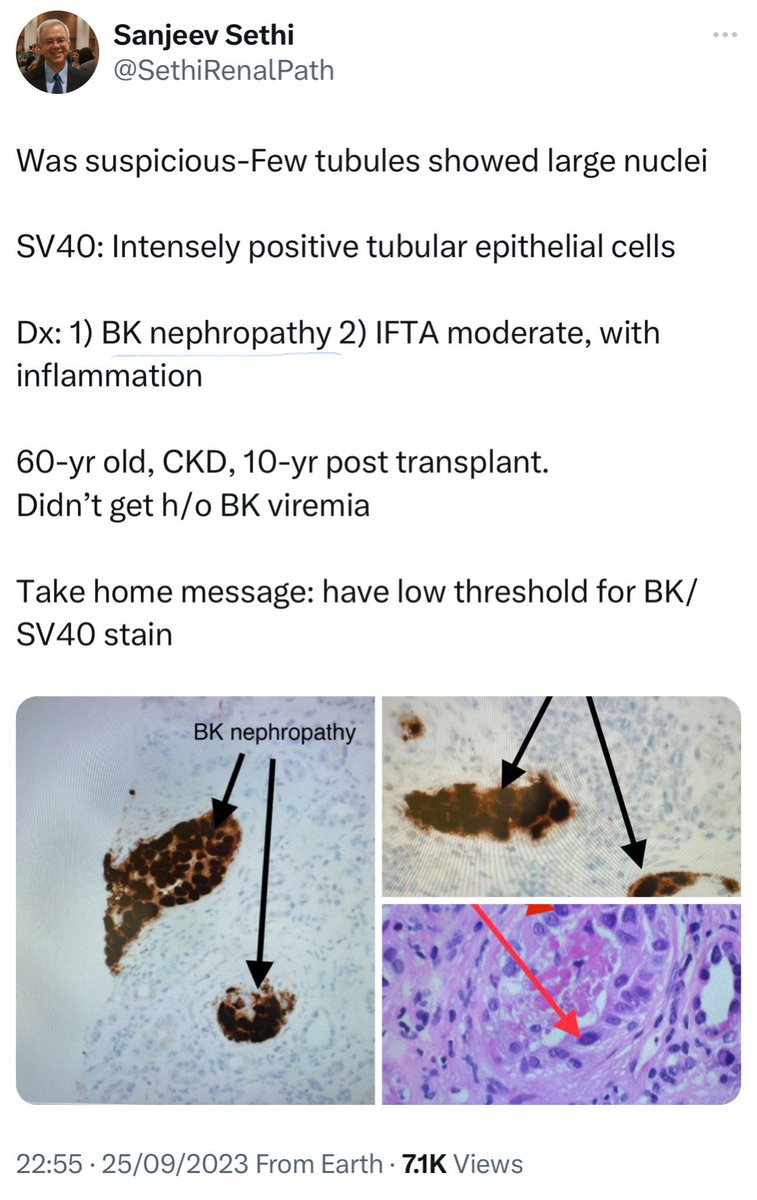
🔹BK Virus and AIN:
➖ BK virus also causes TIN, esp. in renal transplant patients and immunosuppressed individuals (leukemia post-chemo or BMT)
🔘Fungi
🔹Histoplasma and Cryptococcus:
➖ associated with granulomatous lesions, ➖AIN should be a differential diagnosis, esp. in immunosupp. individuals.
👇This is a post from @SethiRenalPath regarding a case of Bk Nephropathy
⏩️ continue
1️⃣Infection-Associated AIN:
🔘virus AIN
🔹Adenovirus and AIN:
➖ can cause severe illness in immunosuppressed patients
➖Biopsy: lymphocyte, plasma cell & macrophage infiltrate
➖Treatment: IVIG + modifying Immunosupp.
🔹Other Viruses and AIN:
➖Influenza and COVID-19 have also been reported to cause AIN.
➖COVID-19 related AKI can result from direct viral invasion or an immunologic response.
🔹HIV and Renal Disease:
➖ HIV can cause HIVAN, FSGS, MCD, and AIN
➖ AIN often results from meds, coinfections, or autoimmune syndromes.
➖ Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome can cause AKI after starting ART in HIV-TB coinfected patients.
➖Biopsies: granulomatous interstitial nephritis.
➖Treatment: ART+ steroids can restore kidney function.
🔹Cytomegalovirus and AIN:
➖In kidney transplant recipients, CMV can cause interstitial nephritis.
➖Treatment: ganciclovir or valganciclovir + adjusting immunosupp.
🔹BK Virus and AIN:
➖ BK virus also causes TIN, esp. in renal transplant patients and immunosuppressed individuals (leukemia post-chemo or BMT)
🔘Fungi
🔹Histoplasma and Cryptococcus:
➖ associated with granulomatous lesions, ➖AIN should be a differential diagnosis, esp. in immunosupp. individuals.
👇This is a post from @SethiRenalPath regarding a case of Bk Nephropathy
4/14
2️⃣Systemic Diseases and AIN
(Sjögren's, Sarcoidosis, IgG4-RD, SLE, Anti-TBM nephritis)
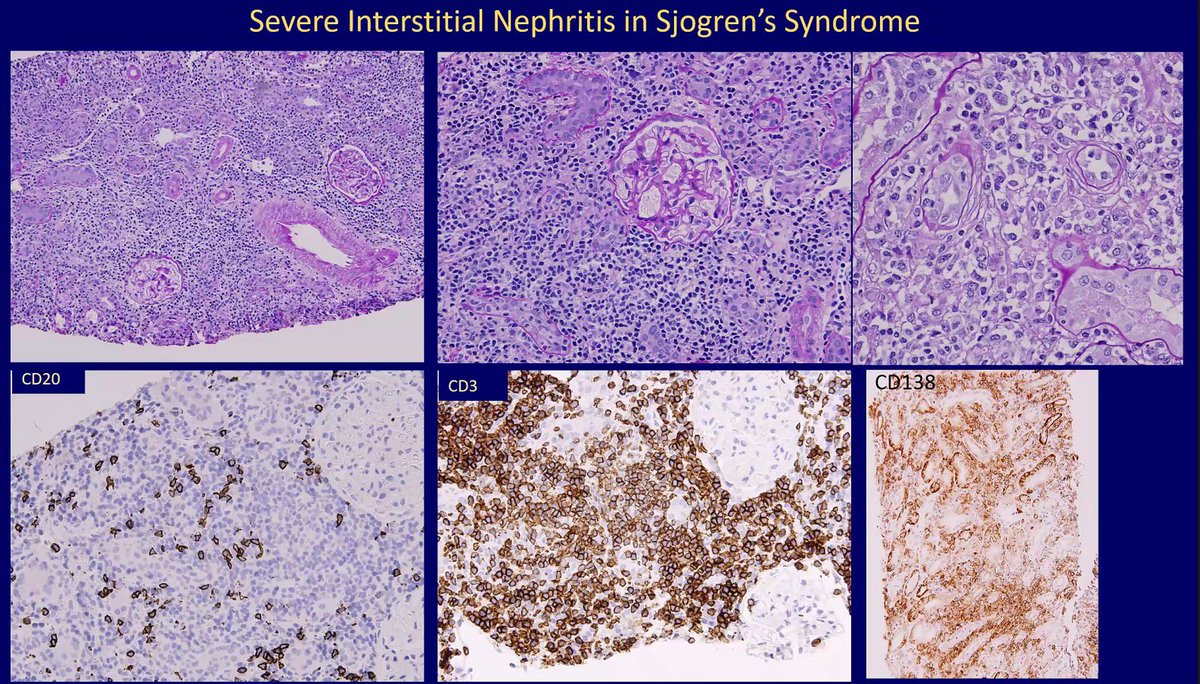
🔘Sjögren's Syndrome
➖Autoimmune disease causing lymphocytic infiltration in exocrine glands, leading to sicca symptoms.
➖5% of SS patients have renal issues; 75% of biopsied SS patients show TIN.
➖ present with acute or chronic TIN, dry mouth, dry eyes, and arthralgias.
➖Lab findings: ↑gamma globulin, ↓complement, ↓K+.
➖CD4+ T cells drive inflammation; CD8+ T cells, plasma cells, and granulomas also present.
➖Corticosteroids are first-line; MMF and rituximab for refractory cases.
➖steroids improved function in a study of 24 patients with TIN.
➖One patient improved with rituximab and prednisone.
➖No benefit of Immunosupp. in 75% of cases; cyclophosphamide showed some benefit.
➖TIN patients have a better prognosis than those with glomerular diseases; rarely progress to ESKD.
2️⃣Systemic Diseases and AIN
(Sjögren's, Sarcoidosis, IgG4-RD, SLE, Anti-TBM nephritis)
🔘Sjögren's Syndrome
➖Autoimmune disease causing lymphocytic infiltration in exocrine glands, leading to sicca symptoms.
➖5% of SS patients have renal issues; 75% of biopsied SS patients show TIN.
➖ present with acute or chronic TIN, dry mouth, dry eyes, and arthralgias.
➖Lab findings: ↑gamma globulin, ↓complement, ↓K+.
➖CD4+ T cells drive inflammation; CD8+ T cells, plasma cells, and granulomas also present.
➖Corticosteroids are first-line; MMF and rituximab for refractory cases.
➖steroids improved function in a study of 24 patients with TIN.
➖One patient improved with rituximab and prednisone.
➖No benefit of Immunosupp. in 75% of cases; cyclophosphamide showed some benefit.
➖TIN patients have a better prognosis than those with glomerular diseases; rarely progress to ESKD.
5/14
⏩️ continue
2️⃣Systemic Diseases and AIN
(Sjögren's, Sarcoidosis, IgG4-RD, SLE, Anti-TBM nephritis)
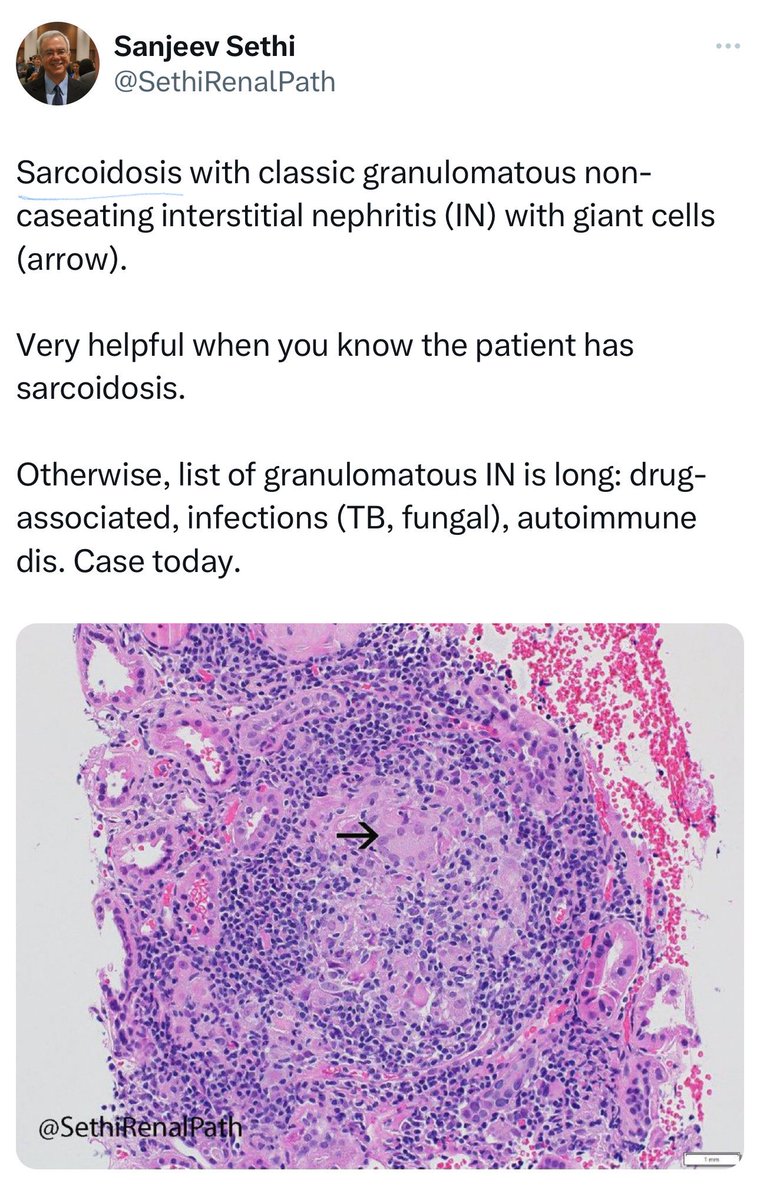
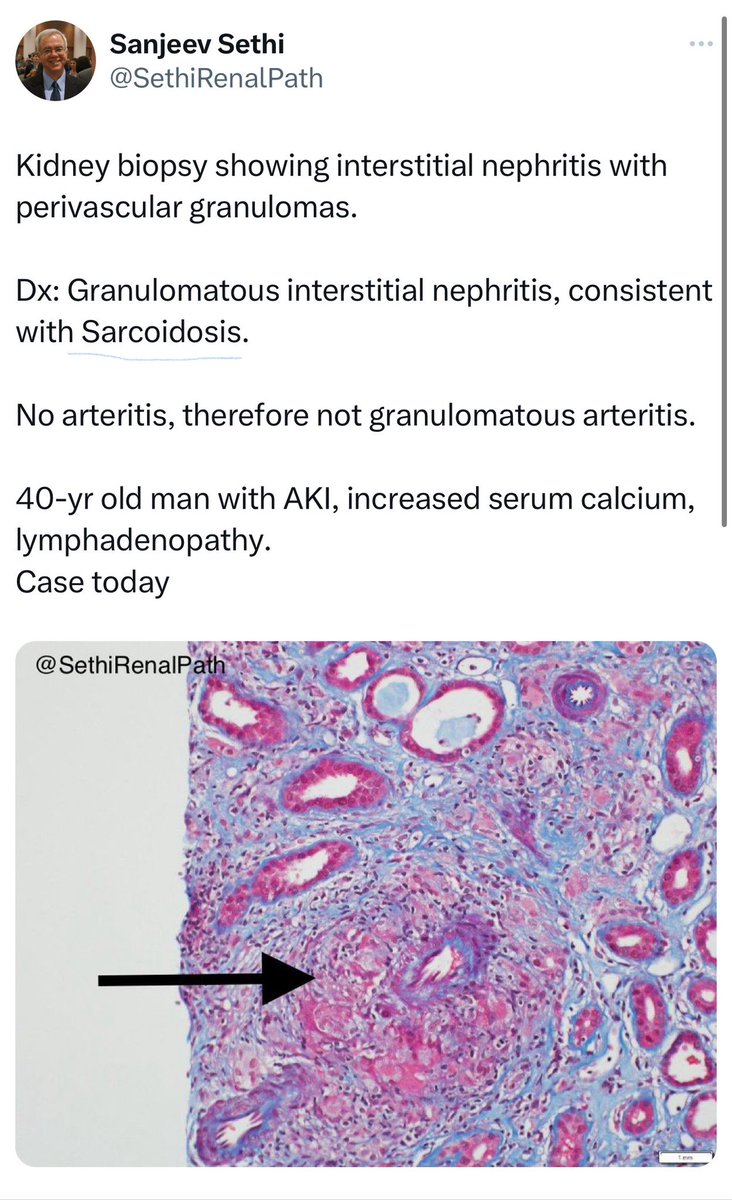
🔘 Sarcoidosis
➖Chronic multisystemic noncaseating granulomatous disease often affecting kidneys, linked to ↑Ca and ↑Ca in urine
➖incidence is 0.1% in 🇯🇵 biopsy series.
➖In a single-center study, 85% of sarcoidosis patients with kidney disease had TIN.
➖Glucocorticoids (0.5-1.0 mg/kg/day) effectively improve renal function in sarcoid-related TIN.
➖Most patients show significant renal improvement with steroid.
➖ In Mahevas' 2009 study, interstitial fibrosis reduced steroid response. No other histologic features predicted response.
➖ Mahevas also found no benefit between pulsed methylprednisolone and oral prednisone in a trial with 40 participants.
➖ eGFR and adverse events were similar between groups.
➖ For steroid intolerance, consider azathioprine, mycophenolate, or TNF antagonists.
➖ There is partial or no response in cases with interstitial fibrosis.
👇This is a post from @SethiRenalPath regarding sarcoidosis
⏩️ continue
2️⃣Systemic Diseases and AIN
(Sjögren's, Sarcoidosis, IgG4-RD, SLE, Anti-TBM nephritis)
🔘 Sarcoidosis
➖Chronic multisystemic noncaseating granulomatous disease often affecting kidneys, linked to ↑Ca and ↑Ca in urine
➖incidence is 0.1% in 🇯🇵 biopsy series.
➖In a single-center study, 85% of sarcoidosis patients with kidney disease had TIN.
➖Glucocorticoids (0.5-1.0 mg/kg/day) effectively improve renal function in sarcoid-related TIN.
➖Most patients show significant renal improvement with steroid.
➖ In Mahevas' 2009 study, interstitial fibrosis reduced steroid response. No other histologic features predicted response.
➖ Mahevas also found no benefit between pulsed methylprednisolone and oral prednisone in a trial with 40 participants.
➖ eGFR and adverse events were similar between groups.
➖ For steroid intolerance, consider azathioprine, mycophenolate, or TNF antagonists.
➖ There is partial or no response in cases with interstitial fibrosis.
👇This is a post from @SethiRenalPath regarding sarcoidosis
6/14
⏩️ continue
2️⃣Systemic Diseases and AIN
(Sjögren's, Sarcoidosis, IgG4-RD, SLE, Anti-TBM nephritis)
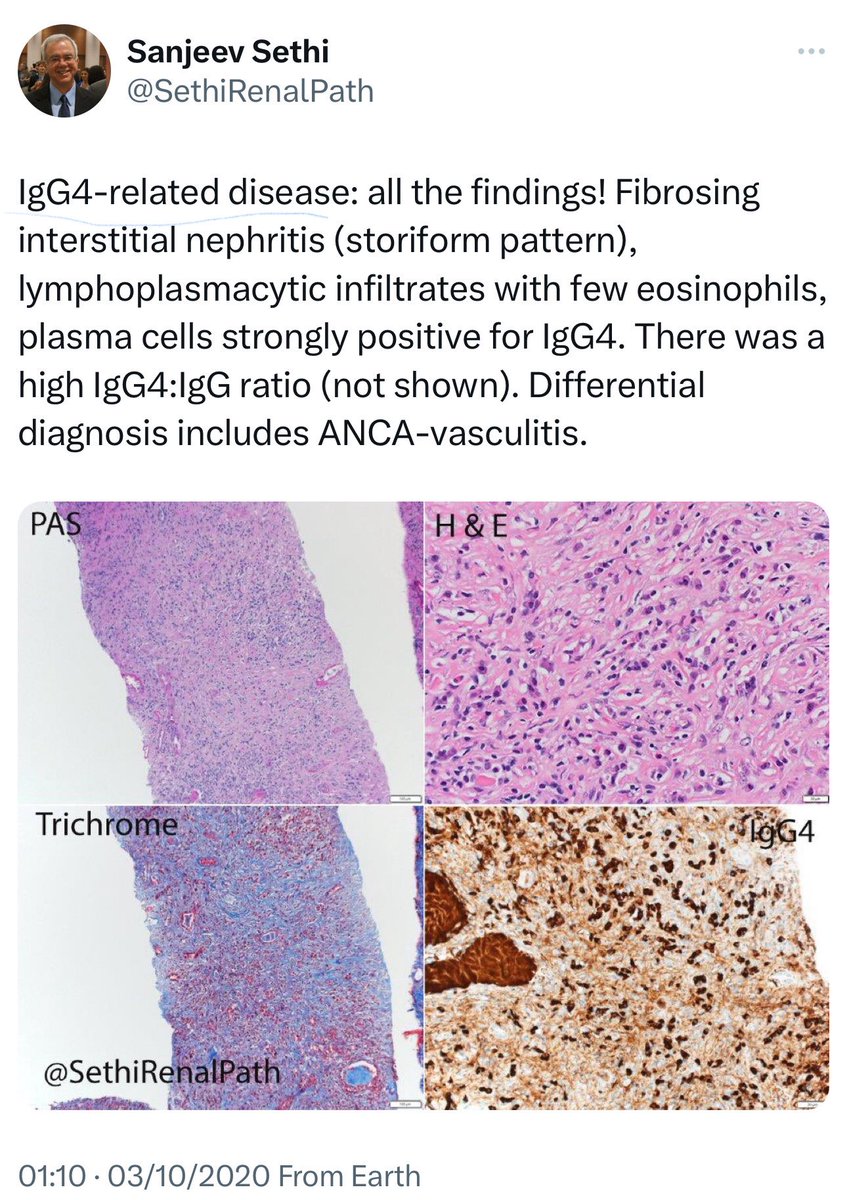
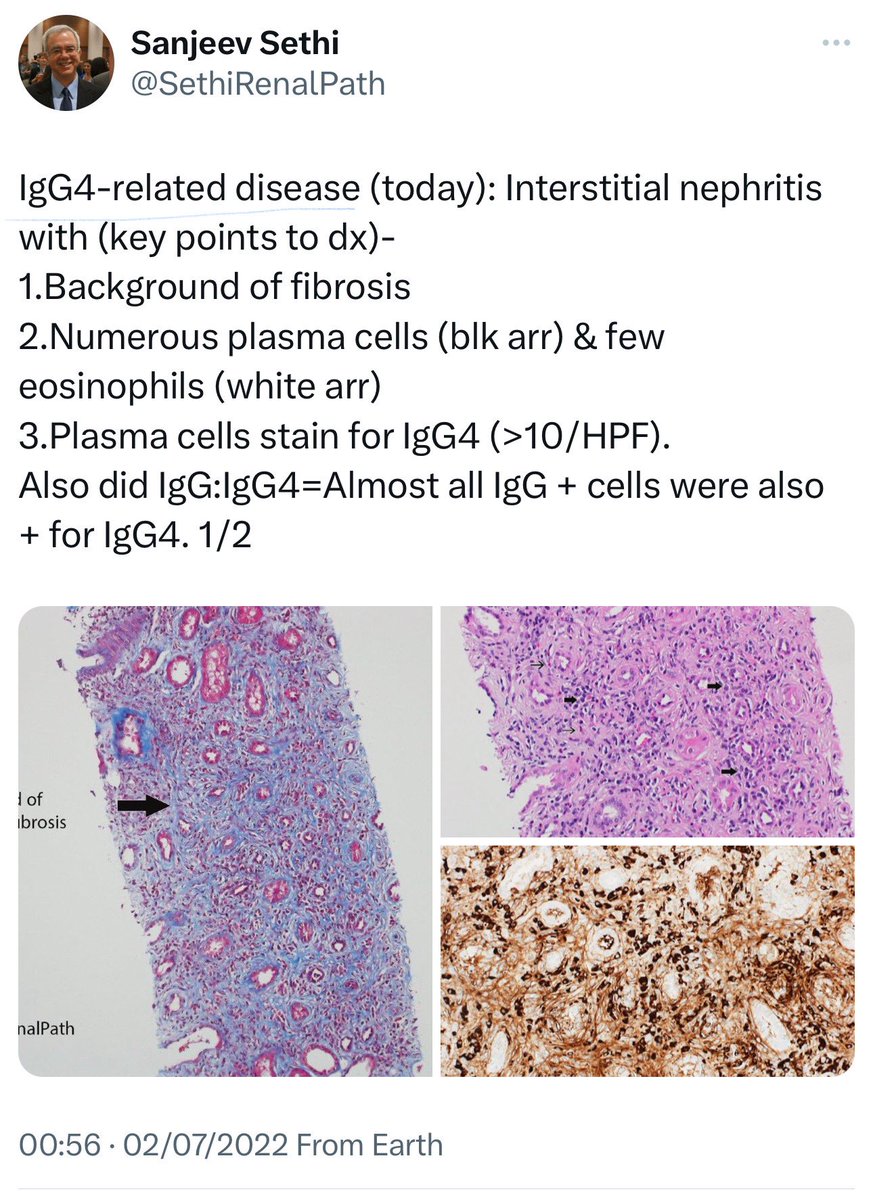
🔘Immunoglobulin G4–related disease (IgG4-RD) :
➖ Immune-mediated fibroinflammatory condition with diffuse lymphoplasmacytic infiltration affecting multiple organs.
➖ More commonly affects men.
➖ Clinical manifestations: interstitial lung disease, sclerosing cholangitis, retroperitoneal fibrosis with ureteral obstruction, large-vessel vasculitis.
➖ IgG4-RD and SS have overlapping features like sicca symptoms, arthralgia, ↑gamma globulin and ↓complement
➖ Key diagnostic features: tissue fibrosis with storiform pattern, diffuse lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate (mainly IgG4+ plasma cells), and moderate eosinophilia.
➖ IgG4-related kidney disease shows rapid response to steroid therapy, often within weeks.
➖ In a study of 19 🇯🇵 patients with IgG4-TIN, 18 showed improved renal function and radiology after 1 month of steroids.
➖ Raissian et al. found 90% of patients (17/19) had a clinical response to steroids therapy.
➖ Long-term prognosis needs further understanding; kidney relapses can occur.
👇This is a post from @SethiRenalPath regarding IgG4-RD
⏩️ continue
2️⃣Systemic Diseases and AIN
(Sjögren's, Sarcoidosis, IgG4-RD, SLE, Anti-TBM nephritis)
🔘Immunoglobulin G4–related disease (IgG4-RD) :
➖ Immune-mediated fibroinflammatory condition with diffuse lymphoplasmacytic infiltration affecting multiple organs.
➖ More commonly affects men.
➖ Clinical manifestations: interstitial lung disease, sclerosing cholangitis, retroperitoneal fibrosis with ureteral obstruction, large-vessel vasculitis.
➖ IgG4-RD and SS have overlapping features like sicca symptoms, arthralgia, ↑gamma globulin and ↓complement
➖ Key diagnostic features: tissue fibrosis with storiform pattern, diffuse lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate (mainly IgG4+ plasma cells), and moderate eosinophilia.
➖ IgG4-related kidney disease shows rapid response to steroid therapy, often within weeks.
➖ In a study of 19 🇯🇵 patients with IgG4-TIN, 18 showed improved renal function and radiology after 1 month of steroids.
➖ Raissian et al. found 90% of patients (17/19) had a clinical response to steroids therapy.
➖ Long-term prognosis needs further understanding; kidney relapses can occur.
👇This is a post from @SethiRenalPath regarding IgG4-RD
7/14
⏩️ continue
2️⃣Systemic Diseases and AIN
(Sjögren's, Sarcoidosis, IgG4-RD, SLE, Anti-TBM nephritis)
🔘 SLE
➖ in lupus nephritis (LN), TIN can occur with or without immune deposits in the TBM.
➖ The extent of TIN may predict renal outcomes.
➖TBM immune deposits correlate with serologic activity but not prognosis.
➖ In a study of 313 LN patients, TIN was linked to doubling serum creatinine or a 2-fold risk of ESKD.
➖ A 2020 study of 98 LN cases showed a 20% ↓ treatment response rate in those with TIN vs those without TIN.
➖ These findings suggest LN with TIN may require aggressive treatment.
➖ Case reports show TIN as the predominant lesion in LN, with kidney function stabilizing or improving after corticosteroids.
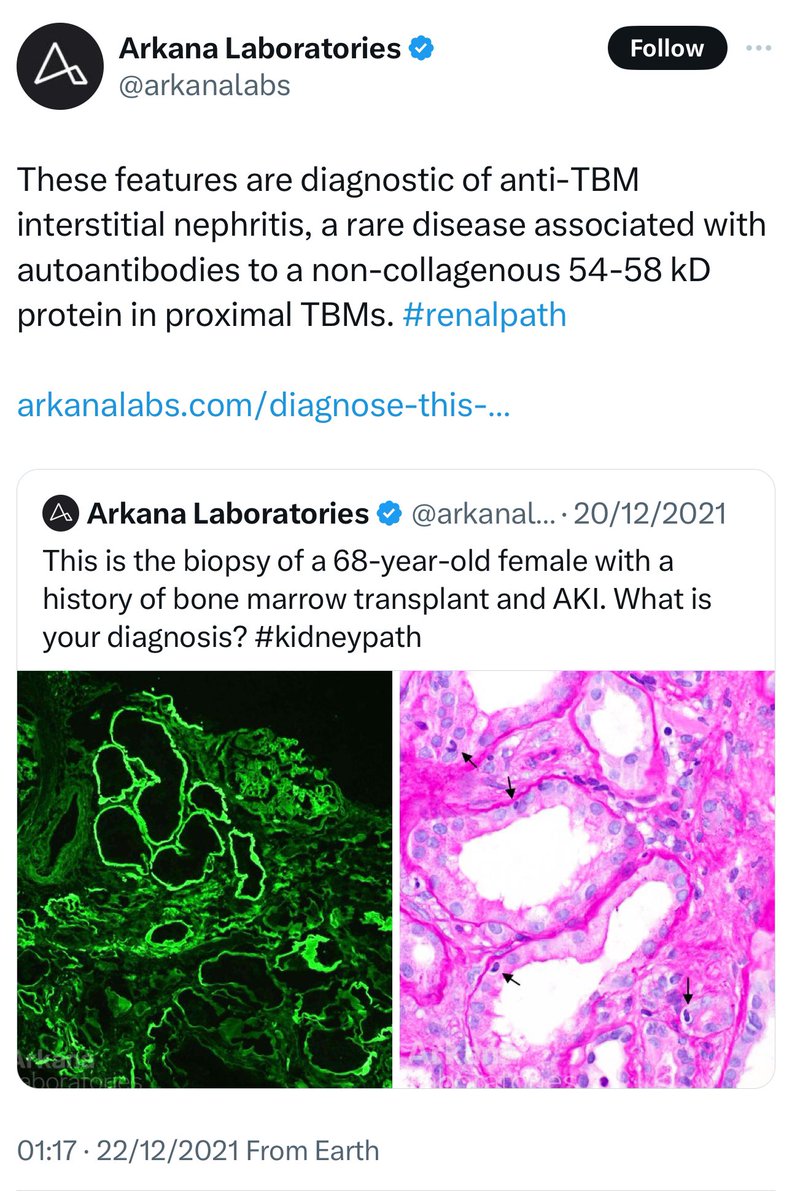
🔘 Anti-TBM nephritis (Tubular Basement Membrane)
➖ Rare with linear deposition of immunoglobulins and complements along the TBM.
➖ Autoantibodies target the TIN antigen in the proximal TBM, sometimes triggered by drug exposure.
➖ The antigen interacts with type IV collagen, laminin, and integrins.
➖ can be primary or secondary to MN, LN, and allograft nephropathy.
➖ MN with extensive TBM deposits occurs post-allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant, likely due to graft vs host disease antibodies.
➖ In kidney allografts, anti-TBM disease can occur in recipients without the antigen in their native kidneys.
👇This is a post from @arkanalabs regarding Anti-TBM nephritis
⏩️ continue
2️⃣Systemic Diseases and AIN
(Sjögren's, Sarcoidosis, IgG4-RD, SLE, Anti-TBM nephritis)
🔘 SLE
➖ in lupus nephritis (LN), TIN can occur with or without immune deposits in the TBM.
➖ The extent of TIN may predict renal outcomes.
➖TBM immune deposits correlate with serologic activity but not prognosis.
➖ In a study of 313 LN patients, TIN was linked to doubling serum creatinine or a 2-fold risk of ESKD.
➖ A 2020 study of 98 LN cases showed a 20% ↓ treatment response rate in those with TIN vs those without TIN.
➖ These findings suggest LN with TIN may require aggressive treatment.
➖ Case reports show TIN as the predominant lesion in LN, with kidney function stabilizing or improving after corticosteroids.
🔘 Anti-TBM nephritis (Tubular Basement Membrane)
➖ Rare with linear deposition of immunoglobulins and complements along the TBM.
➖ Autoantibodies target the TIN antigen in the proximal TBM, sometimes triggered by drug exposure.
➖ The antigen interacts with type IV collagen, laminin, and integrins.
➖ can be primary or secondary to MN, LN, and allograft nephropathy.
➖ MN with extensive TBM deposits occurs post-allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplant, likely due to graft vs host disease antibodies.
➖ In kidney allografts, anti-TBM disease can occur in recipients without the antigen in their native kidneys.
👇This is a post from @arkanalabs regarding Anti-TBM nephritis
8/14
⏩️ continue
2️⃣Systemic Diseases and AIN
(Sjögren's, Sarcoidosis, IgG4-RD, SLE, Anti-TBM nephritis)
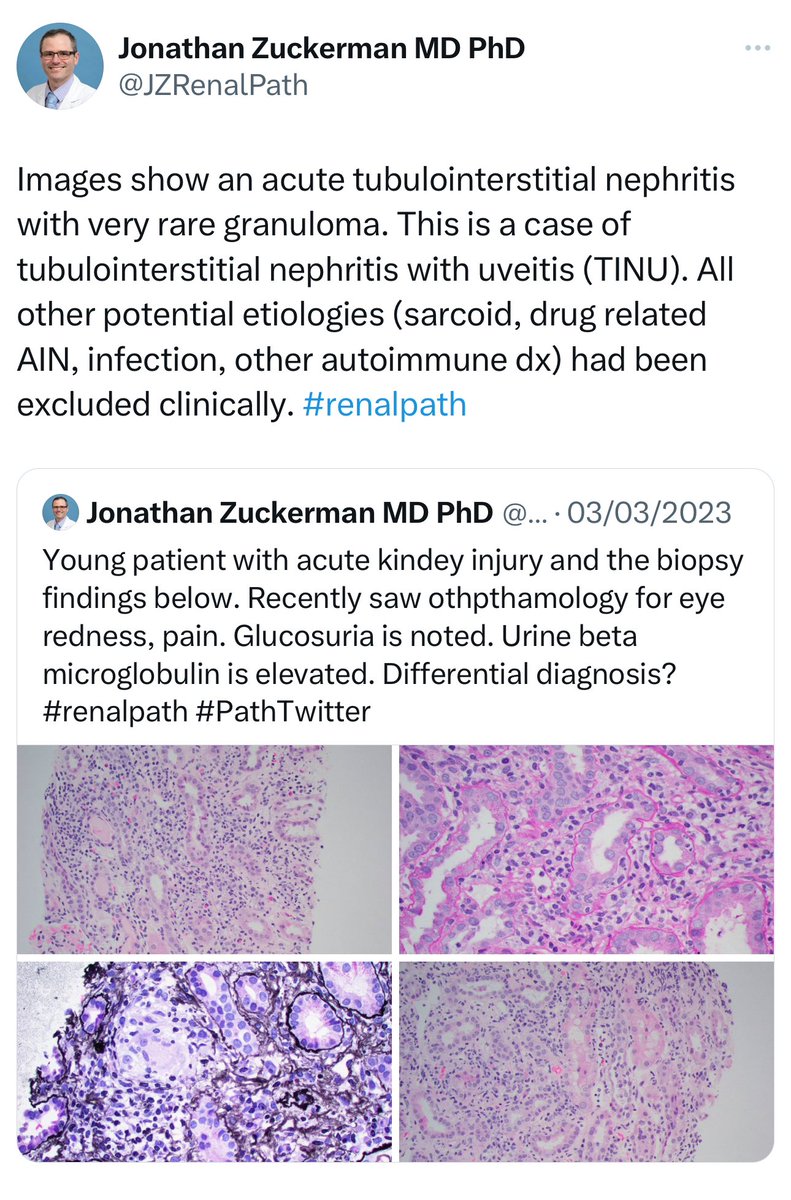
🔘Tubulointerstitial Nephritis and Uveitis (TINU) 👁️🩺
➖ immune-mediated, described in 1975.
➖Mostly in young women; onset age 20-76.
➖Cause unclear, linked to HLA-DQ &-DR. ➖Consider TINU if TIN and anterior uveitis occur together without other diseases.
➖Ocular and kidney disease progress independently.
➖Kidney prognosis is favorable.
➖Treatment: corticosteroids, though no RCT.
➖Case series show improvement with ~19 weeks of steroids.
👇This is a post from @JZRenalPath regarding TINU
⏩️ continue
2️⃣Systemic Diseases and AIN
(Sjögren's, Sarcoidosis, IgG4-RD, SLE, Anti-TBM nephritis)
🔘Tubulointerstitial Nephritis and Uveitis (TINU) 👁️🩺
➖ immune-mediated, described in 1975.
➖Mostly in young women; onset age 20-76.
➖Cause unclear, linked to HLA-DQ &-DR. ➖Consider TINU if TIN and anterior uveitis occur together without other diseases.
➖Ocular and kidney disease progress independently.
➖Kidney prognosis is favorable.
➖Treatment: corticosteroids, though no RCT.
➖Case series show improvement with ~19 weeks of steroids.
👇This is a post from @JZRenalPath regarding TINU
9/14
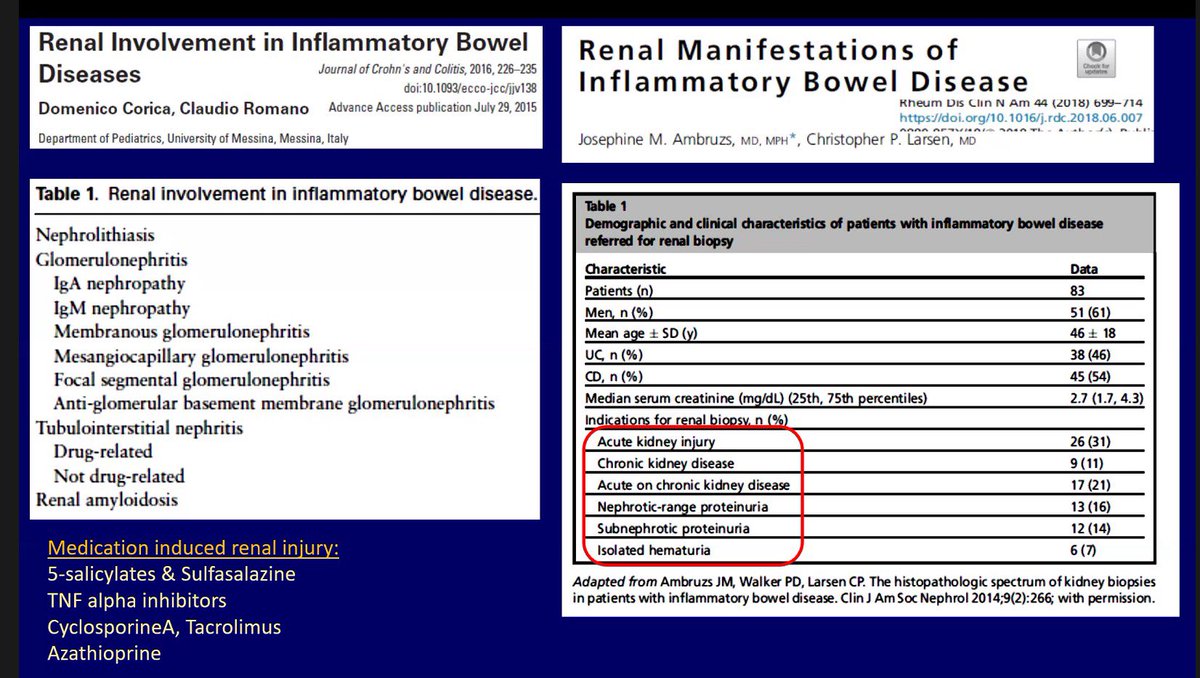
3️⃣inflammatory bowel disease (IBD):
➖ TIN is a common renal manifestation IBD
➖ A biopsy series in adults with IBD showed TIN in 19% of cases:
▪️44% acute TIN
▪️31% granulomatous TIN
▪️25% chronic TIN
➖ All patients with granulomatous interstitial nephritis had exposure to aminosalicylates (ASA).
➖ 5-ASA and its derivatives (sulfasalazine, mesalamine) are known causes of TIN, but TIN can also occur without medication.
➖ Corticosteroids are the treatment of choice for IBD-TIN.
➖ In a case series of 4 adults with Crohn + TIN, 1 patient with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy showed no improvement with steroid .
➖ Tubular proteins as disease markers show conflicting results; some link to IBD activity, others to tubular damage independent of 5-ASA.
3️⃣inflammatory bowel disease (IBD):
➖ TIN is a common renal manifestation IBD
➖ A biopsy series in adults with IBD showed TIN in 19% of cases:
▪️44% acute TIN
▪️31% granulomatous TIN
▪️25% chronic TIN
➖ All patients with granulomatous interstitial nephritis had exposure to aminosalicylates (ASA).
➖ 5-ASA and its derivatives (sulfasalazine, mesalamine) are known causes of TIN, but TIN can also occur without medication.
➖ Corticosteroids are the treatment of choice for IBD-TIN.
➖ In a case series of 4 adults with Crohn + TIN, 1 patient with interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy showed no improvement with steroid .
➖ Tubular proteins as disease markers show conflicting results; some link to IBD activity, others to tubular damage independent of 5-ASA.
10/14
4️⃣ Metabolic Disorders
(Urate, hypokalemia, hypercalcemia, hyperoxaluria)
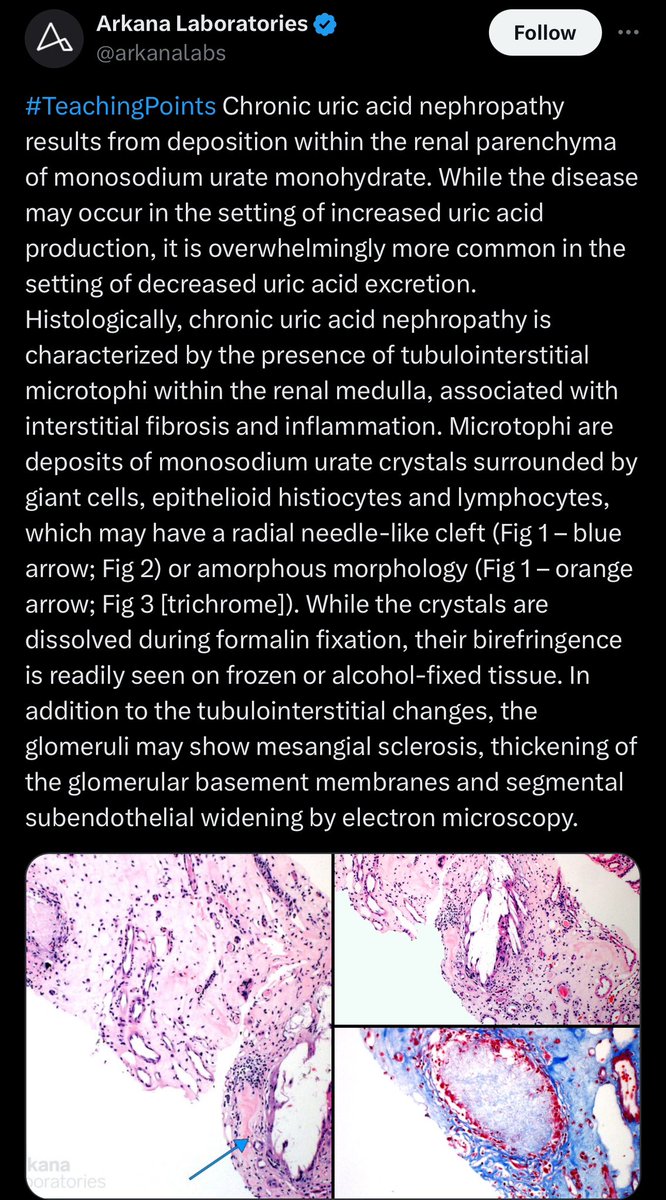
🔘Chronic Urate Nephropathy:
➖Gouty nephropathy is debated due to coexistence with HTN or vascular disease.
➖Urate crystals in the medullary interstitium may cause chronic inflammation.
➖ ↓ uric acid and lifestyle modifications are the main therapies.
🔘Hypokalemia Nephropathy:
➖Prolonged ↓K+ can cause CIN and kidney function loss.
➖Histology: tubules vacuolar lesions
➖ K+ repletion can reverse these changes.
4️⃣ Metabolic Disorders
(Urate, hypokalemia, hypercalcemia, hyperoxaluria)
🔘Chronic Urate Nephropathy:
➖Gouty nephropathy is debated due to coexistence with HTN or vascular disease.
➖Urate crystals in the medullary interstitium may cause chronic inflammation.
➖ ↓ uric acid and lifestyle modifications are the main therapies.
🔘Hypokalemia Nephropathy:
➖Prolonged ↓K+ can cause CIN and kidney function loss.
➖Histology: tubules vacuolar lesions
➖ K+ repletion can reverse these changes.
11/14
⏩️ continue
4️⃣ Metabolic Disorders
(Urate, hypokalemia, hypercalcemia, hyperoxaluria)
🔘Hypercalcemia Nephropathy:
➖Prolonged ↑Ca leads to nephrocalcinosis and CIN, with tubular/interstitial calcifications, lymphocyte infiltration, and fibrosis.
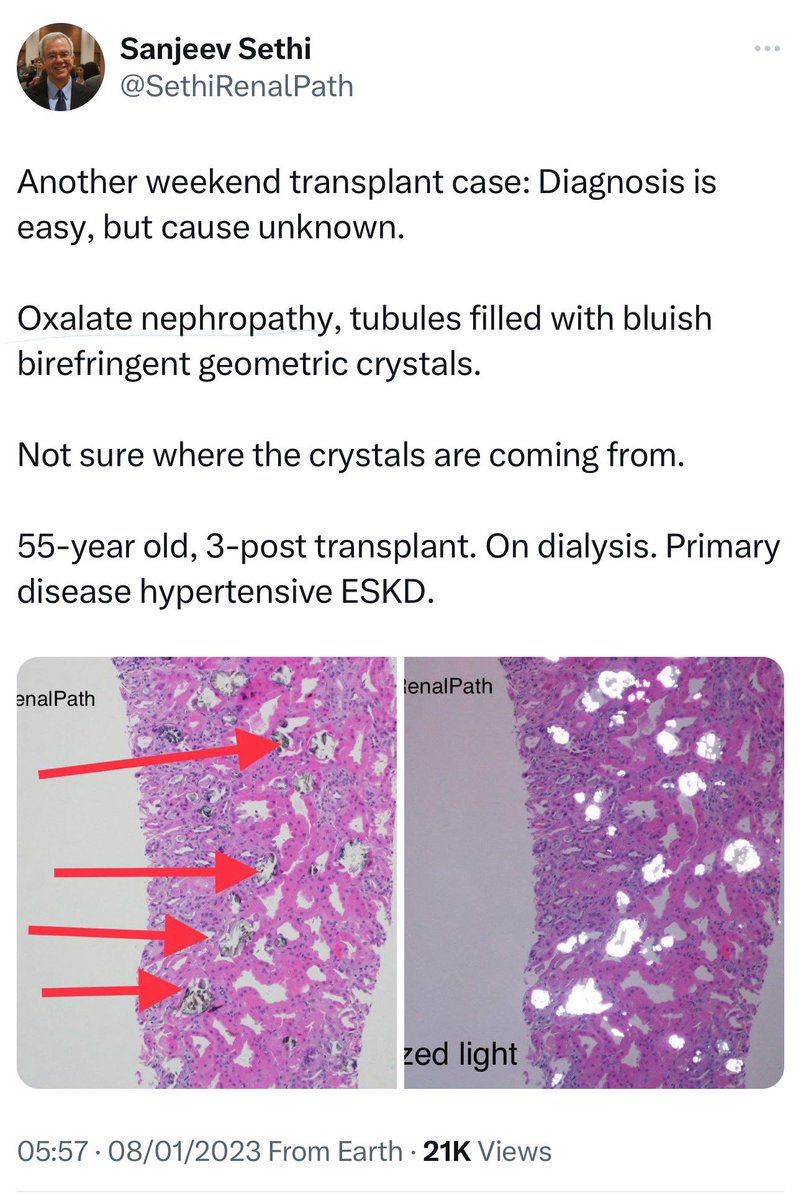
🔘Oxalate Nephropathy:
➖Ca oxalate crystals in the kidney tubules lead to renal impairment, acute tubular injury, and interstitial nephritis.
➖Primary hyperoxaluria is genetic🧬➖secondary is due to diet or malabsorption.
➖studies found 1-4% cases in biopsies, with ↑ risk of progression to ESKD.
➖Treatment: IV fluids, ↑Ca intake & dietary advice.
 👇This is a post from @SethiRenalPath regarding Oxalate Nephropathy
⏩️ continue
4️⃣ Metabolic Disorders
(Urate, hypokalemia, hypercalcemia, hyperoxaluria)
🔘Hypercalcemia Nephropathy:
➖Prolonged ↑Ca leads to nephrocalcinosis and CIN, with tubular/interstitial calcifications, lymphocyte infiltration, and fibrosis.
🔘Oxalate Nephropathy:
➖Ca oxalate crystals in the kidney tubules lead to renal impairment, acute tubular injury, and interstitial nephritis.
➖Primary hyperoxaluria is genetic🧬➖secondary is due to diet or malabsorption.
➖studies found 1-4% cases in biopsies, with ↑ risk of progression to ESKD.
➖Treatment: IV fluids, ↑Ca intake & dietary advice.
 👇This is a post from @SethiRenalPath regarding Oxalate Nephropathy
12/14
5️⃣Hereditary/Genetic Disorders
🔘Nephronophthisis:
➖Autosomal recessive disease with chronic TIN🧬
➖Infantile form progresses to ESRD before age 5, juvenile form in the second decade.
➖Ciliopathy with small cysts.
➖Diagnosis via extrarenal manifestations and genetic testing, not biopsy.
➖Histology shows TBM thickening, tubular atrophy, and interstitial fibrosis.
🔘ADTKD "previously summarized."
🔘Other Disorders:
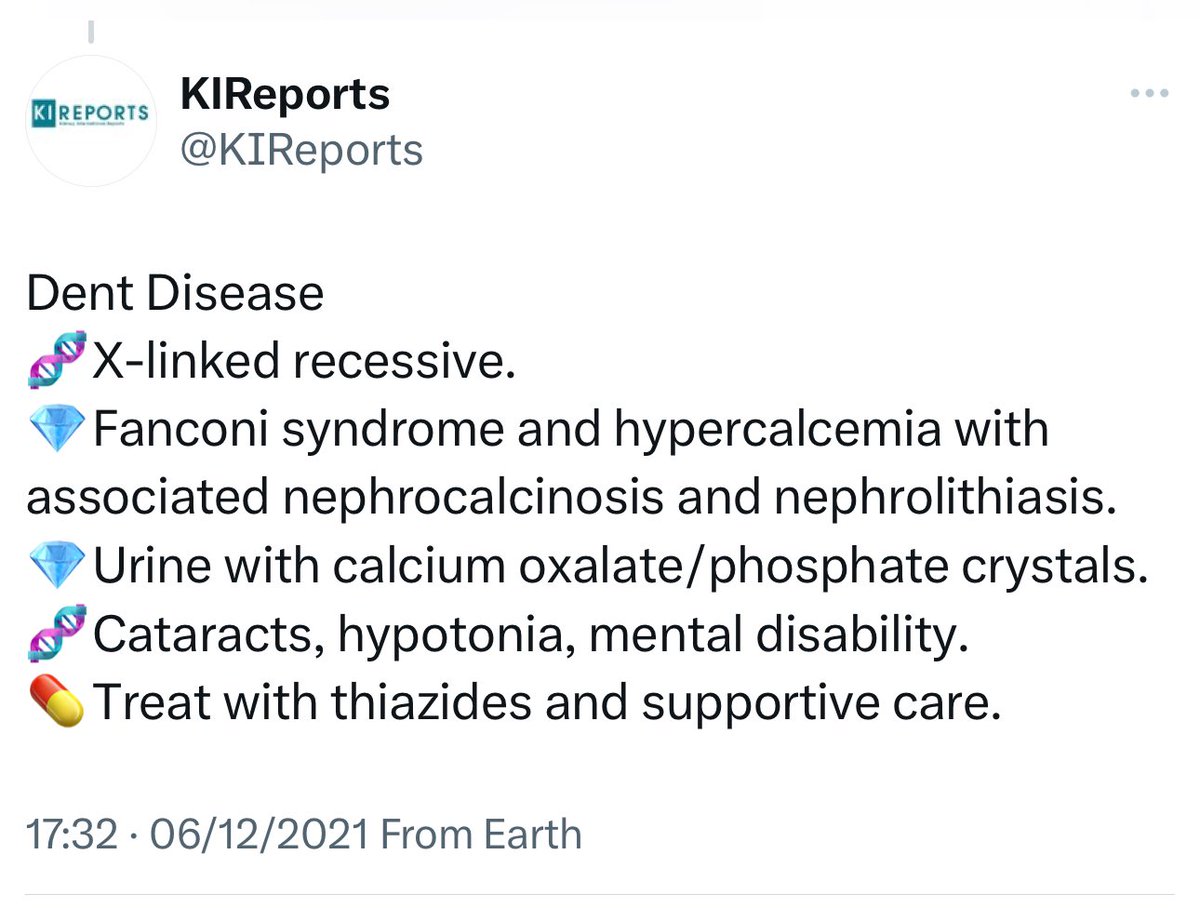
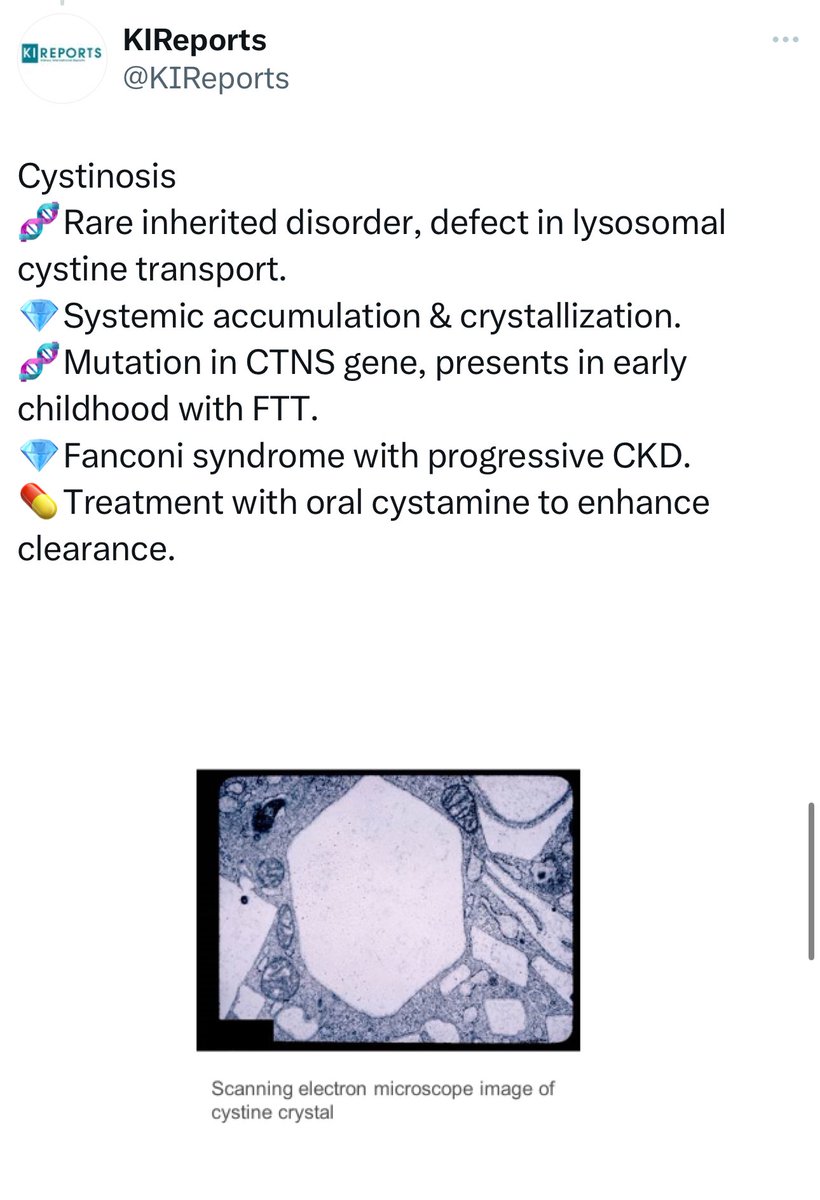
➖Dent disease, cystinosis, and sickle-cell nephropathy also cause tubulointerstitial nephritis.
5️⃣Hereditary/Genetic Disorders
🔘Nephronophthisis:
➖Autosomal recessive disease with chronic TIN🧬
➖Infantile form progresses to ESRD before age 5, juvenile form in the second decade.
➖Ciliopathy with small cysts.
➖Diagnosis via extrarenal manifestations and genetic testing, not biopsy.
➖Histology shows TBM thickening, tubular atrophy, and interstitial fibrosis.
🔘ADTKD "previously summarized."
🔘Other Disorders:
➖Dent disease, cystinosis, and sickle-cell nephropathy also cause tubulointerstitial nephritis.
13/14
6️⃣Environmental exposures and endemic association
🔘 Lead Exposure:
➖Acute: neuro symptoms, abdominal pain, hemolysis, AKI with Fanconi's.
➖Chronic: tubulointerstitial damage, HTN, hyperuricemia, minimal proteinuria.
➖Treatment: EDTA chelation or oral succimer.
🔘 Cadmium Exposure:
➖Chronic: irreversible Fanconi syndrome, tubulointerstitial nephritis, glycosuria, aminoaciduria, tubular proteinuria.
➖Diagnosis: urinary cadmium excretion.
➖Treatment: supportive.
🔘 CKD of Unknown Cause (CKDu):
➖Affects agricultural workers in Central America, Sri Lanka, India.
➖Not linked to traditional CKD risk factors.
➖Suspected causes: heat stress, dehydration, toxins, heavy metals. Symptoms: mild lymphocytic inflammation, interstitial fibrosis.
🔘 Balkan Endemic Nephropathy (BEN):
➖Affects Balkan peninsula residents. Linked to aristolochic acid from contaminated wheat.
➖Presents with interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy, ↓ ESKD progression, ↑ upper urothelial cancer.
➖Treatment: supportive.
🔘 Radiation Nephropathy:
➖Caused by radiotherapy, leading to DNA damage and cell death.
➖Acute: vascular and glomerular damage.
➖Chronic: interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy, glomerular scarring.
➖Treatment: supportive.
👇This is from Nephrology Secrets
6️⃣Environmental exposures and endemic association
🔘 Lead Exposure:
➖Acute: neuro symptoms, abdominal pain, hemolysis, AKI with Fanconi's.
➖Chronic: tubulointerstitial damage, HTN, hyperuricemia, minimal proteinuria.
➖Treatment: EDTA chelation or oral succimer.
🔘 Cadmium Exposure:
➖Chronic: irreversible Fanconi syndrome, tubulointerstitial nephritis, glycosuria, aminoaciduria, tubular proteinuria.
➖Diagnosis: urinary cadmium excretion.
➖Treatment: supportive.
🔘 CKD of Unknown Cause (CKDu):
➖Affects agricultural workers in Central America, Sri Lanka, India.
➖Not linked to traditional CKD risk factors.
➖Suspected causes: heat stress, dehydration, toxins, heavy metals. Symptoms: mild lymphocytic inflammation, interstitial fibrosis.
🔘 Balkan Endemic Nephropathy (BEN):
➖Affects Balkan peninsula residents. Linked to aristolochic acid from contaminated wheat.
➖Presents with interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy, ↓ ESKD progression, ↑ upper urothelial cancer.
➖Treatment: supportive.
🔘 Radiation Nephropathy:
➖Caused by radiotherapy, leading to DNA damage and cell death.
➖Acute: vascular and glomerular damage.
➖Chronic: interstitial fibrosis, tubular atrophy, glomerular scarring.
➖Treatment: supportive.
👇This is from Nephrology Secrets
14/14
🔍 Prognosis
Prognosis of TIN depends on the cause, therapy response, and renal impairment degree.
🔸 Chronicity = worse outcome
🔸 Early diagnosis improves renal health
🔸 Identification & monitoring challenging
🩺 Autoimmune markers (IgG, complements, anti-Ro/La) help identify IgG4, SLE, SS-related TIN.
💧 Urinary biomarkers (B2M, A1M) help identify TIN and monitor therapy response.
📊 Study: A1M ratios higher in chronic TIN vs. glomerular disease.
🧪 IL-9 and TNF-a distinguish AIN from other AKI causes and guide immunosupp. therapy.
🔍 Prognosis
Prognosis of TIN depends on the cause, therapy response, and renal impairment degree.
🔸 Chronicity = worse outcome
🔸 Early diagnosis improves renal health
🔸 Identification & monitoring challenging
🩺 Autoimmune markers (IgG, complements, anti-Ro/La) help identify IgG4, SLE, SS-related TIN.
💧 Urinary biomarkers (B2M, A1M) help identify TIN and monitor therapy response.
📊 Study: A1M ratios higher in chronic TIN vs. glomerular disease.
🧪 IL-9 and TNF-a distinguish AIN from other AKI causes and guide immunosupp. therapy.
Loading suggestions...