This thread is in collaboration
@OmkarBanne
He is a fellow trader and all credits to this thread goes to him.
@OmkarBanne
He is a fellow trader and all credits to this thread goes to him.
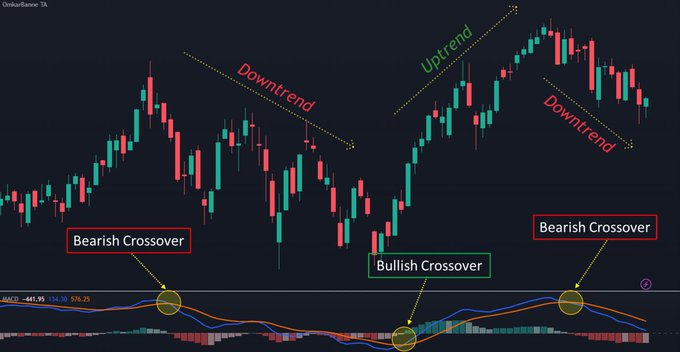
2. MACD
- The MACD is calculated by subtracting a long-term EMA (26) from a short-term EMA (12)
- The MACD indicator has three main components: the MACD line, the signal line, and the histogram
- The MACD is calculated by subtracting a long-term EMA (26) from a short-term EMA (12)
- The MACD indicator has three main components: the MACD line, the signal line, and the histogram
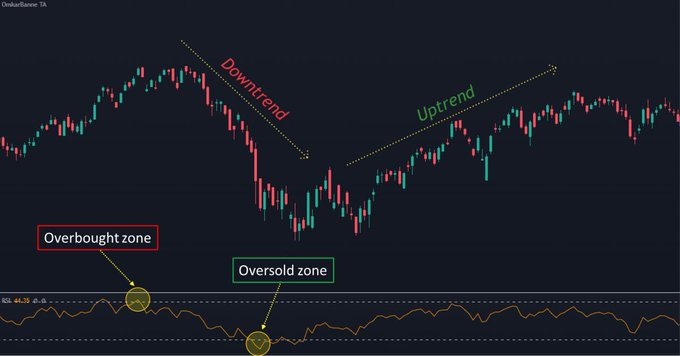
3. Relative Strength Index
- RSI is used to identify potential trend reversals and overbought or oversold conditions
- It is calculated by comparing the average gains & losses of a stock over a specified period of time (default of 14 days)
- RSI ranges from 0 to 100
- RSI is used to identify potential trend reversals and overbought or oversold conditions
- It is calculated by comparing the average gains & losses of a stock over a specified period of time (default of 14 days)
- RSI ranges from 0 to 100
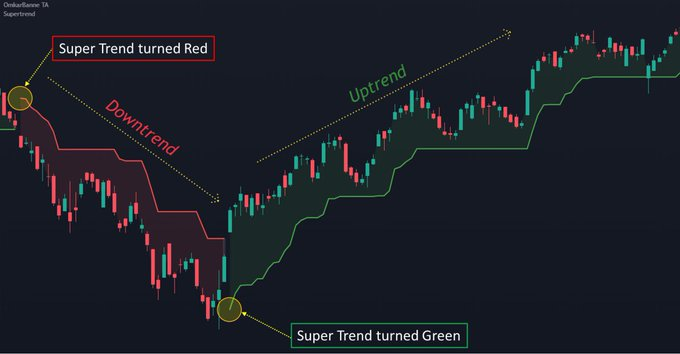
4. Super Trend
- It is similar to moving averages
- It is a very simple indicator and is constructed with the help of just two parameters- period (10) & multiplier (3)
- As a trending indicator, Super Trend performs excellently in trending markets (both uptrends & downtrends)
- It is similar to moving averages
- It is a very simple indicator and is constructed with the help of just two parameters- period (10) & multiplier (3)
- As a trending indicator, Super Trend performs excellently in trending markets (both uptrends & downtrends)
5. Average Directional Index (ADX)
- It is used to measure the strength of a trend
- The ADX ranges from 0 to 100
- It is calculated by taking the difference between +ve directional indicator (+DI) & -ve directional indicator (-DI) and dividing it by the sum of the two
- It is used to measure the strength of a trend
- The ADX ranges from 0 to 100
- It is calculated by taking the difference between +ve directional indicator (+DI) & -ve directional indicator (-DI) and dividing it by the sum of the two
- ADX does not indicate the direction of the trend
👉How to use it?
- The higher the ADX, the stronger the trend
- ADX of 30 or higher is considered a strong trend
- ADX below 20 suggests a weak trend
👉How to use it?
- The higher the ADX, the stronger the trend
- ADX of 30 or higher is considered a strong trend
- ADX below 20 suggests a weak trend
6. Parabolic SAR (Stop and Reverse)
- Used to identify potential reversals in trends
- It is calculated by taking the prior period's high/low & adjusting it by an acceleration factor (0.02)
- This factor increases with the trend, it helps the indicator catch up to the price
- Used to identify potential reversals in trends
- It is calculated by taking the prior period's high/low & adjusting it by an acceleration factor (0.02)
- This factor increases with the trend, it helps the indicator catch up to the price
👉How to use it?
- The dots appear below the price when the trend is up and above the price when the trend is down
- The Parabolic SAR can also be used as a stop-loss tool
For long positions, the SL can be placed below
For short positions, it can be placed above
- The dots appear below the price when the trend is up and above the price when the trend is down
- The Parabolic SAR can also be used as a stop-loss tool
For long positions, the SL can be placed below
For short positions, it can be placed above
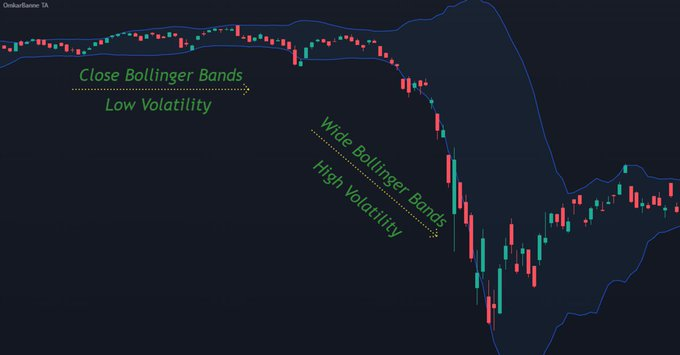
7. Bollinger Bands
- It is used to measure volatility & identify potential reversals
- It consists of three lines, a simple moving average (SMA) in the middle and an upper & lower band that are two standard deviations away from the SMA
- It is used to measure volatility & identify potential reversals
- It consists of three lines, a simple moving average (SMA) in the middle and an upper & lower band that are two standard deviations away from the SMA
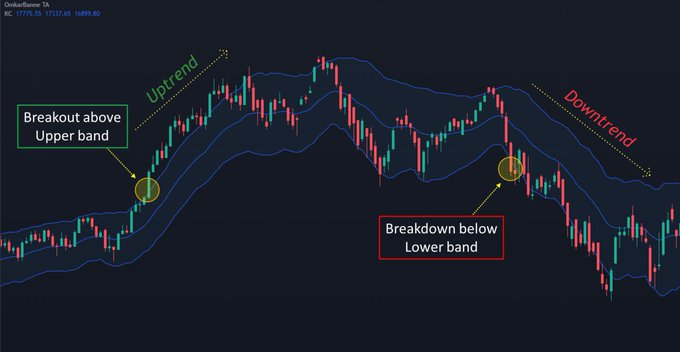
8.Keltner Channel
- It is used to identify potential breakouts & trends
- It consists of two lines, an upper & lower band, that are plotted using the Average True Range (ATR)
- The upper & lower bands are plotted by adding & subtracting a multiple of the ATR from the MA
- It is used to identify potential breakouts & trends
- It consists of two lines, an upper & lower band, that are plotted using the Average True Range (ATR)
- The upper & lower bands are plotted by adding & subtracting a multiple of the ATR from the MA
9. Donchian Channel
- It consists of an upper & lower band, which are plotted using the highest high & lowest low over a set period of time (default 20)
- The upper band represents the highest high while the lower band represents the lowest low over the set period
- It consists of an upper & lower band, which are plotted using the highest high & lowest low over a set period of time (default 20)
- The upper band represents the highest high while the lower band represents the lowest low over the set period
👉How to use it?
- When the price breaks above the upper band, it suggests a potential bullish breakout
- When the price breaks below the lower band, it suggests a potential bearish breakout
- When the price breaks above the upper band, it suggests a potential bullish breakout
- When the price breaks below the lower band, it suggests a potential bearish breakout
10. Average True Range (ATR)
- It is used to measure volatility & identify potential price movements in the market
- It measures the average range of price movement over a set period of time (default 14)
- It is used to measure volatility & identify potential price movements in the market
- It measures the average range of price movement over a set period of time (default 14)
Hope you found this helpful? Want to learn more? 🙂
Just retweet the first tweet and Follow us @Omkarbanne @chartians🔥
Just retweet the first tweet and Follow us @Omkarbanne @chartians🔥
Loading suggestions...