1) Welcome to a LIVE #accredited #tweetorial from #AHA23 @American_Heart in #Philadelphia on advances in #hyperlipidemiamanagement #LLT. Our expert returning faculty is Erin Michos MD @ErinMichos #cardiologist #lipids from @HopkinsMedicine.
#CardioTwitter #MedEd #FOAMed
#CardioTwitter #MedEd #FOAMed
2) This program is supported by an educational grant from Esperion Therapeutics & is intended for #HCPs. Statement of accreditation & faculty disclosures at cardiometabolic-ce.com. Earn .75hr 🆓CE/#CME by following this 🧵!
@MedTweetorials
@MedTweetorials
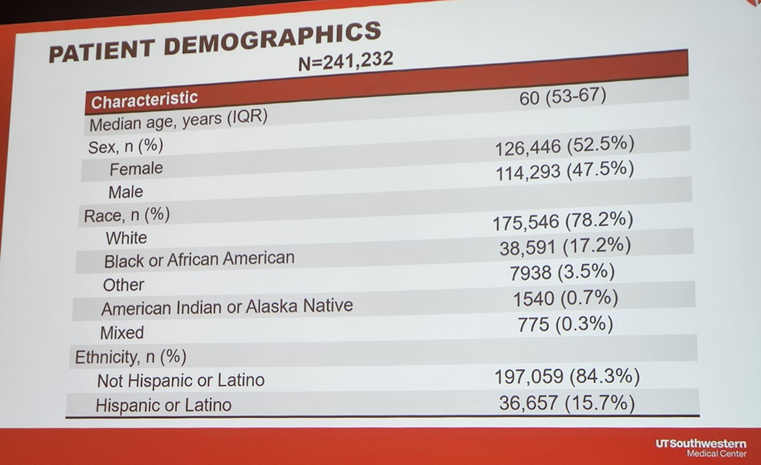
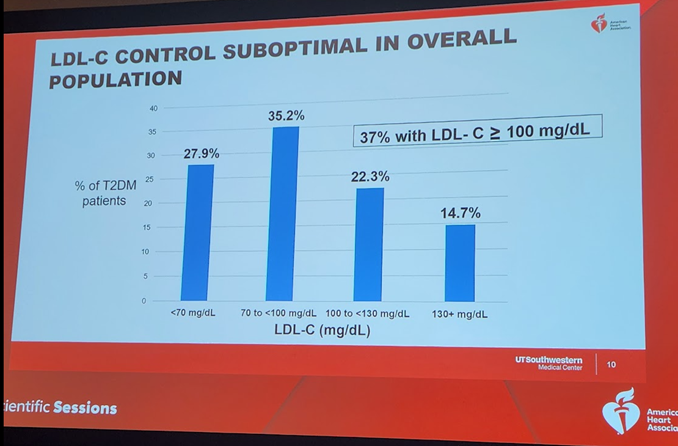
4a) Let's start with an important presentation on 11/11 #AHA23 by Drs @emily_decicco & @AnnMarieNavar about lipid lowering therapy #LLT and #LDLC control for primary #ASCVD prevention in persons with #diabetes across 90 US health systems.
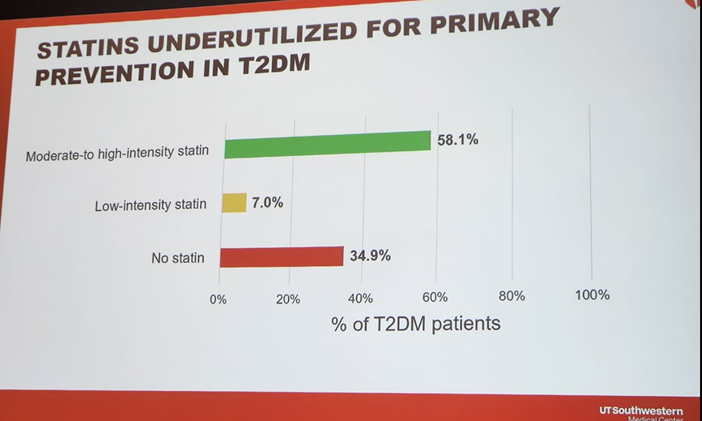
4b) #ASCVD remains the leading cause of ☠️in persons with #diabetes ➡️ the 2019 @ACCinTouch @American_Heart guideline gave a class I recommendation for use of #statins in persons with diabetes for the primary ASCVD prevention. So how well is this recommendation implemented?
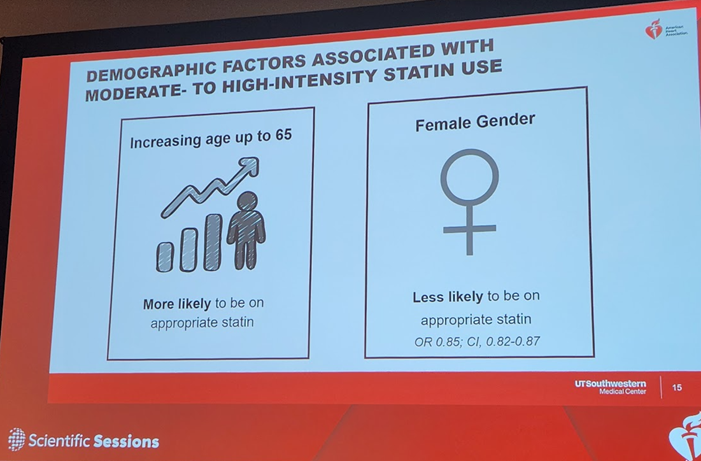
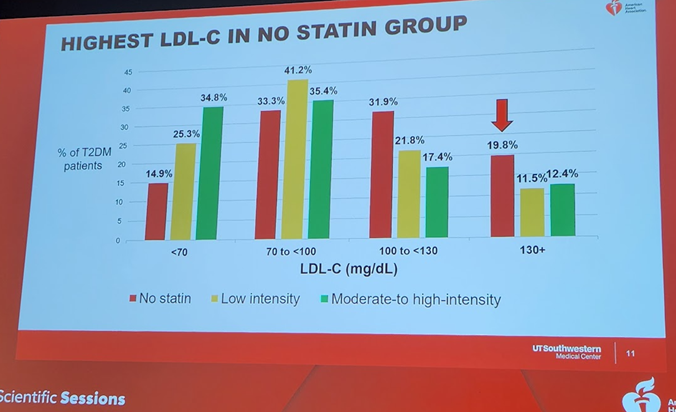
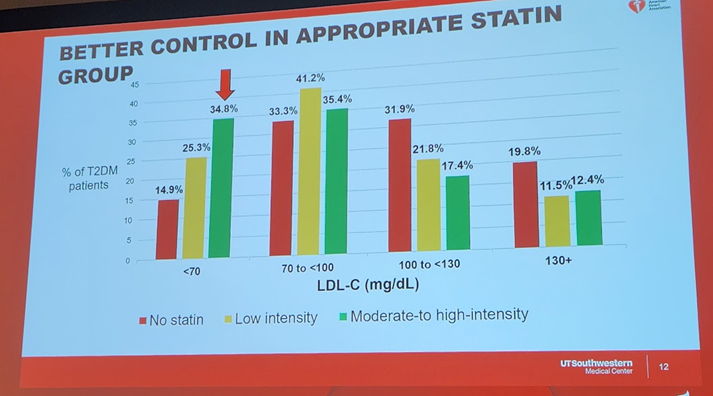
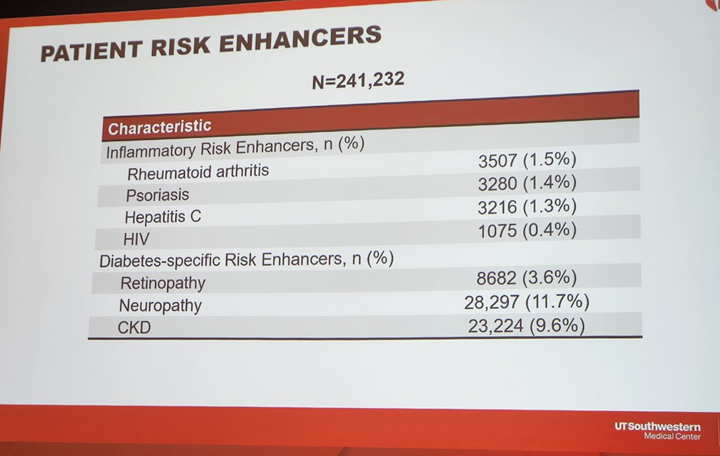
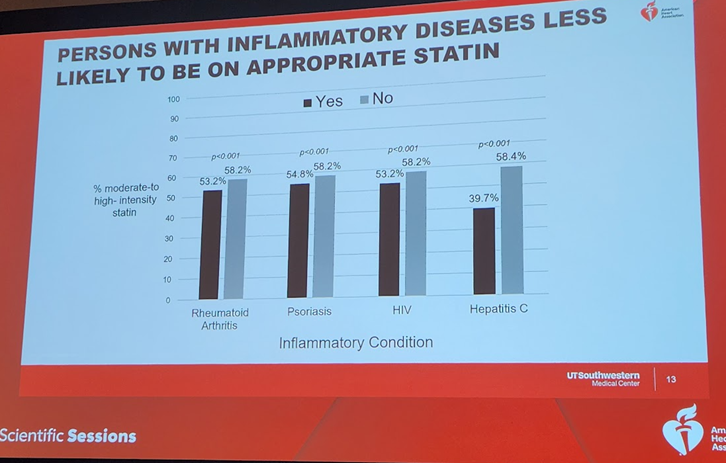
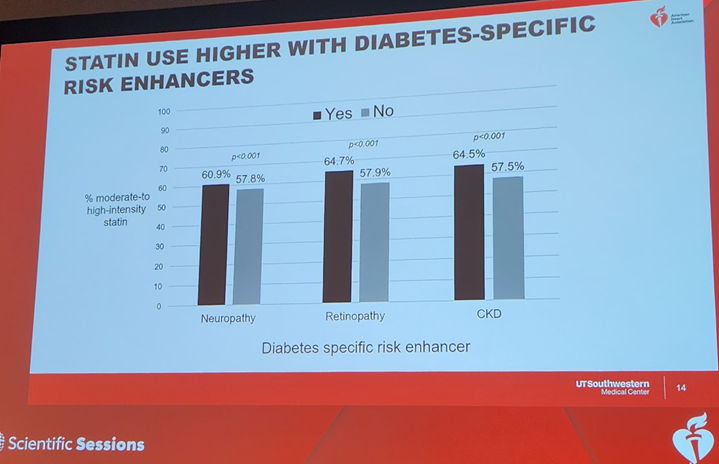
7b) Persons with #diabetes with #inflammatory risk enhancers were LESS likely to be on #statins, but those with diabetes-specific risk enhancers of #retinopathy & #neuropathy& #CKD were more likely to be on statins.
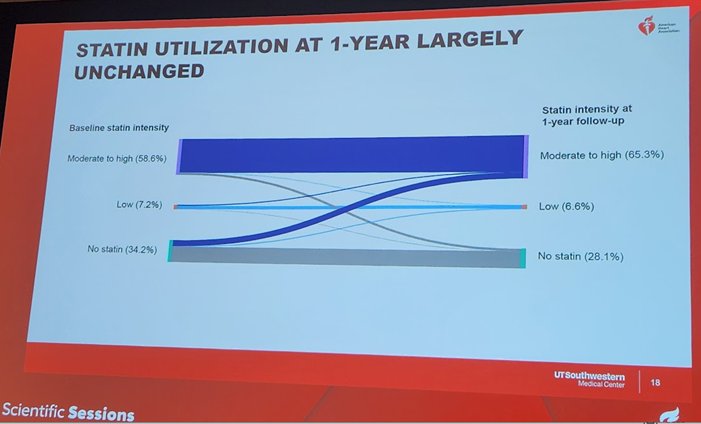
8) In sum, this work identified significant care gaps among persons with #diabetes. Efforts are needed to improve #lipid management in this group at high CV risk. This work was simultaneously published in @AJPCardio: 🔓
sciencedirect.com
sciencedirect.com
9) Congratulations to @emily_decicco, @AnnMarieNavar, and colleagues on their work and simultaneous publication!
#AHA23
#AHA23
10a) More from #AHA23! So, #hsCRP as a marker for #ASCVD risk.
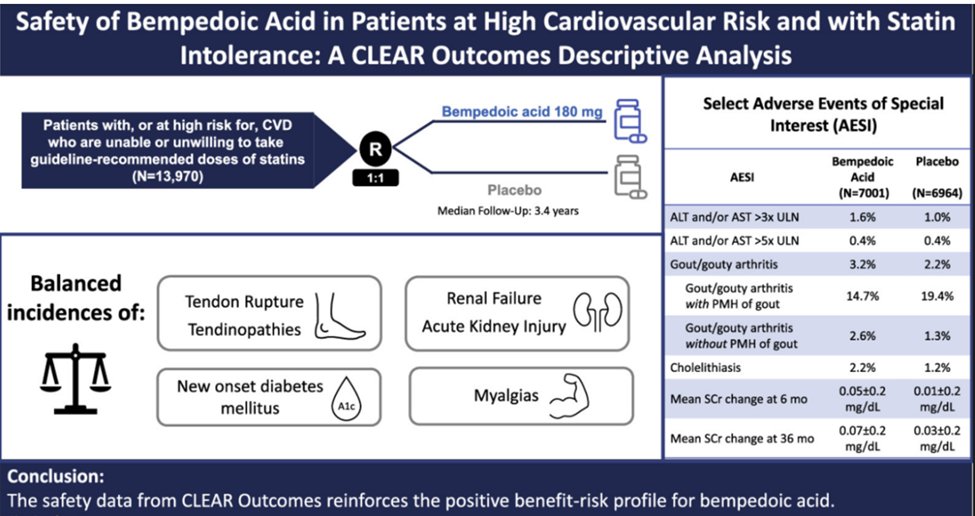
On 13NOV the esteemed #lipidologist #PaulRidkerMD presented 🆕 data from #CLEAR_OUTCOMES: #bempedoic_acid v placebo in 13,970 pts with #ASCVD or high #CV risk, #LDL_C 100+, & documented #statin intolerance.
On 13NOV the esteemed #lipidologist #PaulRidkerMD presented 🆕 data from #CLEAR_OUTCOMES: #bempedoic_acid v placebo in 13,970 pts with #ASCVD or high #CV risk, #LDL_C 100+, & documented #statin intolerance.
10b) You recall those data--and you can still earn 🆓 CE/#CME on the topic from @CMichaelGibson, @cpcannon, & @PamTaubMD at cardiometabolic-ce.com. The main trial ➡️ highly significant 13% ⬇️ in the primary EP of 4 point #MACE & 15% ⬇️ in 3 point MACE.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
10c) Substudies have shown similar benefits in the #primary_prevention cohort & in #diabetic vs #nondiabetic cohorts. No safety concerns in any (just confirmed pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov ⤵️)
But what about data on #hsCRP & its response to #bempedoic_acid? Why is that of interest?
But what about data on #hsCRP & its response to #bempedoic_acid? Why is that of interest?
11a) In 2007 (!) Ridker wrote in 🔓 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov that #hsCRP is a strong, independent predictor of future #MI/#stroke among apparently healthy asx ♂️, w/ similar impact to that of #cholesterol & #htn.
11b) This helped advance the concept of #atherosclerosis as--at least in part--an #inflammatory disorder. Though lipid management remains 1st line for #cvPrev, CV events still occur in statin-Rx patients, w/#hsCRP established as an effective marker of residual inflammatory risk.
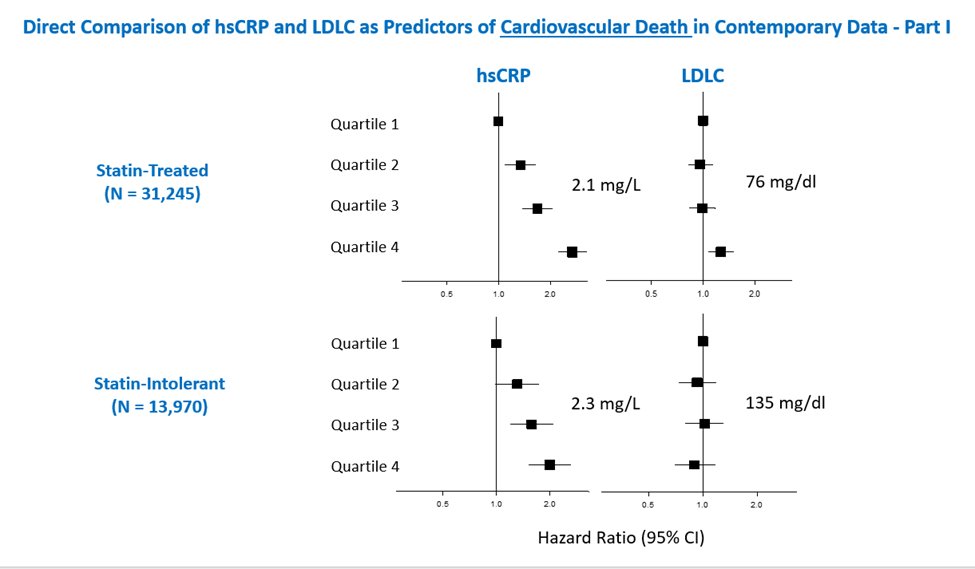
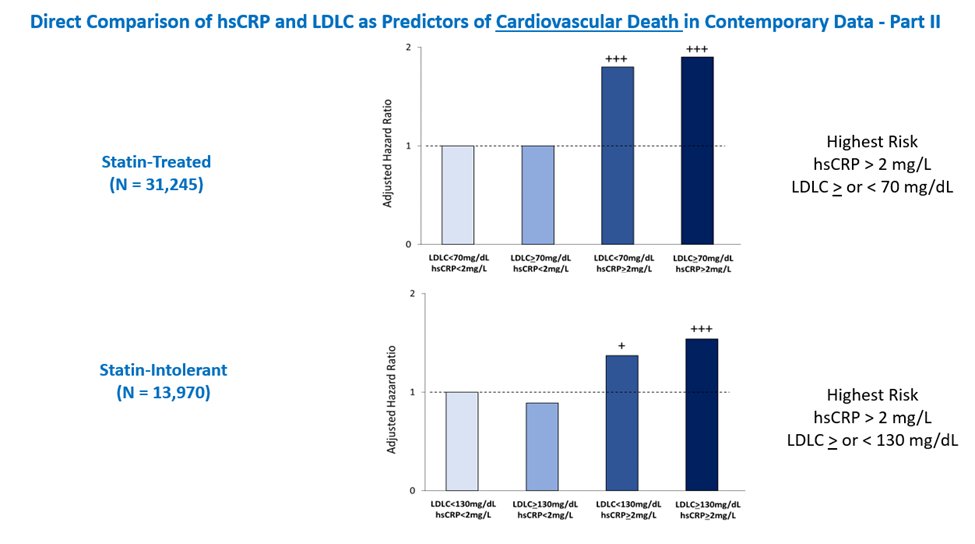
11c) In a recent analysis of 31,245 statin-treated patients at high ASCVD risk, residual inflammatory risk (as assessed by #hsCRP) was a more powerful determinant of CV death than residual cholesterol risk (as assessed by #LDLC). pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
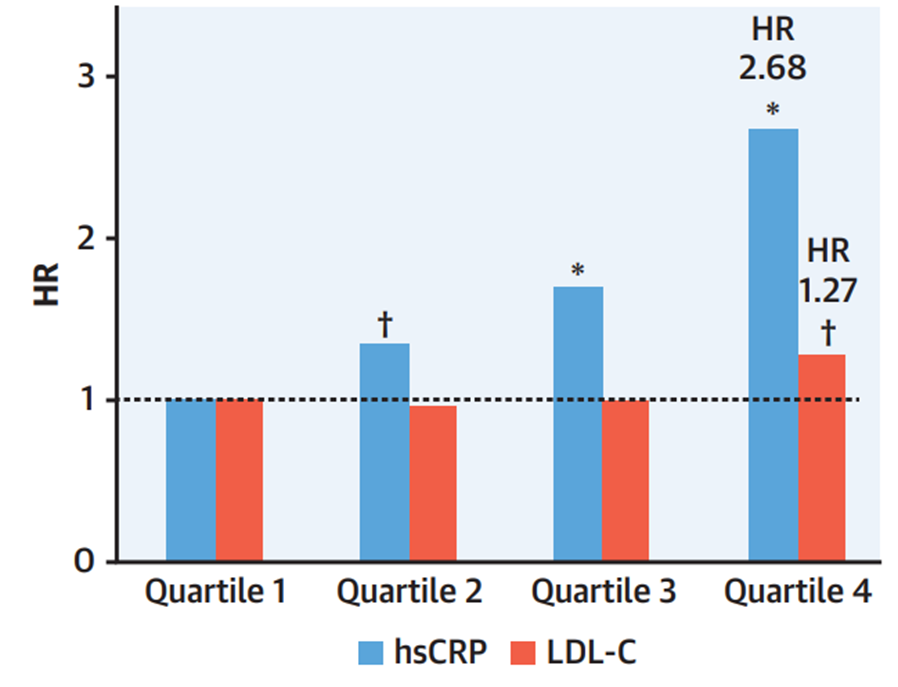
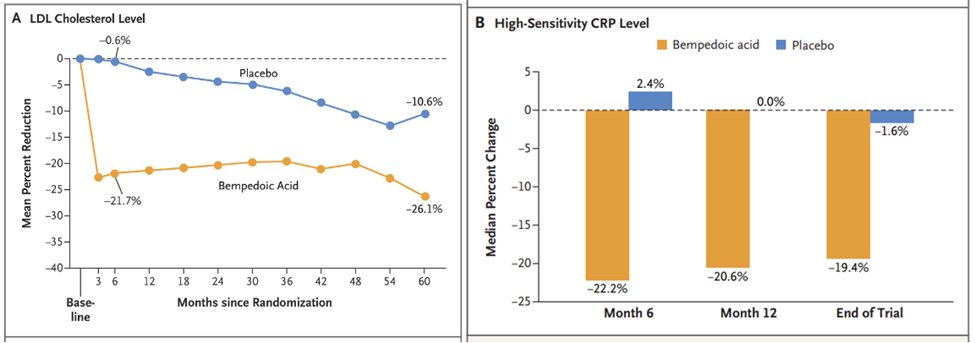
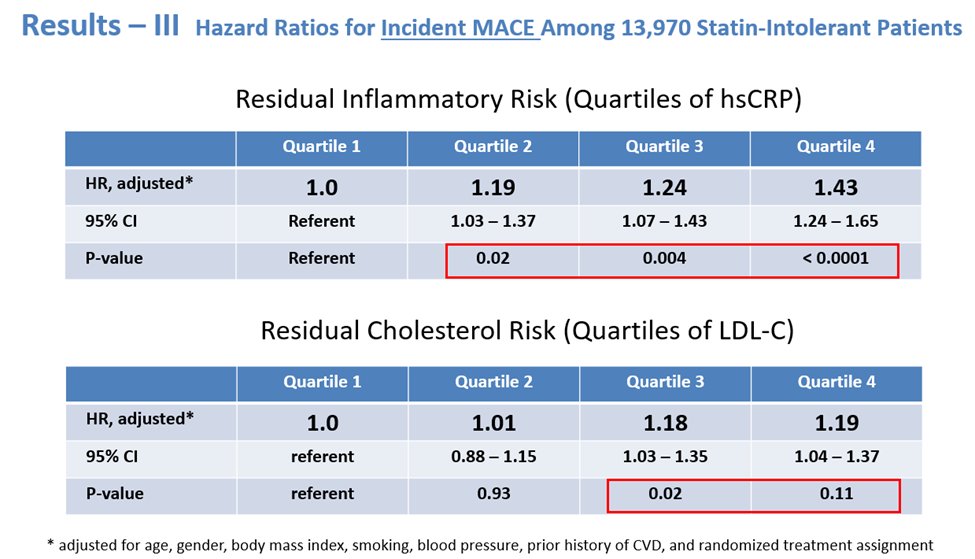
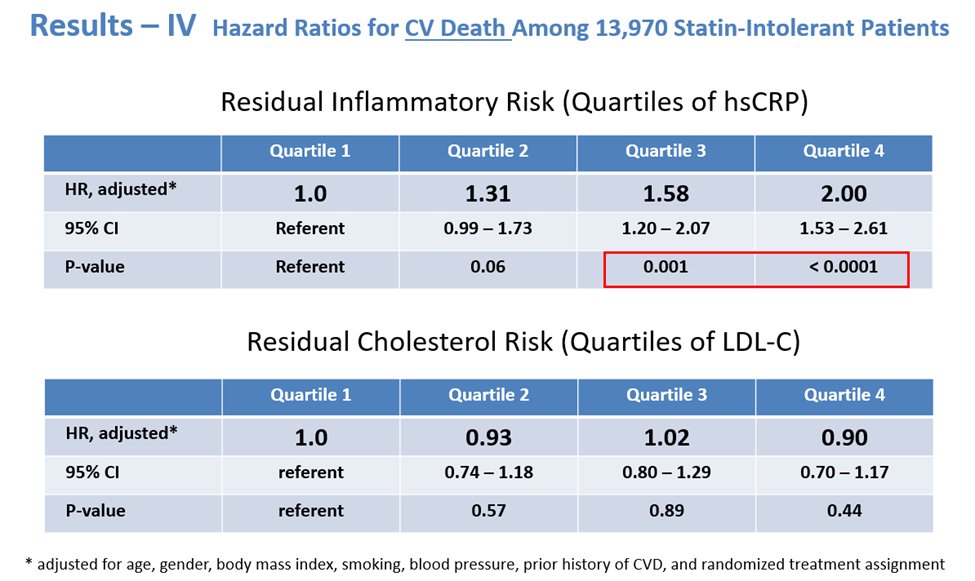
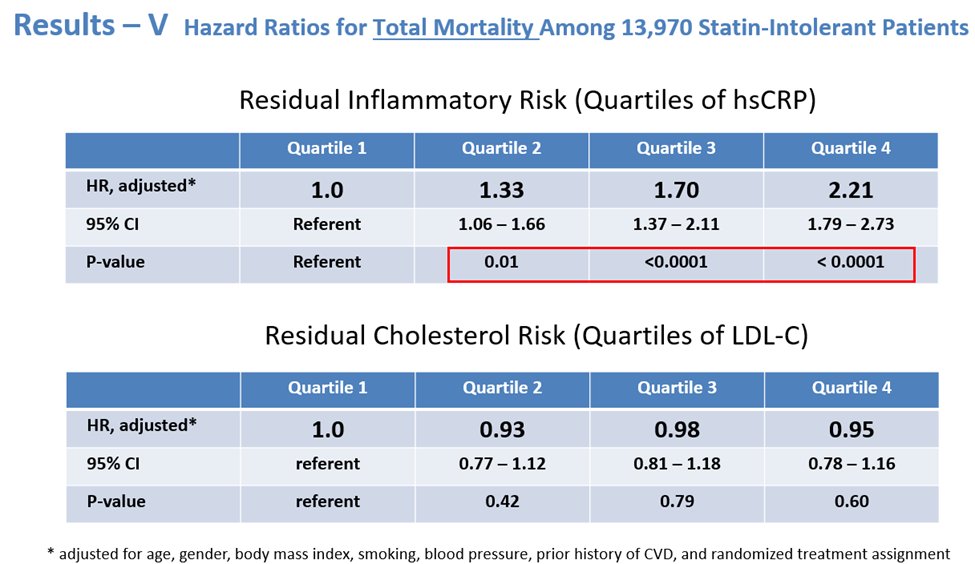
12a) Let’s look to another 2o analysis of #CLEAR_OUTCOMES! As we saw in the main trial, #bempedoic acid reduced median #hsCRP by 21.6% and mean #LDLC levels by 21.1% at 6 months, compared to placebo.
12c) On other hand, the highest vs lowest baseline #LDLC was less strongly associated with the primary 4pt #MACE endpoint [HR 1.19 (1.04-1.37) and not associated with #CV #mortality [HR 0.90 (0.70-1.17)] or all-cause mortality [HR 0.95 (0.78-1.16)].
12d) In other words, among these contemporary patients with #statin_intolerance, #inflammation assessed by #hsCRP predicted risk of future #CV events and mortality more strongly than lipids assessed by #LDLC, similar to prior analysis of statin-Rx patients
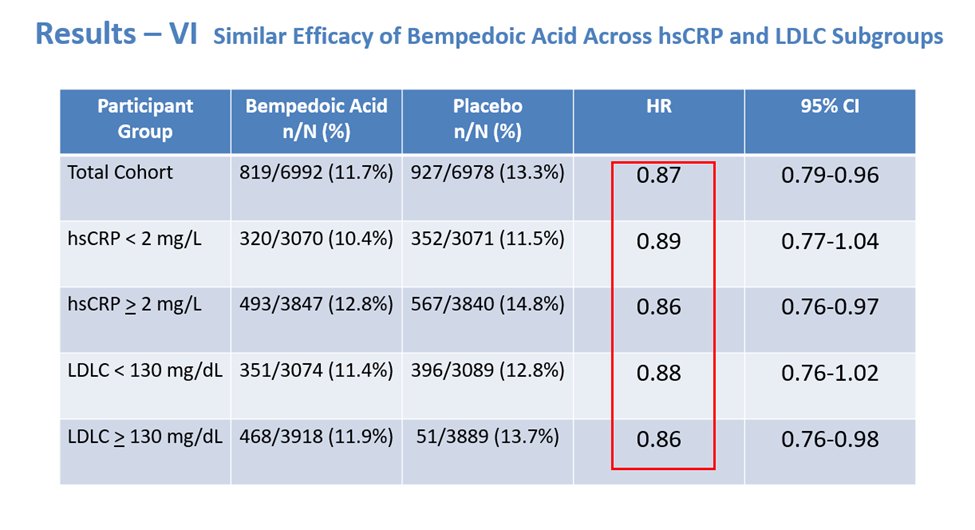
14) It should be noted that compared with placebo, #Bempedoic acid reduced #cardiovascular events similarly across all levels of #hsCRP and #LDLC, with effect modification.
15) In sum, the CLEAR Outcomes trial provides a sound rationale for use of #bempedoic acid to reduce major adverse #CV outcomes in patients intolerant to statins, including those at high #inflammatory risk.
#AHA23
#AHA23
16b) (cont)
🫀 #Bempedoic_acidis a great non-statin alternative for statin intolerant patients with proven efficacy to reduce #CV events
🫀 Nevertheless, even on #LLT, elevated #hsCRP predicts residual risk, offering opportunities to specifically address inflammatory pathways
🫀 #Bempedoic_acidis a great non-statin alternative for statin intolerant patients with proven efficacy to reduce #CV events
🫀 Nevertheless, even on #LLT, elevated #hsCRP predicts residual risk, offering opportunities to specifically address inflammatory pathways
17a) Quick knowledge checks before we go:
According to new data from #AHA23, persons with #diabetes and elevated #ASCVD risk are more likely to use which non-statin therapy, despite lack of evidence of ASCVD benefit?
A. #bempedoic acid
B. #ezetimibe
C. fibrates
D. #PCSK9i
According to new data from #AHA23, persons with #diabetes and elevated #ASCVD risk are more likely to use which non-statin therapy, despite lack of evidence of ASCVD benefit?
A. #bempedoic acid
B. #ezetimibe
C. fibrates
D. #PCSK9i
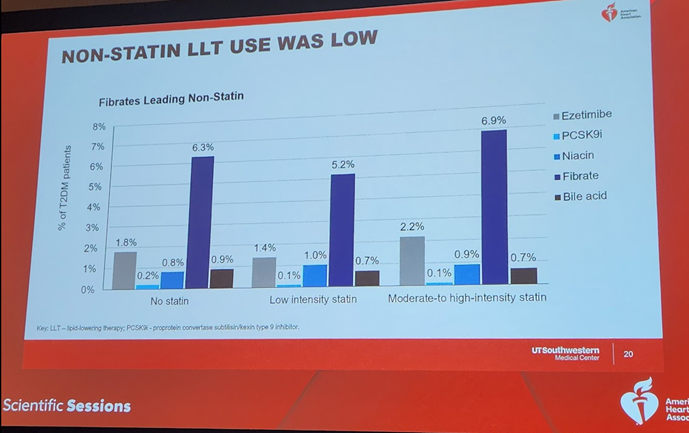
17b) Unfortunately the correct answer is C. Same applies to niacin—no known help, but used alot, whereas efficacious options such as the other 3 are UNDERutilized in pts with #diabetes.
18b) It's C. As shown in the #AHA23 data presented by Ridker, #bempedoic_acid can reduce #LDLC levels beyond the benefit of statins, and also reduces #hsCRP levels, indicating a positive impact on inflammation.
19) So thank you for joining us--@cardiomet_ce LIVE IN THE HOUSE from #AHA23--you feel like you were there, right? That's due to great work by expert author @ErinMichos! Now celebrate by claiming 0.75hr 🆓 CE/#CME at cardiometabolic-ce.com & then 🖱️ back here & FOLLOW US!
TYPO HERE: should be WITHOUT effect modification
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...