1/ 🚀 Q: What is Kubernetes and why is it essential for container orchestration?
A: Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications, ensuring high availability and reliability.
A: Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications, ensuring high availability and reliability.
2/ 🛠️ Q: Name the key components of a Kubernetes cluster.
A: A Kubernetes cluster consists of the Master (API Server, Controller Manager, Scheduler, etcd) and Nodes (where containers run).
#Kubernetes #Interview
A: A Kubernetes cluster consists of the Master (API Server, Controller Manager, Scheduler, etcd) and Nodes (where containers run).
#Kubernetes #Interview
3/ 📦 Q: What is a Pod in Kubernetes?
A: A Pod is the smallest deployable unit in Kubernetes, containing one or more containers sharing the same network namespace. #Kubernetes #Interview
A: A Pod is the smallest deployable unit in Kubernetes, containing one or more containers sharing the same network namespace. #Kubernetes #Interview
4/ ⚖️ Q: Differentiate between a Deployment and a StatefulSet.
A: Deployments manage stateless apps with rolling updates, while StatefulSets are used for stateful apps with stable network identities. #Kubernetes #Interview
A: Deployments manage stateless apps with rolling updates, while StatefulSets are used for stateful apps with stable network identities. #Kubernetes #Interview
5/ 🌐 Q: How does Kubernetes handle service discovery?
A: Kubernetes uses DNS for service discovery, and you can access services via their DNS names. #Kubernetes #Interview
A: Kubernetes uses DNS for service discovery, and you can access services via their DNS names. #Kubernetes #Interview
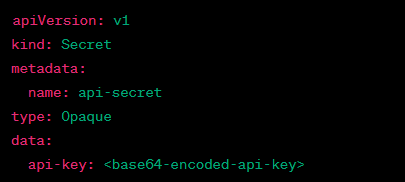
6/ 🔒 Q: Explain the concept of Kubernetes Secrets.
A: Kubernetes Secrets are used to securely store sensitive information like API keys, passwords, and tokens. They are base64 encoded and can be mounted as volumes or used as environment variables. #Kubernetes #Interview
A: Kubernetes Secrets are used to securely store sensitive information like API keys, passwords, and tokens. They are base64 encoded and can be mounted as volumes or used as environment variables. #Kubernetes #Interview
7/ 🔄 Q: What is a Kubernetes ConfigMap, and why is it useful?
A: ConfigMaps store configuration data as key-value pairs, which can be injected into Pods as environment variables or mounted as files. Useful for separating configuration from application code. #Kubernetes
A: ConfigMaps store configuration data as key-value pairs, which can be injected into Pods as environment variables or mounted as files. Useful for separating configuration from application code. #Kubernetes
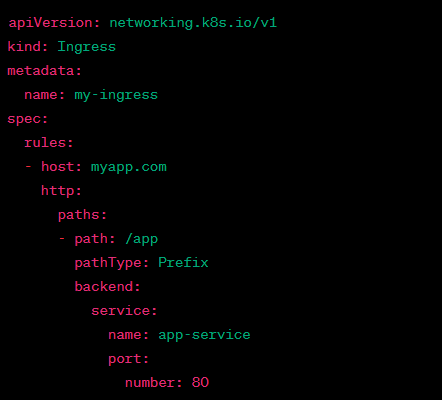
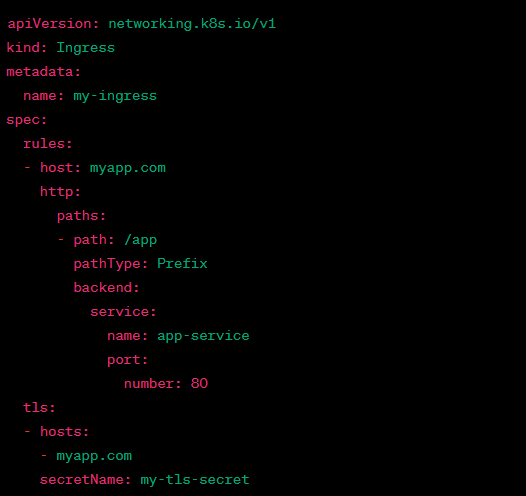
8/ 📝 Q: How can you expose an application outside the Kubernetes cluster?
A: You can expose an app using Services (ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer) or Ingress controllers to manage HTTP traffic. #Kubernetes #Interview
A: You can expose an app using Services (ClusterIP, NodePort, LoadBalancer) or Ingress controllers to manage HTTP traffic. #Kubernetes #Interview
9/ 🧩 Q: What are Labels and Selectors in Kubernetes?
A: Labels are key-value pairs attached to resources, and Selectors are used to filter and group resources based on labels. #Kubernetes #Interview
A: Labels are key-value pairs attached to resources, and Selectors are used to filter and group resources based on labels. #Kubernetes #Interview
10/ 🧹 Q: Explain Kubernetes Rolling Updates and Rollbacks.
A: Rolling Updates gradually replace old Pods with new ones to ensure zero downtime. Rollbacks revert to a previous version if issues arise. #Kubernetes #Interview
A: Rolling Updates gradually replace old Pods with new ones to ensure zero downtime. Rollbacks revert to a previous version if issues arise. #Kubernetes #Interview
11/ 🔄Q: How can you perform a rolling update in a Kubernetes Deployment?
A: You can use kubectl set image to update a Deployment's image.
For example, to update a "web" container in a Deployment named "myapp," run:
kubectl set image deployment/myapp web=mynewimage:v2
A: You can use kubectl set image to update a Deployment's image.
For example, to update a "web" container in a Deployment named "myapp," run:
kubectl set image deployment/myapp web=mynewimage:v2
12/ 🕵️ Q: How do you troubleshoot a Pod that is stuck in the "Pending" state?
A: Check events with kubectl describe pod, inspect resource requests/limits, and ensure the node has available resources.
Example: kubectl describe pod mypod.
A: Check events with kubectl describe pod, inspect resource requests/limits, and ensure the node has available resources.
Example: kubectl describe pod mypod.
21/ 🔄 Q: How can you perform a rollback in Kubernetes when an update goes wrong?
A: Use kubectl rollout undo to revert a Deployment to a previous version.
Example: Rollback "myapp" Deployment to the previous revision:
kubectl rollout undo deployment/myapp
A: Use kubectl rollout undo to revert a Deployment to a previous version.
Example: Rollback "myapp" Deployment to the previous revision:
kubectl rollout undo deployment/myapp
24/ 🌍 Q: What is Kubernetes Federation, and when is it useful?
A: Kubernetes Federation allows managing multiple clusters as a single entity, helpful for multi-cloud or multi-region deployments. #Kubernetes #Interview
A: Kubernetes Federation allows managing multiple clusters as a single entity, helpful for multi-cloud or multi-region deployments. #Kubernetes #Interview
25/ 💡 Q: How can you ensure application configuration consistency across multiple environments in Kubernetes?
A: Use Helm charts, ConfigMaps, and environment-specific overrides to manage configuration effectively.
A: Use Helm charts, ConfigMaps, and environment-specific overrides to manage configuration effectively.
26/ 📈 Q: Explain the concept of Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) in Kubernetes.
A: CRDs extend Kubernetes to support custom resource types, allowing you to define and manage your own resources and controllers.
A: CRDs extend Kubernetes to support custom resource types, allowing you to define and manage your own resources and controllers.
27/ 🛡️ Q: What is Kubernetes RBAC, and why is it important?
A: Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) defines who can perform actions in a cluster, ensuring fine-grained access control for users and service accounts.
A: Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) defines who can perform actions in a cluster, ensuring fine-grained access control for users and service accounts.
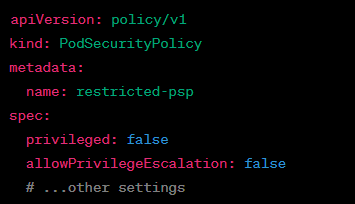
28/ 🕵️ Q: How can you secure a Kubernetes cluster?
A: Secure the cluster with RBAC, Pod Security Policies, network policies, and use tools like Helm for package management.
A: Secure the cluster with RBAC, Pod Security Policies, network policies, and use tools like Helm for package management.
29/ ⚙️ Q: Explain the differences between a Pod, a ReplicaSet, and a Deployment.
A: A Pod is the smallest unit, a ReplicaSet ensures a specified number of Pods run, and a Deployment manages rolling updates and rollbacks.
A: A Pod is the smallest unit, a ReplicaSet ensures a specified number of Pods run, and a Deployment manages rolling updates and rollbacks.
30/ 🌐 Q: What is Network Policy in Kubernetes?
A: Network Policies define rules for controlling ingress and egress traffic to and from Pods, providing network segmentation.
A: Network Policies define rules for controlling ingress and egress traffic to and from Pods, providing network segmentation.
Repost the thread if you find it useful. Thanks!
Loading suggestions...