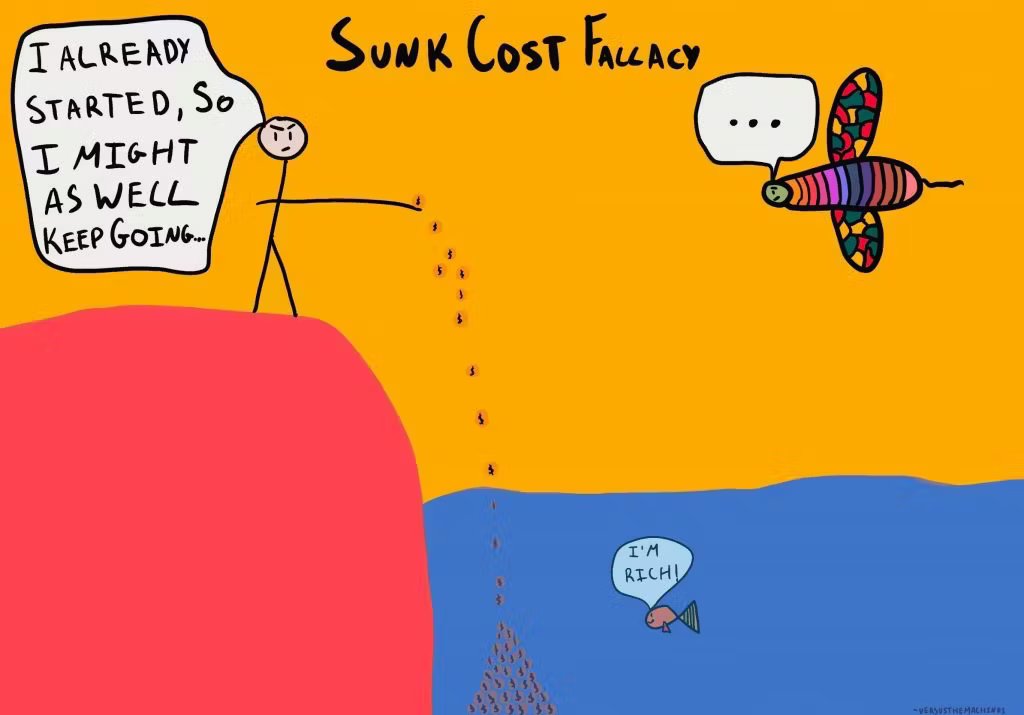
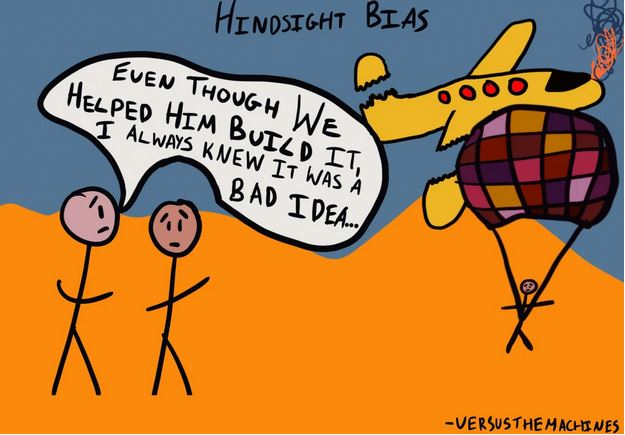
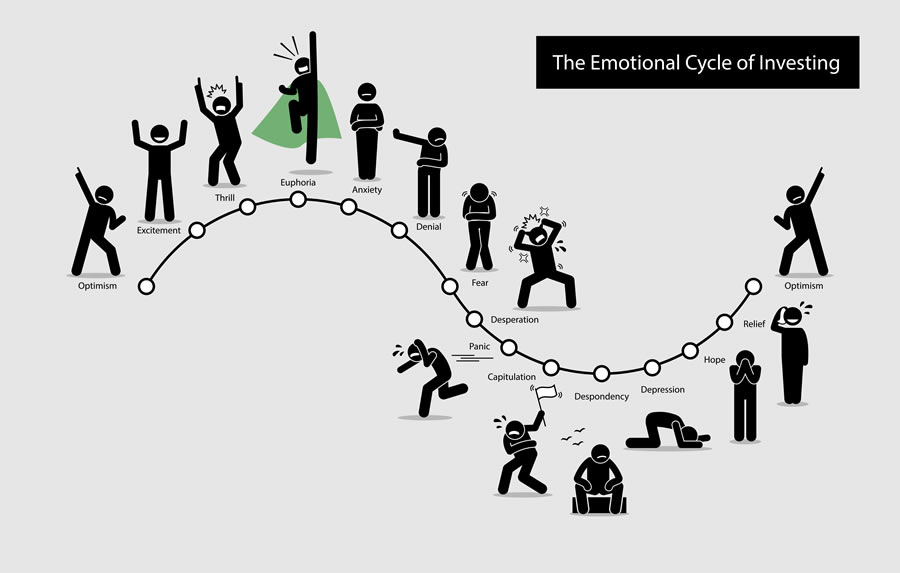
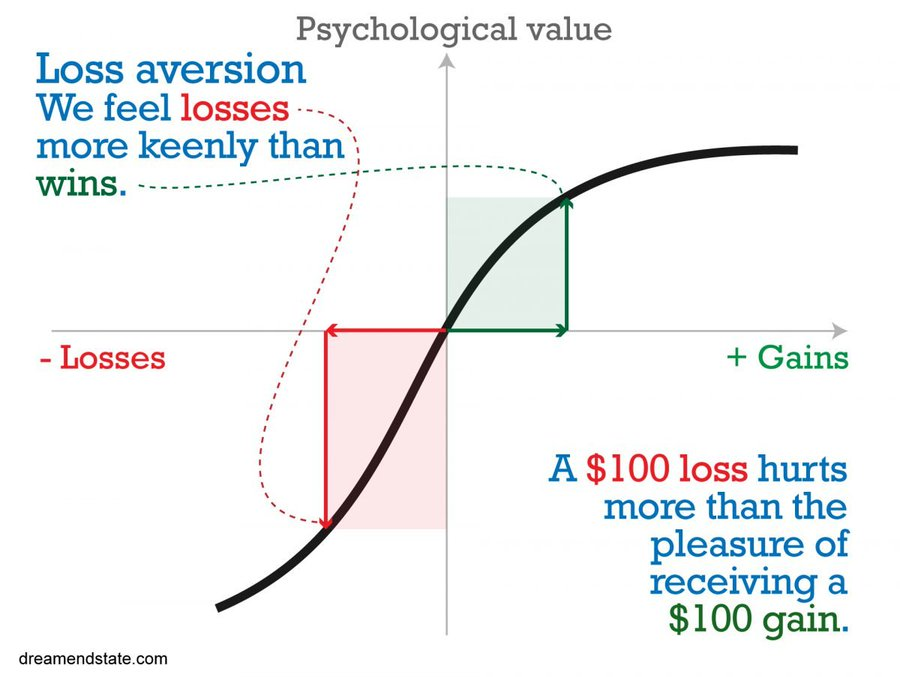
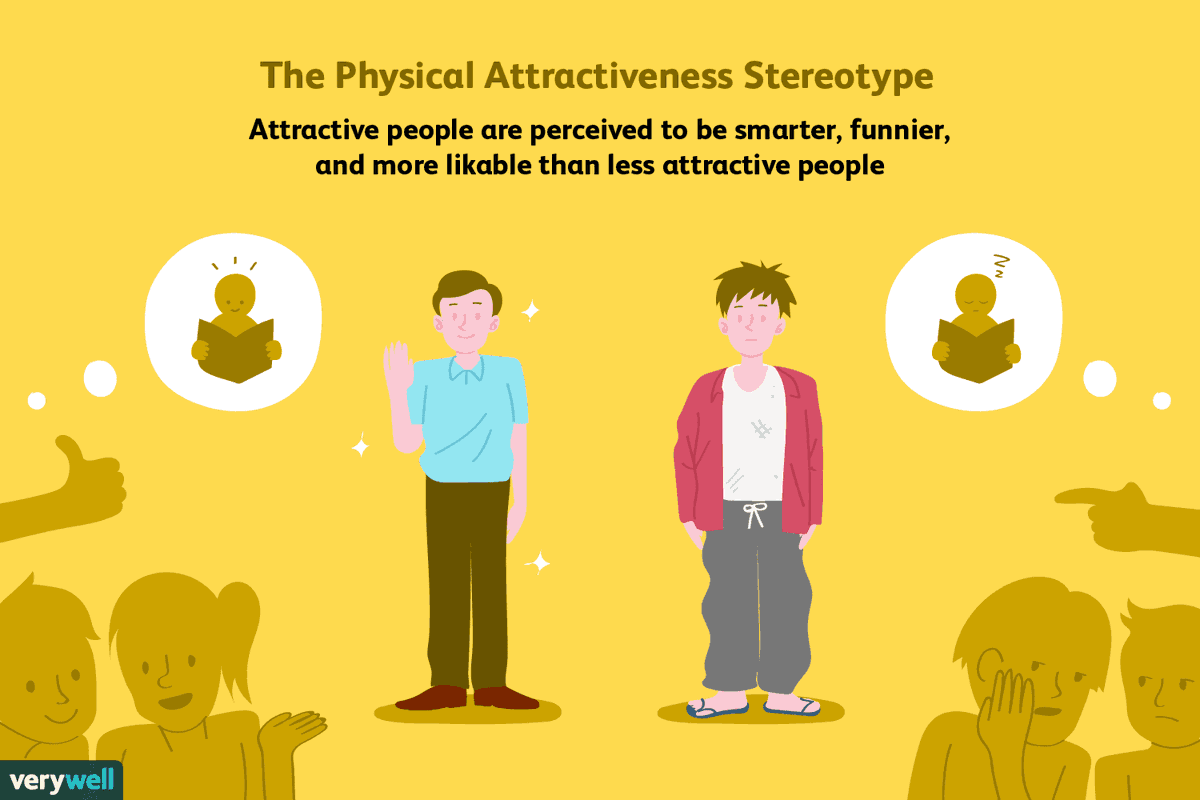
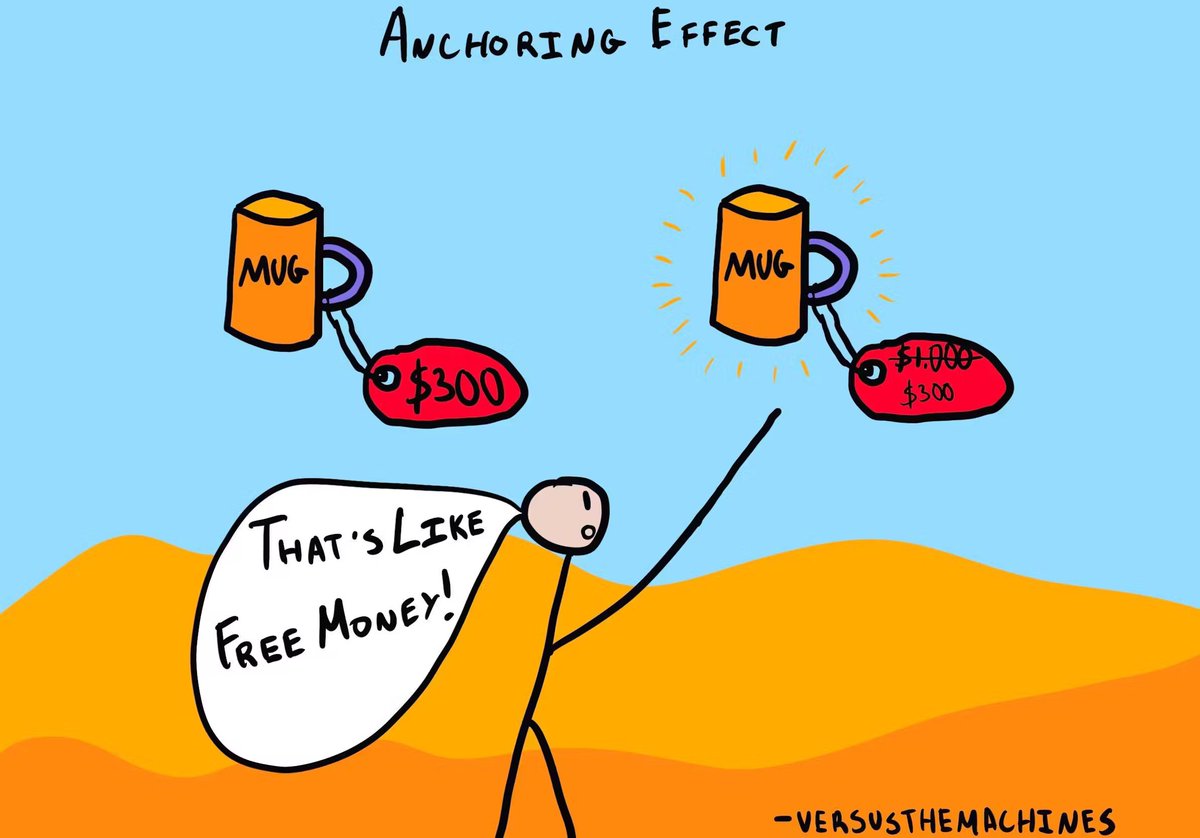
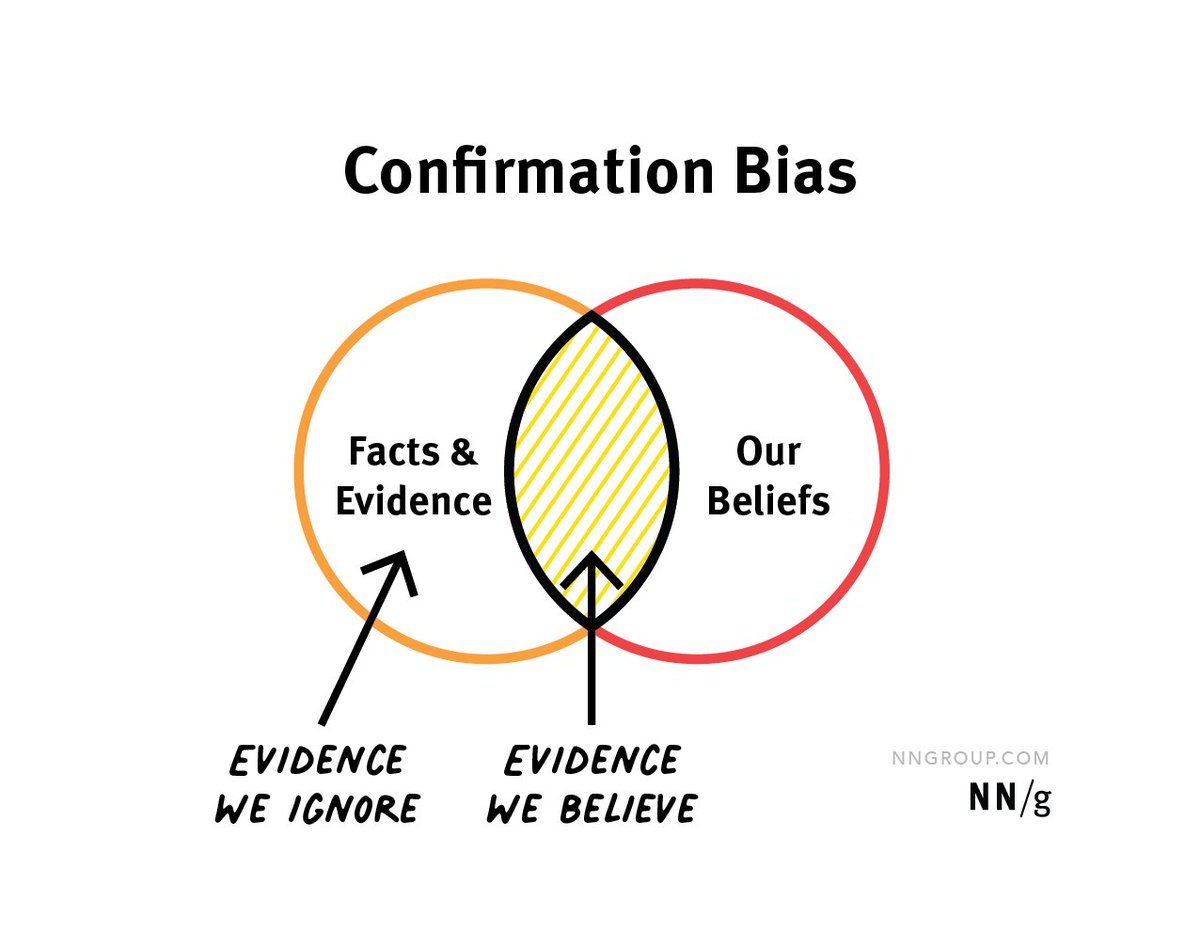
2️⃣ Irrational Behavior
People aren't always rational. We often make irrational choices.
For instance, about 90% of Americans believe they're better drivers than average, and around 70% consider themselves smarter than the average person.
People aren't always rational. We often make irrational choices.
For instance, about 90% of Americans believe they're better drivers than average, and around 70% consider themselves smarter than the average person.
The word is out!
I left my job to transform Compounding Quality into a full investment platform.
To celebrate, I am sharing an e-book with 300 pages (!) full of investment wisdom.
Sign up here if you want to receive it for free: eepurl.com
I left my job to transform Compounding Quality into a full investment platform.
To celebrate, I am sharing an e-book with 300 pages (!) full of investment wisdom.
Sign up here if you want to receive it for free: eepurl.com
Loading suggestions...