✅ Gradient Boosting and XGBoost explained in simple terms and how to use it ( with code).
A quick thread 🧵👇🏻
#Python #DataScience #MachineLearning #DataScientist #Programming #Coding #100DaysofCode #hubofml #deeplearning
Pic credits : ResearchGate
A quick thread 🧵👇🏻
#Python #DataScience #MachineLearning #DataScientist #Programming #Coding #100DaysofCode #hubofml #deeplearning
Pic credits : ResearchGate
1/ Imagine you have a really smart friend who is really good at solving puzzles. They're so good that they can solve almost any puzzle, but sometimes they make small mistakes. Gradient boosting is a way to combine the knowledge of many friends like this to solve a puzzle.
2/ Imagine you have a puzzle to solve, but it's complicated. You ask your 1st friend to solve it, and they do their best, but they make some mistakes. Then you ask your second friend to solve the same puzzle, and they also make some mistakes, but different ones from 1st friend.
3/ Now, instead of giving up, you decide to learn from the mistakes of your friends and try to improve the puzzle-solving. You pay more attention to the parts of the puzzle that your friends struggled with.
4/ You focus on those areas and try to find a better solution. This is called "boosting" because you're boosting your knowledge by learning from your friends' mistakes. Repeat this with more friends, and each time you focus on the areas that haven't been solved correctly yet.
5/ Gradually, you become better and better at solving the puzzle because you've learned from all your friends' different attempts. In gradient boosting, the "gradient" part refers to the direction you take to improve.
6/ Gradient boosting is a powerful machine learning technique used to solve problems like predicting values or classifying data. It's often used when you have a lot of data and want to make accurate predictions or decisions.
7/ Gradient boosting is beneficial because it can handle complex patterns in the data and make highly accurate predictions. It's commonly used in various domains, including finance, healthcare, and marketing, where accurate predictions are crucial.
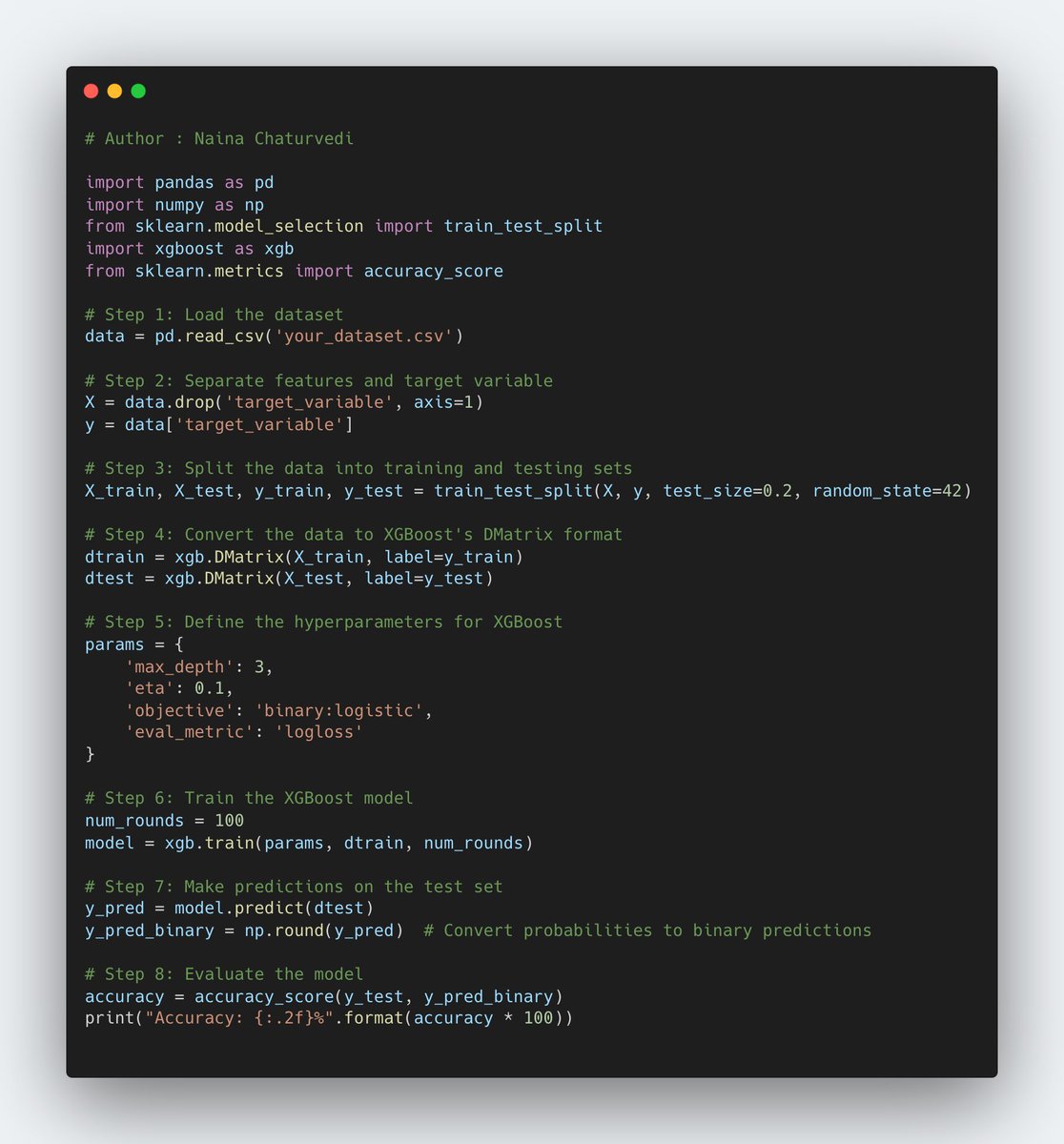
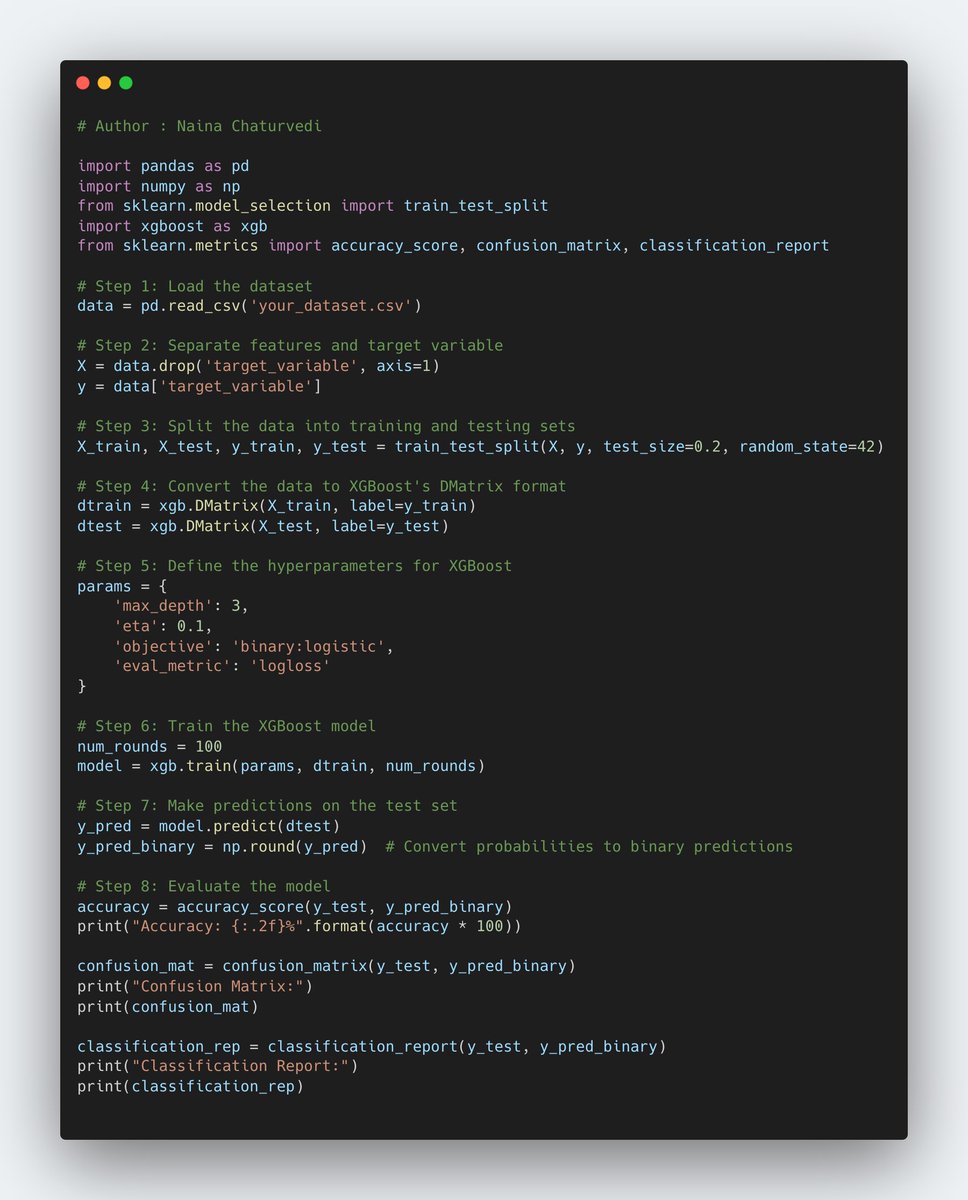
8/ XGBoost (Extreme Gradient Boosting) is an optimized and scalable gradient boosting framework that is widely used for machine learning tasks. It is based on the gradient boosting algorithm and has become popular due to its efficiency, accuracy, and flexibility.
9/ Regularization: XGBoost provides various techniques for controlling model complexity and preventing overfitting, such as L1 and L2 regularization terms added to the loss function.
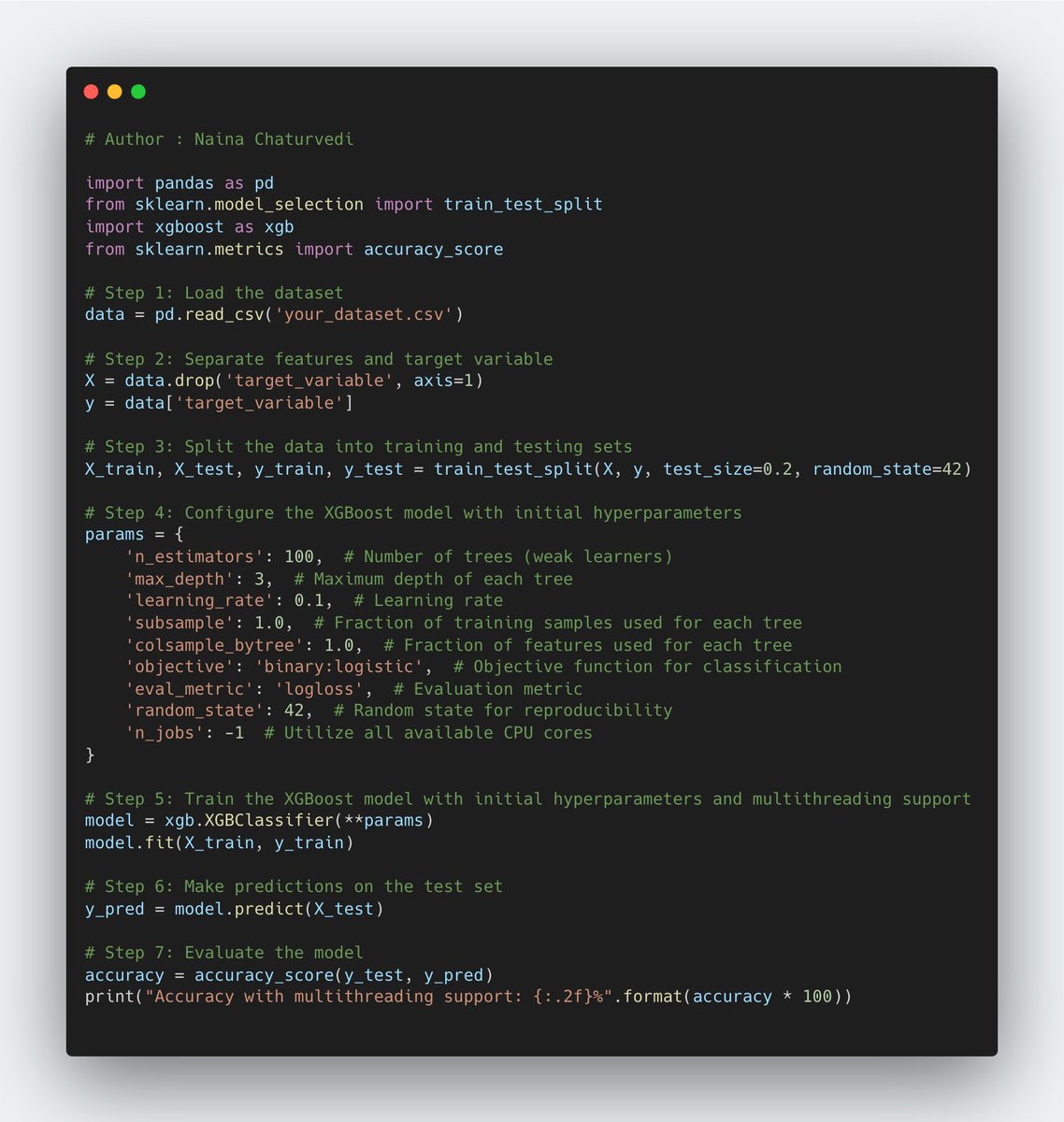
10/ Parallelization: XGBoost supports parallel processing, allowing it to efficiently utilize multiple CPU cores during training and prediction, leading to faster computation.
11/ Tree Pruning: XGBoost applies a technique called "tree pruning" to remove unnecessary splits in each decision tree, which improves the overall efficiency and reduces the complexity of the model.
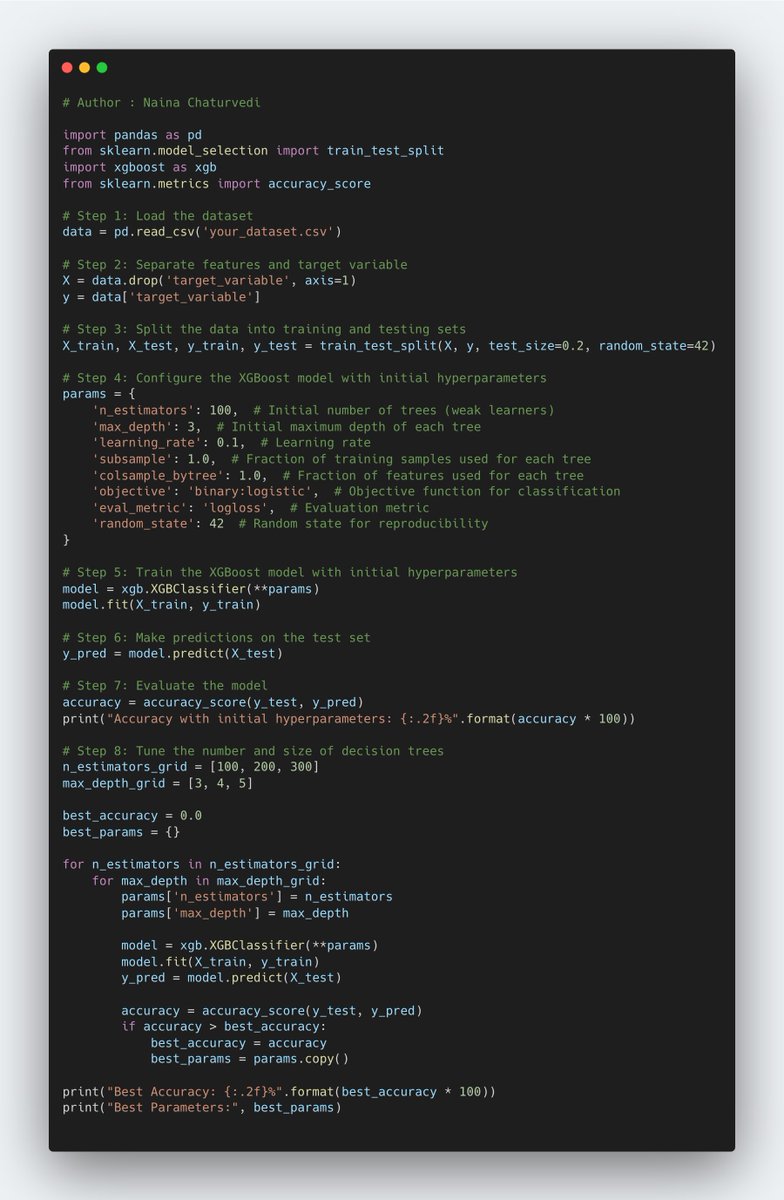
15/ Feature importance and Feature Importance in XGBoost refers to the process of determining the relative importance or contribution of each feature in predicting the target variable. It helps in understanding which features have the most impact on the model's performance.
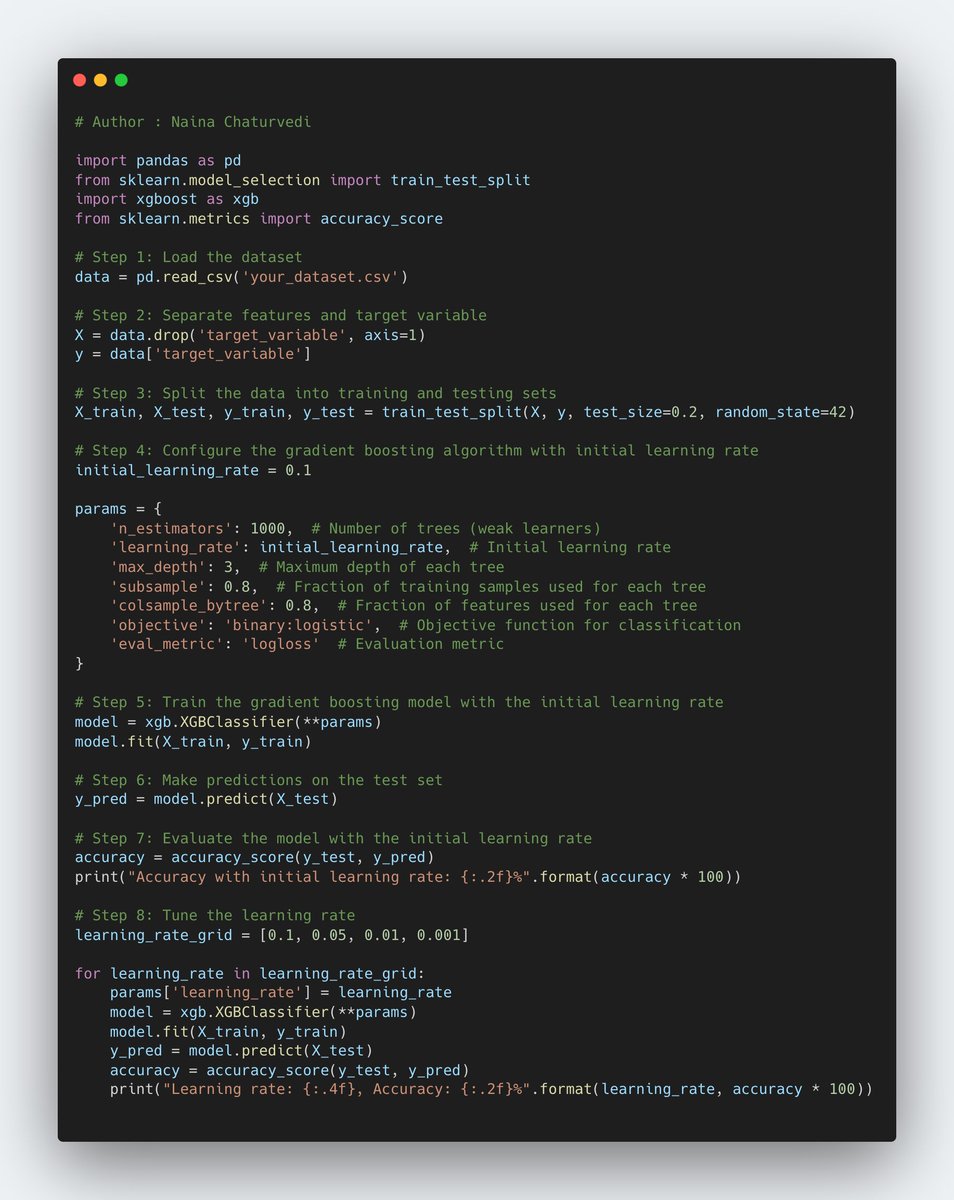
22/ Learning Rate (or Shrinkage Rate): This hyperparameter controls the contribution of each weak learner to the overall prediction. A lower learning rate makes the model more conservative, reducing the impact of each weak learner.
23/ Number of Estimators: This refers to the number of weak learners that are sequentially added to the model during the boosting process. Increasing the number of estimators allows the model to learn more complex relationships in the data, but it can also increase training time

github.com/Coder-World04/…
GitHub - Coder-World04/Complete-Machine-Learning-: This repository contains everything you need to become proficient in Machine Learning
This repository contains everything you need to become proficient in Machine Learning - GitHub - Cod...

naina0405.substack.com
Ignito | Naina Chaturvedi | Substack
Data Science, ML, AI and more... Click to read Ignito, by Naina Chaturvedi, a Substack publication w...
Read more - LSTM and ARIMA in simple terms-
Loading suggestions...