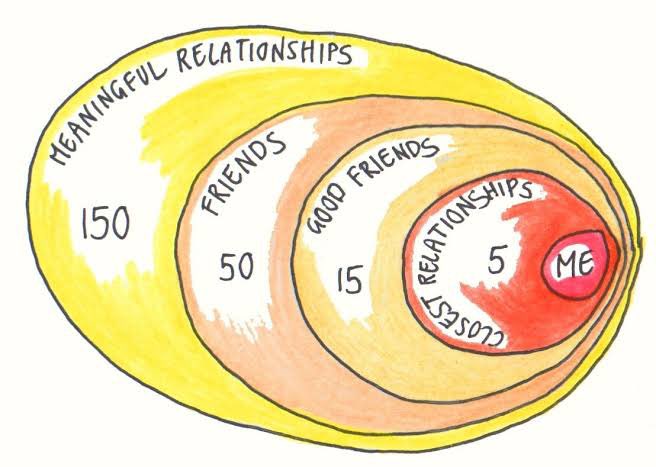
Some rules of thumb that provide simplified guidelines for decision-making and understanding various phenomena: #Threads
1/ Zeigarnik Effect: “Unfinished tasks are remembered more easily than completed ones.”
1/ Zeigarnik Effect: “Unfinished tasks are remembered more easily than completed ones.”
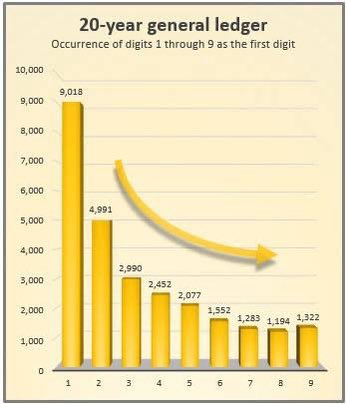
3/Benford's Law: “In many datasets, the leading digits are more likely to be smaller than larger digits.”
⏪In naturally occurring numerical data, the probability of the first digit being small (1, 2, 3) is higher than the probability of it being large (8, 9).
⏪The distribution of leading digits follows a specific pattern. The digit 1 appears as the leading digit about 30% of the time, followed by 2 at around 18%, and the frequency decreases progressively for higher digits, with 9 appearing as the leading digit only about 5% of the time.
⏪In naturally occurring numerical data, the probability of the first digit being small (1, 2, 3) is higher than the probability of it being large (8, 9).
⏪The distribution of leading digits follows a specific pattern. The digit 1 appears as the leading digit about 30% of the time, followed by 2 at around 18%, and the frequency decreases progressively for higher digits, with 9 appearing as the leading digit only about 5% of the time.
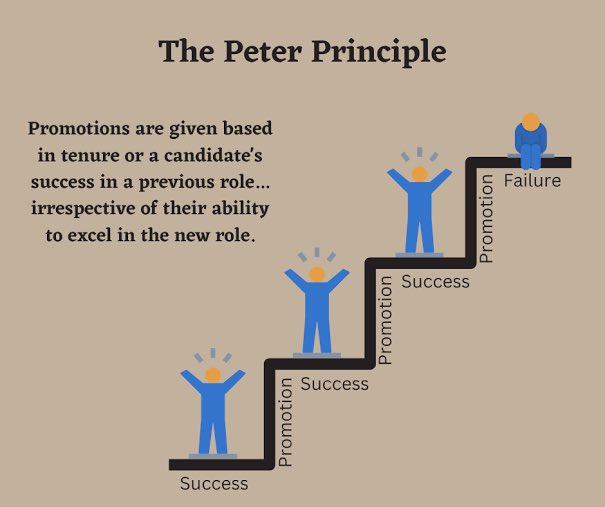
6/Peter Principle: “In a hierarchy, individuals tend to rise to their level of incompetence.”#PeterPrinciple
Occam’s Razor: “The simplest explanation is usually the correct one.”
#OccamsRazor
#SimplicityPrinciple
#SimpleExplanations
#OccamsRazor
#SimplicityPrinciple
#SimpleExplanations
8/Murphy’s Law: “Anything that can go wrong will go wrong.”
#MurphysLaw
#ExpectTheUnexpected
#LawOfUnforeseenEvents
#MurphysLaw
#ExpectTheUnexpected
#LawOfUnforeseenEvents
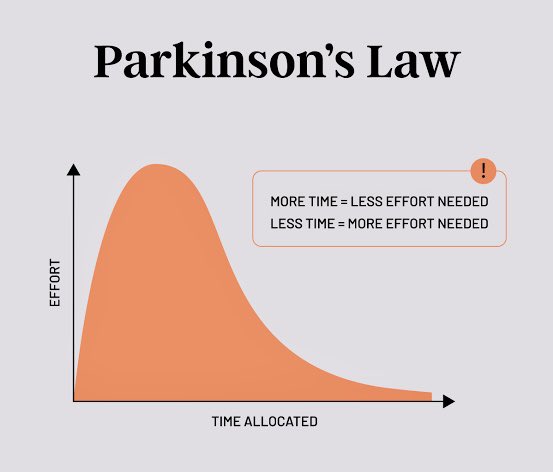
9/Parkinson’s Law: “Work expands to fill the time available for its completion.”
#ParkinsonsLaw
#WorkExpandsToFillTime
#TimeManagement
#ParkinsonsLaw
#WorkExpandsToFillTime
#TimeManagement
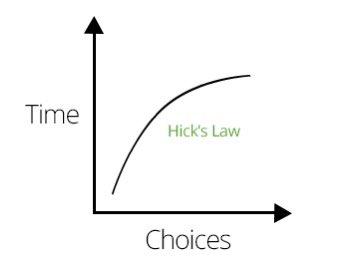
10/“The time it takes to make a decision increases as the number of alternatives increases.”
-Hick’s Law
#DecisionMaking
#HicksLaw
#InformationOverload
-Hick’s Law
#DecisionMaking
#HicksLaw
#InformationOverload
11/“Where you stand depends on where you sit.”
-Mile’s Law
#PerspectiveMatters
#MilesLaw
#InfluenceofPosition
-Mile’s Law
#PerspectiveMatters
#MilesLaw
#InfluenceofPosition
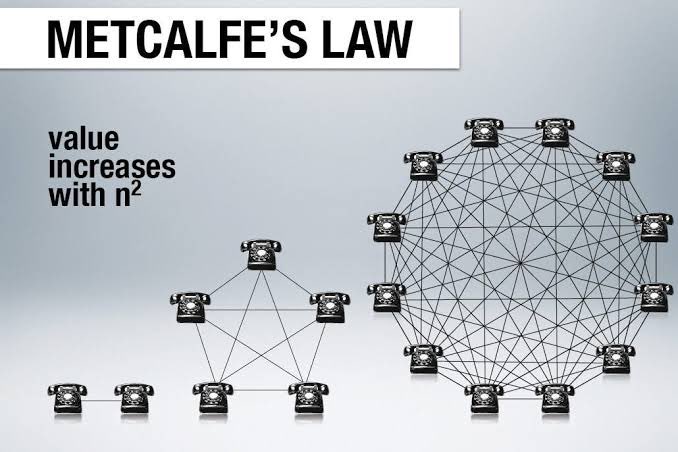
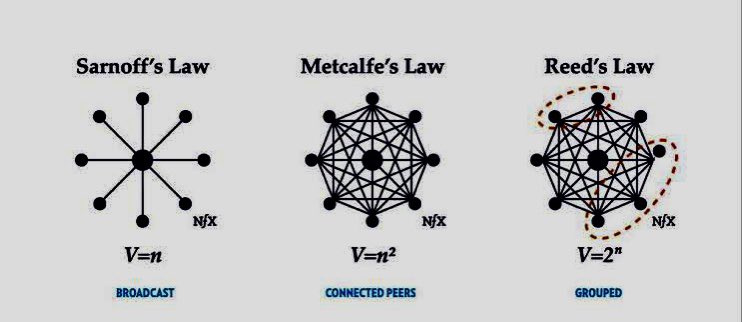
12/Metcalfe’s Law: “The value of a network is proportional to the square of the number of its users.”
#MetcalfesLaw
#NetworkValue
#NetworkEffect
#MetcalfesLaw
#NetworkValue
#NetworkEffect
13/Reed's Law: “The value of a network grows exponentially with the number of its users and the potential for forming subgroups or communities within the network.”
#ReedsLaw #NetworkValue #CommunityFormation
#ReedsLaw #NetworkValue #CommunityFormation
14/Sarnoff's Law: “The value of a broadcast network increases with the number of viewers.”
#SarnoffsLaw #BroadcastNetworkValue #AudienceImpact
#SarnoffsLaw #BroadcastNetworkValue #AudienceImpact
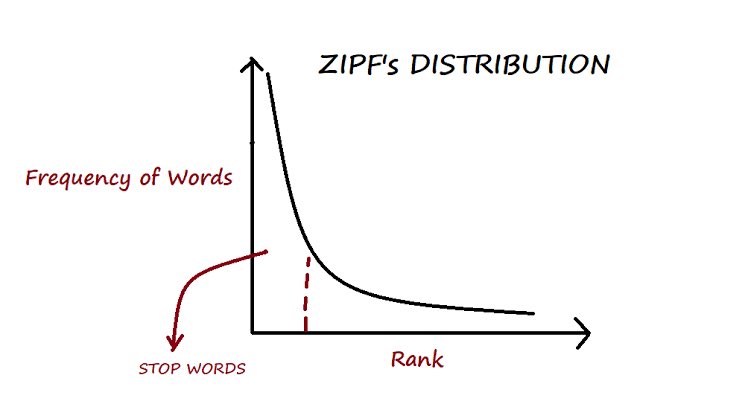
15/Zipf’s Law: “In any corpus of natural language, the frequency of any word is inversely proportional to its rank in the frequency table.”
#ZipfsLaw #WordFrequency #LanguageCorpus
#ZipfsLaw #WordFrequency #LanguageCorpus
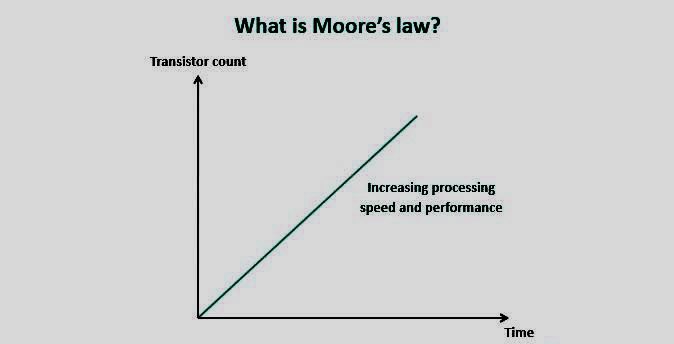
16/Moore’s Law: “The number of transistors on a microchip doubles approximately every two years.”
#MooresLaw #TransistorGrowth #TechnologicalAdvancement
#MooresLaw #TransistorGrowth #TechnologicalAdvancement
17/Amdahl's Law: “The speedup of a computing task is limited by the portion of the task that cannot be parallelized.”
#AmdahlsLaw #ParallelizationLimit #ComputingSpeedup
#AmdahlsLaw #ParallelizationLimit #ComputingSpeedup
18/Sayre's Law: “In any dispute, the intensity of feeling is inversely proportional to the value of the issues at stake.”
#SayresLaw #DisputeIntensity #ValueOfIssues
#EmotionalIntensity #ConflictResolution #PerceivedValue
#SayresLaw #DisputeIntensity #ValueOfIssues
#EmotionalIntensity #ConflictResolution #PerceivedValue
19/ Brandolini's Law (The Bullshit Asymmetry Principle): “The effort required to refute bullshit is an order of magnitude greater than that needed to produce it.”
#BrandolinisLaw #BullshitAsymmetry #RefutingEffort
#InformationVerification #CriticalThinking #Debunking
#BrandolinisLaw #BullshitAsymmetry #RefutingEffort
#InformationVerification #CriticalThinking #Debunking
20/ Cunningham's Law: “The best way to get the right answer on the internet is not to ask a question, but to post the wrong answer.”
#CunninghamsLaw #InternetWisdom #WrongAnswerRightSolution
#ReverseQuestioning #CreativeThinking #ProblemSolving
#CunninghamsLaw #InternetWisdom #WrongAnswerRightSolution
#ReverseQuestioning #CreativeThinking #ProblemSolving
21/ Hofstadter's Law: “It always takes longer than you expect, even when you take into account Hofstadter's Law.”
#HofstadtersLaw #TimeExpectations #Procrastination #TimeManagement
#HofstadtersLaw #TimeExpectations #Procrastination #TimeManagement
22/Gresham’s Law: “Bad money drives out good money from circulation.”
#GreshamsLaw #CurrencyTheory #MoneyCirculation #BadMoneyDrivesOutGood #MonetaryEconomics
#GreshamsLaw #CurrencyTheory #MoneyCirculation #BadMoneyDrivesOutGood #MonetaryEconomics
23/ ⏪20 laws from the field of psychology:
🪜Law of Effect: Behaviors followed by positive consequences are more likely to be repeated, while behaviors followed by negative consequences are less likely to be repeated.
🪜Law of Primacy: Information that is learned first is often better remembered and has a stronger impact than information learned later.
🪜Law of Recency: Information that is learned most recently is often better remembered and has a stronger impact than earlier information.
🪜Law of Exercise: Repeated practice or rehearsal of information improves learning and retention.
🪜Law of Readiness: People learn best when they are mentally and physically ready and motivated to learn.
🪜Law of Intensity: Stronger or more intense stimuli are more likely to be noticed and have a greater impact on behavior and perception.
🪜Law of Proximity: Elements that are close to each other in space or time are perceived as belonging together and are grouped together in our minds.
🪜Law of Similarity: Elements that are similar to each other in appearance are perceived as belonging together and are grouped together in our minds.
🪜Law of Closure: We tend to perceive incomplete or fragmented patterns as complete by mentally filling in missing information.
🪜Law of Contiguity: Stimuli that are experienced together or in close succession are more likely to be associated with each other.
🪜Law of Cognitive Load: The capacity of working memory is limited, and cognitive performance decreases as the cognitive load (amount of mental effort) increases.
🪜Law of Social Facilitation: The presence of others can enhance or inhibit individual performance depending on the nature of the task.
🪜Law of Social Proof: People are more likely to adopt a belief or engage in a behavior if they see others doing the same.
🪜Law of Cognitive Dissonance: People experience psychological discomfort when their beliefs, attitudes, or behaviors are inconsistent and are motivated to reduce this discomfort.
🪜Law of Reciprocity: People tend to feel obligated to return favors or acts of kindness they have received from others.
🪜Law of Anchoring and Adjustment: People tend to rely heavily on the first piece of information they receive (anchor) when making judgments or estimates and adjust from there.
🪜Law of Stereotypes: People often form generalized beliefs and expectations about individuals or groups based on limited information or social categorizations.
🪜Law of Emotional Contagion: Emotions can be contagious, and individuals can “catch” or be influenced by the emotions expressed by others.
🪜Law of Selective Attention: People selectively attend to and focus on certain stimuli or information while filtering out or ignoring others.
🪜Law of Confirmation Bias: People tend to seek, interpret, and remember information in a way that confirms their preexisting beliefs or hypotheses
🪜Law of Effect: Behaviors followed by positive consequences are more likely to be repeated, while behaviors followed by negative consequences are less likely to be repeated.
🪜Law of Primacy: Information that is learned first is often better remembered and has a stronger impact than information learned later.
🪜Law of Recency: Information that is learned most recently is often better remembered and has a stronger impact than earlier information.
🪜Law of Exercise: Repeated practice or rehearsal of information improves learning and retention.
🪜Law of Readiness: People learn best when they are mentally and physically ready and motivated to learn.
🪜Law of Intensity: Stronger or more intense stimuli are more likely to be noticed and have a greater impact on behavior and perception.
🪜Law of Proximity: Elements that are close to each other in space or time are perceived as belonging together and are grouped together in our minds.
🪜Law of Similarity: Elements that are similar to each other in appearance are perceived as belonging together and are grouped together in our minds.
🪜Law of Closure: We tend to perceive incomplete or fragmented patterns as complete by mentally filling in missing information.
🪜Law of Contiguity: Stimuli that are experienced together or in close succession are more likely to be associated with each other.
🪜Law of Cognitive Load: The capacity of working memory is limited, and cognitive performance decreases as the cognitive load (amount of mental effort) increases.
🪜Law of Social Facilitation: The presence of others can enhance or inhibit individual performance depending on the nature of the task.
🪜Law of Social Proof: People are more likely to adopt a belief or engage in a behavior if they see others doing the same.
🪜Law of Cognitive Dissonance: People experience psychological discomfort when their beliefs, attitudes, or behaviors are inconsistent and are motivated to reduce this discomfort.
🪜Law of Reciprocity: People tend to feel obligated to return favors or acts of kindness they have received from others.
🪜Law of Anchoring and Adjustment: People tend to rely heavily on the first piece of information they receive (anchor) when making judgments or estimates and adjust from there.
🪜Law of Stereotypes: People often form generalized beliefs and expectations about individuals or groups based on limited information or social categorizations.
🪜Law of Emotional Contagion: Emotions can be contagious, and individuals can “catch” or be influenced by the emotions expressed by others.
🪜Law of Selective Attention: People selectively attend to and focus on certain stimuli or information while filtering out or ignoring others.
🪜Law of Confirmation Bias: People tend to seek, interpret, and remember information in a way that confirms their preexisting beliefs or hypotheses
24/ ⏪ 20 laws from the field of philosophy:
🪜Law of Non-Contradiction: A statement cannot be both true and false at the same time and in the same sense.
🪜Law of Identity: Each thing is identical to itself, meaning that it has a unique identity.
🪜Law of Excluded Middle: A statement is either true or false, with no middle ground or third option.
🪜Law of Causality: Every event has a cause or causes that precede it.
🪜Law of Sufficient Reason: Everything must have a reason or explanation for its existence or occurrence.
🪜Law of Rationality: Humans possess the capacity for reasoning and rational thought.
🪜Law of Free Will: Individuals have the ability to make choices and act freely.
🪜Law of Morality: There are moral principles or standards that govern human behavior and actions.
🪜Law of Natural Rights: Humans have inherent rights that are derived from their nature or existence.
🪜Law of Justice: Fairness and equity should guide the distribution of benefits and burdens in society.
🪜Law of Universalizability: Moral principles should be applicable universally to all individuals.
🪜Law of Utility: Actions or decisions should maximize overall happiness or utility.
🪜Law of Good Will: Moral actions should be motivated by a sense of goodwill or benevolence.
🪜Law of Autonomy: Individuals have the right to make decisions and govern their own lives.
🪜Law of Aesthetics: Beauty and aesthetic value are subjective and culturally influenced.
🪜Law of Objectivity: There is an objective reality that exists independently of our perceptions or interpretations.
🪜Law of Dualism: There are two fundamental substances or aspects of existence, such as mind and matter.
🪜Law of Necessity and Contingency: Some things or events are necessary and cannot be otherwise, while others are contingent and could have been different.
🪜Law of Personal Identity: Each person has a unique identity that persists over time, despite changes in their physical or mental states.
🪜Law of Discourse: Rational and meaningful communication requires adherence to logical principles and rules.
🪜Law of Non-Contradiction: A statement cannot be both true and false at the same time and in the same sense.
🪜Law of Identity: Each thing is identical to itself, meaning that it has a unique identity.
🪜Law of Excluded Middle: A statement is either true or false, with no middle ground or third option.
🪜Law of Causality: Every event has a cause or causes that precede it.
🪜Law of Sufficient Reason: Everything must have a reason or explanation for its existence or occurrence.
🪜Law of Rationality: Humans possess the capacity for reasoning and rational thought.
🪜Law of Free Will: Individuals have the ability to make choices and act freely.
🪜Law of Morality: There are moral principles or standards that govern human behavior and actions.
🪜Law of Natural Rights: Humans have inherent rights that are derived from their nature or existence.
🪜Law of Justice: Fairness and equity should guide the distribution of benefits and burdens in society.
🪜Law of Universalizability: Moral principles should be applicable universally to all individuals.
🪜Law of Utility: Actions or decisions should maximize overall happiness or utility.
🪜Law of Good Will: Moral actions should be motivated by a sense of goodwill or benevolence.
🪜Law of Autonomy: Individuals have the right to make decisions and govern their own lives.
🪜Law of Aesthetics: Beauty and aesthetic value are subjective and culturally influenced.
🪜Law of Objectivity: There is an objective reality that exists independently of our perceptions or interpretations.
🪜Law of Dualism: There are two fundamental substances or aspects of existence, such as mind and matter.
🪜Law of Necessity and Contingency: Some things or events are necessary and cannot be otherwise, while others are contingent and could have been different.
🪜Law of Personal Identity: Each person has a unique identity that persists over time, despite changes in their physical or mental states.
🪜Law of Discourse: Rational and meaningful communication requires adherence to logical principles and rules.
25/ ⏪10 important laws in forensic science
🪜Locard’s Exchange Principle: Every contact leaves a trace, meaning that whenever two objects come into contact, there will be a transfer of materials.
🪜Frye’s Standard: Scientific evidence must be generally accepted within the scientific community in order to be admissible in court.
🪜Daubert Standard: Criteria used to determine the admissibility of scientific evidence in federal courts in the United States.
🪜Principle of Individuality: Every person and object can be distinguished from others based on unique characteristics or traits.
🪜Principle of Reconstruction: Through careful analysis of evidence, forensic scientists can reconstruct events and circumstances surrounding a crime.
🪜Principle of Class Characteristics: Objects or evidence can be grouped into classes based on similar characteristics, providing potential links to suspects or crime scenes.
🪜Principle of Identification: Forensic experts can determine the identity of a person or object through scientific analysis of physical or biological evidence.
🪜Principle of Chain of Custody: The proper documentation and handling of evidence to maintain its integrity and ensure it can be used in court.
🪜Principle of Preservation: Proper preservation techniques must be employed to prevent contamination or deterioration of evidence.
🪜Principle of Transfer: Traces left behind at a crime scene can be transferred to suspects or their belongings, providing potential evidence of their involvement.
🪜Locard’s Exchange Principle: Every contact leaves a trace, meaning that whenever two objects come into contact, there will be a transfer of materials.
🪜Frye’s Standard: Scientific evidence must be generally accepted within the scientific community in order to be admissible in court.
🪜Daubert Standard: Criteria used to determine the admissibility of scientific evidence in federal courts in the United States.
🪜Principle of Individuality: Every person and object can be distinguished from others based on unique characteristics or traits.
🪜Principle of Reconstruction: Through careful analysis of evidence, forensic scientists can reconstruct events and circumstances surrounding a crime.
🪜Principle of Class Characteristics: Objects or evidence can be grouped into classes based on similar characteristics, providing potential links to suspects or crime scenes.
🪜Principle of Identification: Forensic experts can determine the identity of a person or object through scientific analysis of physical or biological evidence.
🪜Principle of Chain of Custody: The proper documentation and handling of evidence to maintain its integrity and ensure it can be used in court.
🪜Principle of Preservation: Proper preservation techniques must be employed to prevent contamination or deterioration of evidence.
🪜Principle of Transfer: Traces left behind at a crime scene can be transferred to suspects or their belongings, providing potential evidence of their involvement.
26/⏪20 Laws of Photography:
📸 "The Rule of Thirds": This rule is about dividing the frame into a 3x3 grid and placing the subject along those lines or at their intersections for a balanced composition.
📸"The Golden Ratio": This rule is based on a mathematical principle and creates a sense of aesthetic balance and harmony in the image.
📸"Leading Lines": This law encourages photographers to use natural lines to draw the viewer’s attention towards a certain point in the image.
📸"Framing": This rule involves using natural frames like windows, arches, or branches to isolate and highlight the main subject.
📸"Fill the Frame": This rule encourages getting close to the subject to capture details and eliminate distractions.
📸"Simplicity and Minimalism": This rule focuses on having a clean, uncluttered frame with a clear point of interest.
📸"The Rule of Space": This law involves including extra space in the direction that a subject is moving or looking towards.
📸"Depth": Utilizing depth can give a three-dimensional feel to a two-dimensional image.
📸"Color Theory": Understanding colors and their relationships can help create a certain mood or harmony in your images.
📸"Balance": This involves arranging elements so that no one part of the image overpowers another.
📸"Symmetry": Symmetry can be very pleasing to the eye and is often used in architectural and abstract photography.
📸"Texture": Including texture can add a tangible quality to an image.
📸"Pattern and Repetition": Patterns are aesthetically pleasing, but the best photos often break them.
📸"Backgrounds": A poorly chosen background can ruin an otherwise good image.
📸"Juxtaposition": Placing contrasting elements together can be very impactful.
📸"Timing": Often the difference between a good photo and a great one is a matter of seconds.
📸"Perspective": Changing your perspective can dramatically alter the look of an image.
📸"The Rule of Odds": An image is more visually appealing if there are an odd number of subjects.
📸"Experimentation": There are rules, but they should be understood so they can be broken. Don’t be afraid to try something new.
📸"The Decisive Moment": This term, coined by Henri Cartier-Bresson, refers to capturing an event that is ephemeral and spontaneous, where the image represents the essence of the event itself.
📸 "The Rule of Thirds": This rule is about dividing the frame into a 3x3 grid and placing the subject along those lines or at their intersections for a balanced composition.
📸"The Golden Ratio": This rule is based on a mathematical principle and creates a sense of aesthetic balance and harmony in the image.
📸"Leading Lines": This law encourages photographers to use natural lines to draw the viewer’s attention towards a certain point in the image.
📸"Framing": This rule involves using natural frames like windows, arches, or branches to isolate and highlight the main subject.
📸"Fill the Frame": This rule encourages getting close to the subject to capture details and eliminate distractions.
📸"Simplicity and Minimalism": This rule focuses on having a clean, uncluttered frame with a clear point of interest.
📸"The Rule of Space": This law involves including extra space in the direction that a subject is moving or looking towards.
📸"Depth": Utilizing depth can give a three-dimensional feel to a two-dimensional image.
📸"Color Theory": Understanding colors and their relationships can help create a certain mood or harmony in your images.
📸"Balance": This involves arranging elements so that no one part of the image overpowers another.
📸"Symmetry": Symmetry can be very pleasing to the eye and is often used in architectural and abstract photography.
📸"Texture": Including texture can add a tangible quality to an image.
📸"Pattern and Repetition": Patterns are aesthetically pleasing, but the best photos often break them.
📸"Backgrounds": A poorly chosen background can ruin an otherwise good image.
📸"Juxtaposition": Placing contrasting elements together can be very impactful.
📸"Timing": Often the difference between a good photo and a great one is a matter of seconds.
📸"Perspective": Changing your perspective can dramatically alter the look of an image.
📸"The Rule of Odds": An image is more visually appealing if there are an odd number of subjects.
📸"Experimentation": There are rules, but they should be understood so they can be broken. Don’t be afraid to try something new.
📸"The Decisive Moment": This term, coined by Henri Cartier-Bresson, refers to capturing an event that is ephemeral and spontaneous, where the image represents the essence of the event itself.
27/⏪10 Most Important Laws of Communication:
🏺1. "Law of Clarity": Clear and concise messages are more likely to be understood and acted upon. Ensure your intent matches the message delivered.
🏺2. "Law of Listening": Effective communication requires active listening. Understanding and acknowledging the speaker fosters positive communication.
🏺3. "Law of Respect": Treat every communication exchange with respect. All parties have a right to voice their perspectives.
🏺4. "Law of Non-Verbal Communication": Body language, facial expressions, and tone often communicate more information than words. Be mindful of your non-verbal cues.
🏺5. "Law of Feedback": Constructive feedback helps ensure the message sent is the message received. Always provide a chance for response and clarification.
🏺6. "Law of Context": Consider the context in which communication occurs. The same message can have different meanings in different contexts.
🏺7. "Law of Consistency": Regular and consistent communication builds trust and understanding, fostering stronger relationships.
🏺8. "Law of Adaptation": Tailor your message to your audience. The better you understand them, the more effective your communication will be.
🏺9. "Law of Honesty": Authentic and honest communication builds trust and integrity, which are fundamental to effective communication.
🏺10. "Law of Empathy": Putting yourself in the other person's shoes enhances understanding and connection. Empathy promotes open and honest communication.
#ClearCommunication #ActiveListening #RespectfulDialogue #NonVerbalCues #ConstructiveFeedback #ContextMatters #ConsistentMessaging #AudienceAdaptation #HonestDialogue #EmpatheticUnderstanding
🏺1. "Law of Clarity": Clear and concise messages are more likely to be understood and acted upon. Ensure your intent matches the message delivered.
🏺2. "Law of Listening": Effective communication requires active listening. Understanding and acknowledging the speaker fosters positive communication.
🏺3. "Law of Respect": Treat every communication exchange with respect. All parties have a right to voice their perspectives.
🏺4. "Law of Non-Verbal Communication": Body language, facial expressions, and tone often communicate more information than words. Be mindful of your non-verbal cues.
🏺5. "Law of Feedback": Constructive feedback helps ensure the message sent is the message received. Always provide a chance for response and clarification.
🏺6. "Law of Context": Consider the context in which communication occurs. The same message can have different meanings in different contexts.
🏺7. "Law of Consistency": Regular and consistent communication builds trust and understanding, fostering stronger relationships.
🏺8. "Law of Adaptation": Tailor your message to your audience. The better you understand them, the more effective your communication will be.
🏺9. "Law of Honesty": Authentic and honest communication builds trust and integrity, which are fundamental to effective communication.
🏺10. "Law of Empathy": Putting yourself in the other person's shoes enhances understanding and connection. Empathy promotes open and honest communication.
#ClearCommunication #ActiveListening #RespectfulDialogue #NonVerbalCues #ConstructiveFeedback #ContextMatters #ConsistentMessaging #AudienceAdaptation #HonestDialogue #EmpatheticUnderstanding
28/⏪20 Laws of Time Management:
🕰️ "Law of Prioritization": Not all tasks are equally important. Prioritize based on the value tasks add to your goals.
🕰️ "Law of Planning": Invest time in planning your tasks. A well-structured plan boosts efficiency.
🕰️ "Law of Time Boxing": Dedicate specific time slots for similar tasks to improve focus and efficiency.
🕰️ "Law of Delegation": Delegate tasks that others can do. This frees up your time for higher-level tasks.
🕰️ "Law of Concentration": Quality over quantity. Focusing on one task at a time often leads to better results.
🕰️ "Law of Rest": Regular breaks are crucial. They help maintain productivity and prevent burnout.
🕰️ "Law of Flexibility": Build flexibility into your schedule. Unexpected tasks or delays are inevitable.
🕰️ "Law of Balance": Work-life balance is key. Dedicating time to relaxation and personal activities can rejuvenate your mind.
🕰️ "Law of Routine and Habit Development": Developing routines and habits can help automate tasks and improve efficiency.
🕰️ "Law of ‘No’": Learning to say 'no' to non-critical requests is vital to protect your time.
🕰️ "Law of Urgency": Distinguish between what is urgent and what is important. Urgent tasks are not always the most important.
🕰️ "Law of Deadlines": Set deadlines. They provide a clear end point and help maintain focus.
🕰️ "Law of Pareto Principle": 80% of results often come from 20% of efforts. Identify and focus on that 20%.
🕰️ "Law of Procrastination": Delaying tasks can lead to piled-up work. Tackle difficult tasks first to avoid this.
🕰️ "Law of Uninterrupted Blocks": Schedule large blocks of uninterrupted time for high-concentration tasks.
🕰️ "Law of Tools and Technology": Leverage tools and technology to save time and increase productivity.
🕰️ "Law of Clutter-free Environment": A tidy and organized work environment can enhance focus and productivity.
🕰️ "Law of Preparation": Spend time preparing for tasks or events in advance to ensure smooth execution.
🕰️ "Law of Reflection": Regularly review and reflect on how you spend your time to identify areas for improvement.
🕰️ "Law of Value": Time is a non-renewable resource. Treat it as such and spend it on activities that add value to your life or work.
🕰️ "Law of Prioritization": Not all tasks are equally important. Prioritize based on the value tasks add to your goals.
🕰️ "Law of Planning": Invest time in planning your tasks. A well-structured plan boosts efficiency.
🕰️ "Law of Time Boxing": Dedicate specific time slots for similar tasks to improve focus and efficiency.
🕰️ "Law of Delegation": Delegate tasks that others can do. This frees up your time for higher-level tasks.
🕰️ "Law of Concentration": Quality over quantity. Focusing on one task at a time often leads to better results.
🕰️ "Law of Rest": Regular breaks are crucial. They help maintain productivity and prevent burnout.
🕰️ "Law of Flexibility": Build flexibility into your schedule. Unexpected tasks or delays are inevitable.
🕰️ "Law of Balance": Work-life balance is key. Dedicating time to relaxation and personal activities can rejuvenate your mind.
🕰️ "Law of Routine and Habit Development": Developing routines and habits can help automate tasks and improve efficiency.
🕰️ "Law of ‘No’": Learning to say 'no' to non-critical requests is vital to protect your time.
🕰️ "Law of Urgency": Distinguish between what is urgent and what is important. Urgent tasks are not always the most important.
🕰️ "Law of Deadlines": Set deadlines. They provide a clear end point and help maintain focus.
🕰️ "Law of Pareto Principle": 80% of results often come from 20% of efforts. Identify and focus on that 20%.
🕰️ "Law of Procrastination": Delaying tasks can lead to piled-up work. Tackle difficult tasks first to avoid this.
🕰️ "Law of Uninterrupted Blocks": Schedule large blocks of uninterrupted time for high-concentration tasks.
🕰️ "Law of Tools and Technology": Leverage tools and technology to save time and increase productivity.
🕰️ "Law of Clutter-free Environment": A tidy and organized work environment can enhance focus and productivity.
🕰️ "Law of Preparation": Spend time preparing for tasks or events in advance to ensure smooth execution.
🕰️ "Law of Reflection": Regularly review and reflect on how you spend your time to identify areas for improvement.
🕰️ "Law of Value": Time is a non-renewable resource. Treat it as such and spend it on activities that add value to your life or work.
29/⏪10 Important Properties of Time:
⏰ "Irreversibility": Time only moves forward, never backward. We always move from the past towards the future.
⏰ "Continuity": Time is continuous. It doesn’t jump or skip but flows smoothly.
⏰ "One-dimensionality": Time has only one dimension, which is often referred to as ‘duration’.
⏰ "Infinity": Time is believed to be infinite. It had no beginning and will have no end.
⏰ "Non-spatial": Time does not occupy space. It is not a physical object.
⏰ "Relativity": According to Einstein’s Theory of Relativity, time can be affected by speed and gravity.
⏰ "Immutability": The rate of time, at least in any given inertial reference frame, remains constant.
⏰ "Directionality": Often referred to as the “arrow of time,” physical processes have a direction and are not reversible.
⏰ "Asymmetry": The future and the past are not the same, showing the asymmetry of time.
⏰ "Quantizability": Some theories suggest time may be quantized, meaning it might be composed of discrete moments rather than a continuous flow.
#TimeProperties #Irreversibility #TimeContinuity #OneDimensionality #TimeInfinity #NonSpatial #TimeRelativity #TimeImmutability #TimeDirectionality #TimeAsymmetry #TimeQuantizability
⏰ "Irreversibility": Time only moves forward, never backward. We always move from the past towards the future.
⏰ "Continuity": Time is continuous. It doesn’t jump or skip but flows smoothly.
⏰ "One-dimensionality": Time has only one dimension, which is often referred to as ‘duration’.
⏰ "Infinity": Time is believed to be infinite. It had no beginning and will have no end.
⏰ "Non-spatial": Time does not occupy space. It is not a physical object.
⏰ "Relativity": According to Einstein’s Theory of Relativity, time can be affected by speed and gravity.
⏰ "Immutability": The rate of time, at least in any given inertial reference frame, remains constant.
⏰ "Directionality": Often referred to as the “arrow of time,” physical processes have a direction and are not reversible.
⏰ "Asymmetry": The future and the past are not the same, showing the asymmetry of time.
⏰ "Quantizability": Some theories suggest time may be quantized, meaning it might be composed of discrete moments rather than a continuous flow.
#TimeProperties #Irreversibility #TimeContinuity #OneDimensionality #TimeInfinity #NonSpatial #TimeRelativity #TimeImmutability #TimeDirectionality #TimeAsymmetry #TimeQuantizability
30/⏪10 Laws of Time:
🐈 "Second Law of Thermodynamics": Time's direction is tied to the increase in entropy or disorder in the universe.
🐈 "Einstein's Theory of Relativity": Time dilation occurs when one object moves relative to another object, meaning time can slow down or speed up depending on the speed of the object and the strength of gravity.
🐈 "Quantum Entanglement": In quantum physics, particles can become entangled and affect each other's states instantly, seemingly bypassing time.
🐈 "Causality Principle": Causes must always precede their effects. The cause-effect relationship defines the forward direction of time.
🐈 "Time's Uncertainty Principle": In quantum mechanics, the energy of a system and the time over which the system persists cannot both be known exactly.
🐈 "Cosmological Arrow of Time": The universe is expanding and not contracting, determining the direction of time.
🐈 "Psychological Arrow of Time": Humans perceive time as always moving forward.
🐈 "Radiative Arrow of Time": Electromagnetic radiation like light only travels in one direction - from the source to the observer.
🐈 "Quantum Arrow of Time": In quantum mechanics, wave functions evolve over time but the process is not reversible.
🐈 "Relativity of Simultaneity": According to the Theory of Relativity, simultaneous events for one observer may not be simultaneous for another observer, depending on their relative motion.
#LawsOfTime #Thermodynamics #TheoryOfRelativity #QuantumEntanglement #CausalityPrinciple #TimeUncertainty #CosmologicalArrow #PsychologicalArrow #RadiativeArrow #QuantumArrow #RelativityOfSimultaneity
🐈 "Second Law of Thermodynamics": Time's direction is tied to the increase in entropy or disorder in the universe.
🐈 "Einstein's Theory of Relativity": Time dilation occurs when one object moves relative to another object, meaning time can slow down or speed up depending on the speed of the object and the strength of gravity.
🐈 "Quantum Entanglement": In quantum physics, particles can become entangled and affect each other's states instantly, seemingly bypassing time.
🐈 "Causality Principle": Causes must always precede their effects. The cause-effect relationship defines the forward direction of time.
🐈 "Time's Uncertainty Principle": In quantum mechanics, the energy of a system and the time over which the system persists cannot both be known exactly.
🐈 "Cosmological Arrow of Time": The universe is expanding and not contracting, determining the direction of time.
🐈 "Psychological Arrow of Time": Humans perceive time as always moving forward.
🐈 "Radiative Arrow of Time": Electromagnetic radiation like light only travels in one direction - from the source to the observer.
🐈 "Quantum Arrow of Time": In quantum mechanics, wave functions evolve over time but the process is not reversible.
🐈 "Relativity of Simultaneity": According to the Theory of Relativity, simultaneous events for one observer may not be simultaneous for another observer, depending on their relative motion.
#LawsOfTime #Thermodynamics #TheoryOfRelativity #QuantumEntanglement #CausalityPrinciple #TimeUncertainty #CosmologicalArrow #PsychologicalArrow #RadiativeArrow #QuantumArrow #RelativityOfSimultaneity
31/🏺20 Laws of Wealth:
🎏 "Law of Value": Your wealth is a reflection of the value you provide. The more value you offer, the more wealth you can generate.
🎏 "Law of Saving": Save and invest a portion of your earnings regularly. Compound interest is a powerful wealth-building tool.
🎏 "Law of Diversification": Don't put all your eggs in one basket. Diversify your investments to mitigate risks.
🎏 "Law of Risk and Reward": Higher potential rewards often come with higher risk. Understand and manage this balance effectively.
🎏 "Law of Education": Continually educate yourself about finance and investments. Knowledge is the foundation of wealth.
🎏 "Law of Persistence": Building wealth usually takes time. Persistence and patience are crucial.
🎏 "Law of Income Streams": Don't rely on a single income source. Multiple streams of income can lead to financial stability and wealth.
🎏 "Law of Spending": Spend less than you earn. Financial discipline is fundamental to wealth accumulation.
🎏 "Law of Leverage": Utilize other people's time, skills, and money whenever possible to scale your wealth.
🎏 "Law of Giving": The more you give, the more you receive. Contributing to others and to your community can often lead to opportunities for wealth.
🎏 "Law of Attraction": Your mindset and beliefs about wealth can influence your financial reality. Positive attitudes can attract prosperity.
🎏 "Law of Consistency": Regular and consistent actions toward wealth building often yield better results than sporadic efforts.
🎏 "Law of Networking": Building strong professional and personal networks can open doors to opportunities and amplify your wealth.
🎏 "Law of Delayed Gratification": Sacrificing immediate pleasures for long-term gains is key to accumulating wealth.
🎏 "Law of Market Understanding": To invest wisely, understanding market trends and dynamics is crucial.
🎏 "Law of Debt Management": Avoid bad debt that doesn't generate income. Use good debt that can be leveraged to increase your wealth.
🎏 "Law of Financial Planning": A clear financial plan serves as a roadmap for wealth accumulation and ensures you stay on track.
🎏 "Law of Self Investment": Investing in your skills and health is one of the best investments. It enhances your capacity to earn and accumulate wealth.
🎏 "Law of Accountability": Take responsibility for your financial situation. Your wealth depends on the decisions you make.
🎏 "Law of Estate Planning": Proper planning of your estate ensures that your wealth benefits those you care about and isn't lost to taxes and legal complications.
#WealthLaws #LawOfAttraction #ConsistencyInWealth #Networking #DelayedGratification #MarketUnderstanding #DebtManagement #FinancialPlanning #SelfInvestment #Accountability #EstatePlanning
🎏 "Law of Value": Your wealth is a reflection of the value you provide. The more value you offer, the more wealth you can generate.
🎏 "Law of Saving": Save and invest a portion of your earnings regularly. Compound interest is a powerful wealth-building tool.
🎏 "Law of Diversification": Don't put all your eggs in one basket. Diversify your investments to mitigate risks.
🎏 "Law of Risk and Reward": Higher potential rewards often come with higher risk. Understand and manage this balance effectively.
🎏 "Law of Education": Continually educate yourself about finance and investments. Knowledge is the foundation of wealth.
🎏 "Law of Persistence": Building wealth usually takes time. Persistence and patience are crucial.
🎏 "Law of Income Streams": Don't rely on a single income source. Multiple streams of income can lead to financial stability and wealth.
🎏 "Law of Spending": Spend less than you earn. Financial discipline is fundamental to wealth accumulation.
🎏 "Law of Leverage": Utilize other people's time, skills, and money whenever possible to scale your wealth.
🎏 "Law of Giving": The more you give, the more you receive. Contributing to others and to your community can often lead to opportunities for wealth.
🎏 "Law of Attraction": Your mindset and beliefs about wealth can influence your financial reality. Positive attitudes can attract prosperity.
🎏 "Law of Consistency": Regular and consistent actions toward wealth building often yield better results than sporadic efforts.
🎏 "Law of Networking": Building strong professional and personal networks can open doors to opportunities and amplify your wealth.
🎏 "Law of Delayed Gratification": Sacrificing immediate pleasures for long-term gains is key to accumulating wealth.
🎏 "Law of Market Understanding": To invest wisely, understanding market trends and dynamics is crucial.
🎏 "Law of Debt Management": Avoid bad debt that doesn't generate income. Use good debt that can be leveraged to increase your wealth.
🎏 "Law of Financial Planning": A clear financial plan serves as a roadmap for wealth accumulation and ensures you stay on track.
🎏 "Law of Self Investment": Investing in your skills and health is one of the best investments. It enhances your capacity to earn and accumulate wealth.
🎏 "Law of Accountability": Take responsibility for your financial situation. Your wealth depends on the decisions you make.
🎏 "Law of Estate Planning": Proper planning of your estate ensures that your wealth benefits those you care about and isn't lost to taxes and legal complications.
#WealthLaws #LawOfAttraction #ConsistencyInWealth #Networking #DelayedGratification #MarketUnderstanding #DebtManagement #FinancialPlanning #SelfInvestment #Accountability #EstatePlanning
Loading suggestions...