1/18
🤔Why is the BUN/Cr elevated in upper gastrointestinal bleeding?
This question has been covered by @AdamRodmanMD and @WilliamAird4 but the literature is SO FASCINATING that I had to review it myself.
🤔Why is the BUN/Cr elevated in upper gastrointestinal bleeding?
This question has been covered by @AdamRodmanMD and @WilliamAird4 but the literature is SO FASCINATING that I had to review it myself.
@AdamRodmanMD @WilliamAird4 2/
In 1933 LV Sanguinetti reported the association between GI bleeding and elevated BUN.
The next two decades were the golden age of experimentation on this question with dozens of studies performed with the goal of identifying the cause.
dx.doi.org
In 1933 LV Sanguinetti reported the association between GI bleeding and elevated BUN.
The next two decades were the golden age of experimentation on this question with dozens of studies performed with the goal of identifying the cause.
dx.doi.org
@AdamRodmanMD @WilliamAird4 3/
Leon Schiff did a lot of this early work.
In a 1939 report of 53 case of hematemesis or melena he showed a clear rise in BUN after episodes of bleeding.
These observation led to a burgeoning enthusiasm for the experimental ingestion of blood!
dx.doi.org
Leon Schiff did a lot of this early work.
In a 1939 report of 53 case of hematemesis or melena he showed a clear rise in BUN after episodes of bleeding.
These observation led to a burgeoning enthusiasm for the experimental ingestion of blood!
dx.doi.org
@AdamRodmanMD @WilliamAird4 4/
In one study from 1946 participants underwent phlebotomy with 580mL or 800mL removed. They then drank it with 100mL of water and had their BUN monitored.
The authors reassure us that for the participants, “the psychic trauma was non-existent.”
Phew.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
In one study from 1946 participants underwent phlebotomy with 580mL or 800mL removed. They then drank it with 100mL of water and had their BUN monitored.
The authors reassure us that for the participants, “the psychic trauma was non-existent.”
Phew.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
@AdamRodmanMD @WilliamAird4 5/
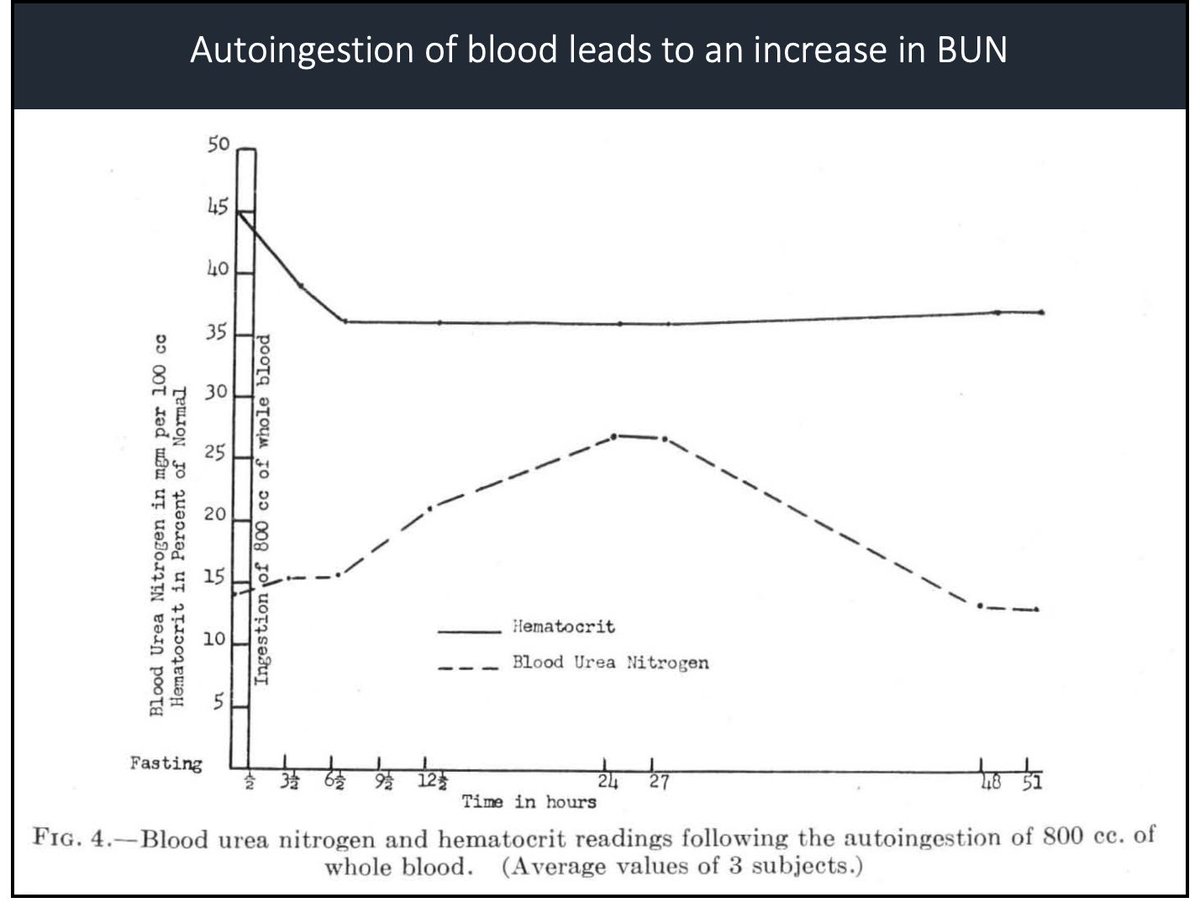
This study showed that autoingestion of blood resulted in a notable rise in BUN.
🤔The question then became: does the SITE of bleeding matter?
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
This study showed that autoingestion of blood resulted in a notable rise in BUN.
🤔The question then became: does the SITE of bleeding matter?
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
@AdamRodmanMD @WilliamAird4 6/
To address this question Schiff enrolled 15 participants and administered blood to various sites within the GI tract.
He then examined how the BUN changed based on the amount of blood delivered and the site of administration.
link.springer.com
To address this question Schiff enrolled 15 participants and administered blood to various sites within the GI tract.
He then examined how the BUN changed based on the amount of blood delivered and the site of administration.
link.springer.com
@AdamRodmanMD @WilliamAird4 7/
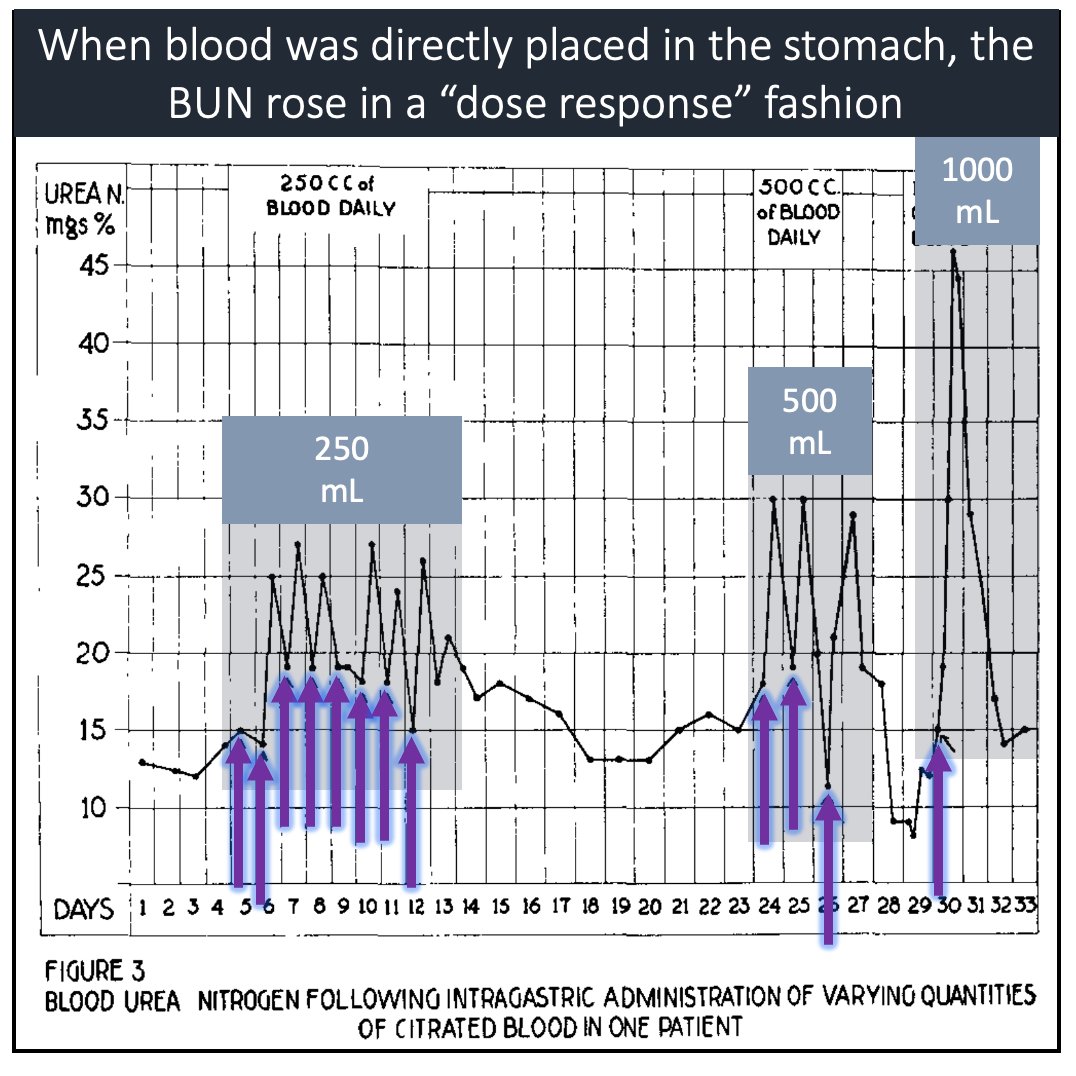
When 250 mL of blood was administered via an orogastric tube, he saw a very small rise in BUN.
As they increased the dose of blood to 500, 1000, and 2000 mL he saw a greater increase in BUN.
link.springer.com
When 250 mL of blood was administered via an orogastric tube, he saw a very small rise in BUN.
As they increased the dose of blood to 500, 1000, and 2000 mL he saw a greater increase in BUN.
link.springer.com
@AdamRodmanMD @WilliamAird4 8/
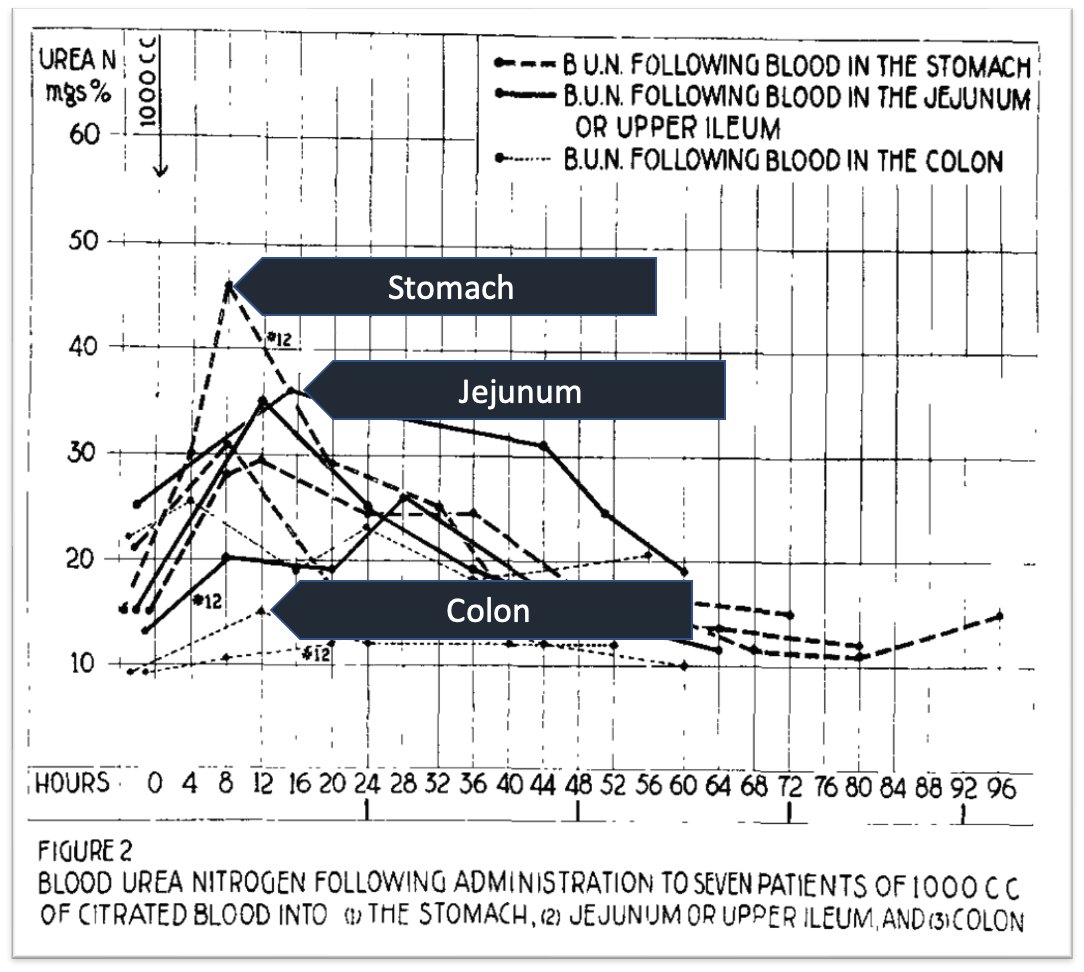
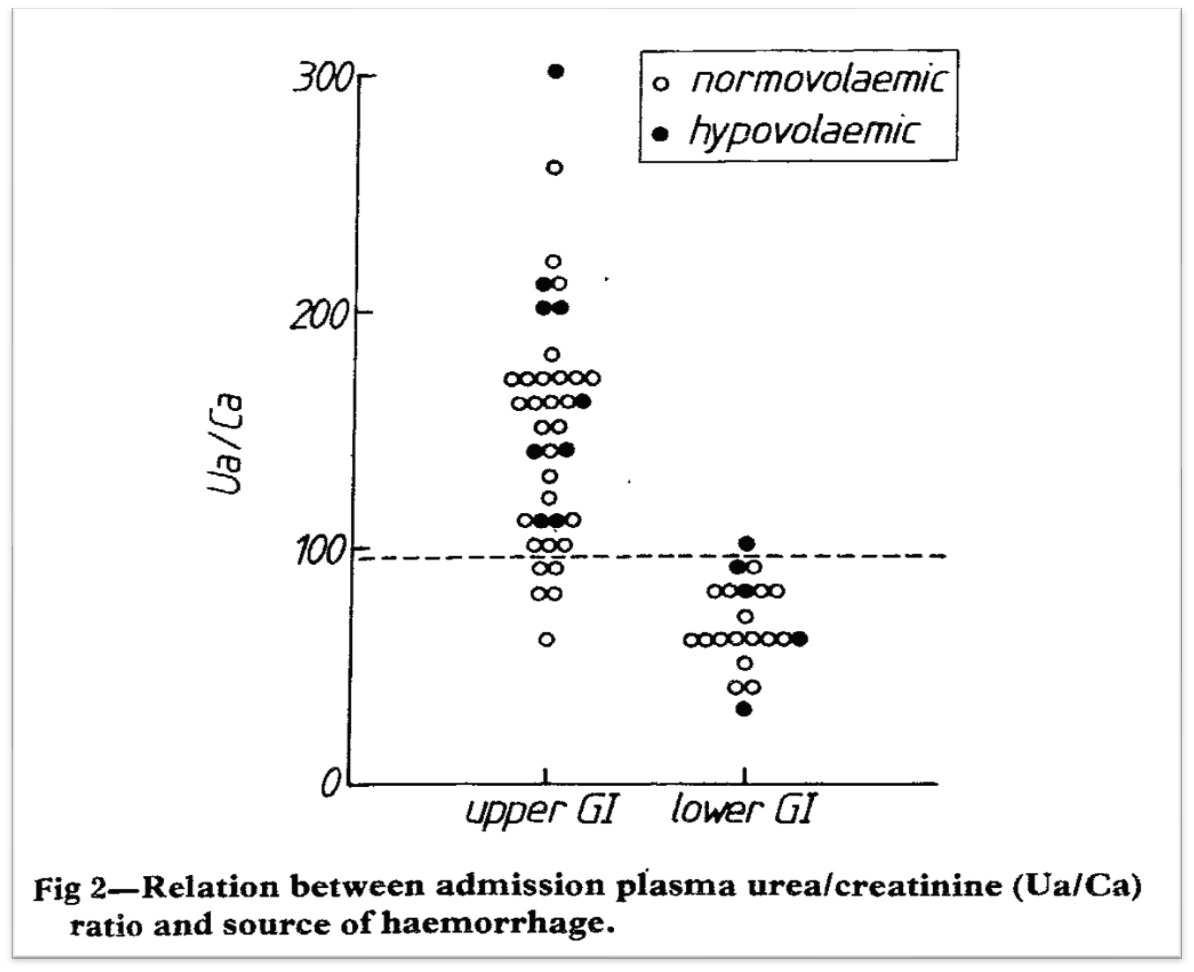
When blood was administered to the jejunum or upper ileum, a smaller rise in BUN was seen. And after colonic administration, no increase in BUN was seen.
💡This supports the notion that there is something special about UPPER gastrointestinal bleeding.
link.springer.com
When blood was administered to the jejunum or upper ileum, a smaller rise in BUN was seen. And after colonic administration, no increase in BUN was seen.
💡This supports the notion that there is something special about UPPER gastrointestinal bleeding.
link.springer.com
@AdamRodmanMD @WilliamAird4 9/
⚡️Interim Summary⚡️
These early studies demonstrate that:
☞Placing blood in the upper GI tract increases BUN; placement in the colon has no affect (tweet 8)
☞Bleeding itself is NOT required (tweet 7)
🤔What is mechanism if not volume depletion from hemorrhage?
⚡️Interim Summary⚡️
These early studies demonstrate that:
☞Placing blood in the upper GI tract increases BUN; placement in the colon has no affect (tweet 8)
☞Bleeding itself is NOT required (tweet 7)
🤔What is mechanism if not volume depletion from hemorrhage?
@AdamRodmanMD @WilliamAird4 10/
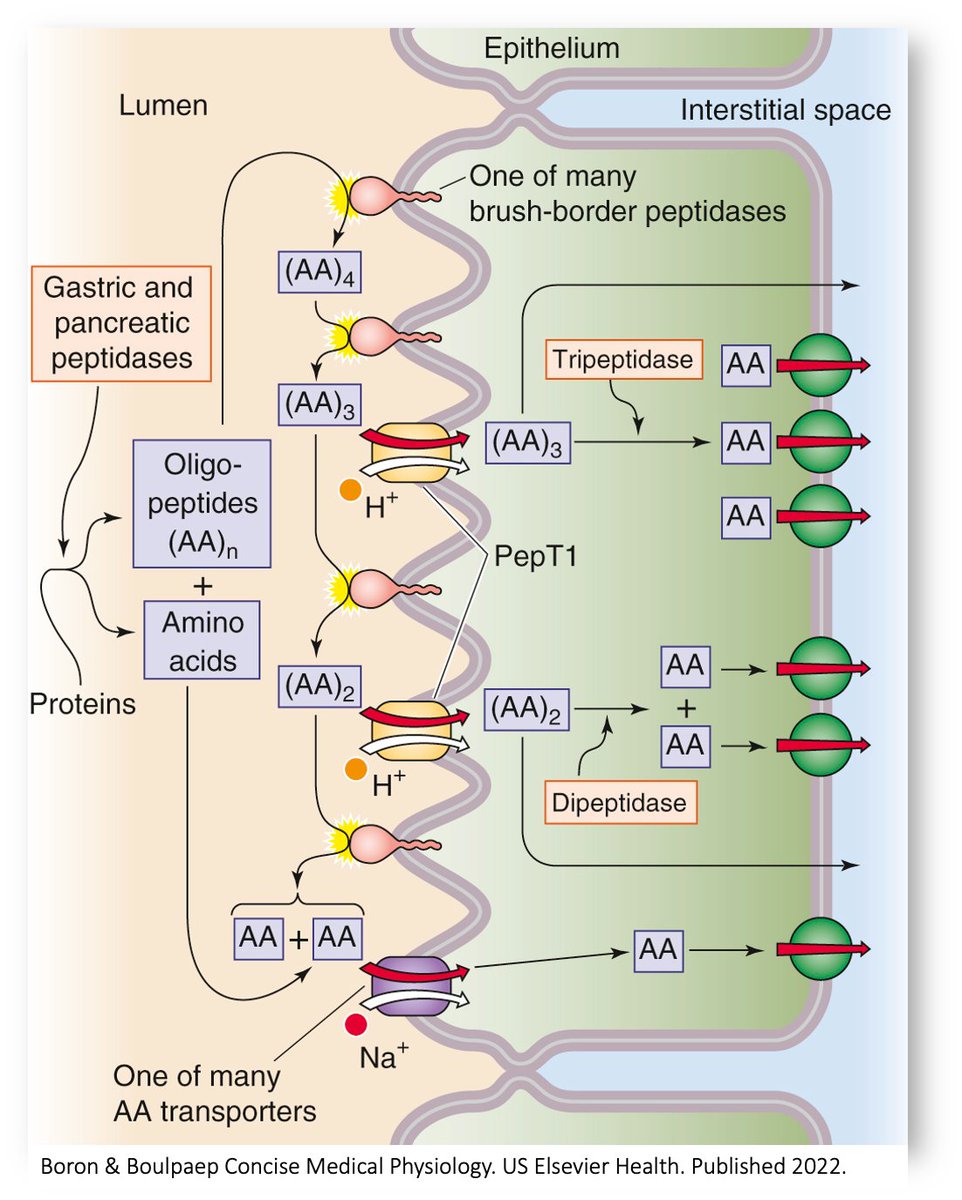
Understanding the full mechanism requires a brief review of protein metabolism.
Ingested proteins are degraded to amino acids which are transported into proximal small intestine enterocytes and then into the blood.
Understanding the full mechanism requires a brief review of protein metabolism.
Ingested proteins are degraded to amino acids which are transported into proximal small intestine enterocytes and then into the blood.
@AdamRodmanMD @WilliamAird4 11/
This helps explain why UPPER gastrointestinal bleeding leads to a rise in BUN.
💡Bleeding at these sites allows for amino acid absorption by the proximal small bowel. Colonic bleeds bypass this site of absoprtion.
What blood protein provides the main source of amino acids?
This helps explain why UPPER gastrointestinal bleeding leads to a rise in BUN.
💡Bleeding at these sites allows for amino acid absorption by the proximal small bowel. Colonic bleeds bypass this site of absoprtion.
What blood protein provides the main source of amino acids?
@AdamRodmanMD @WilliamAird4 12/
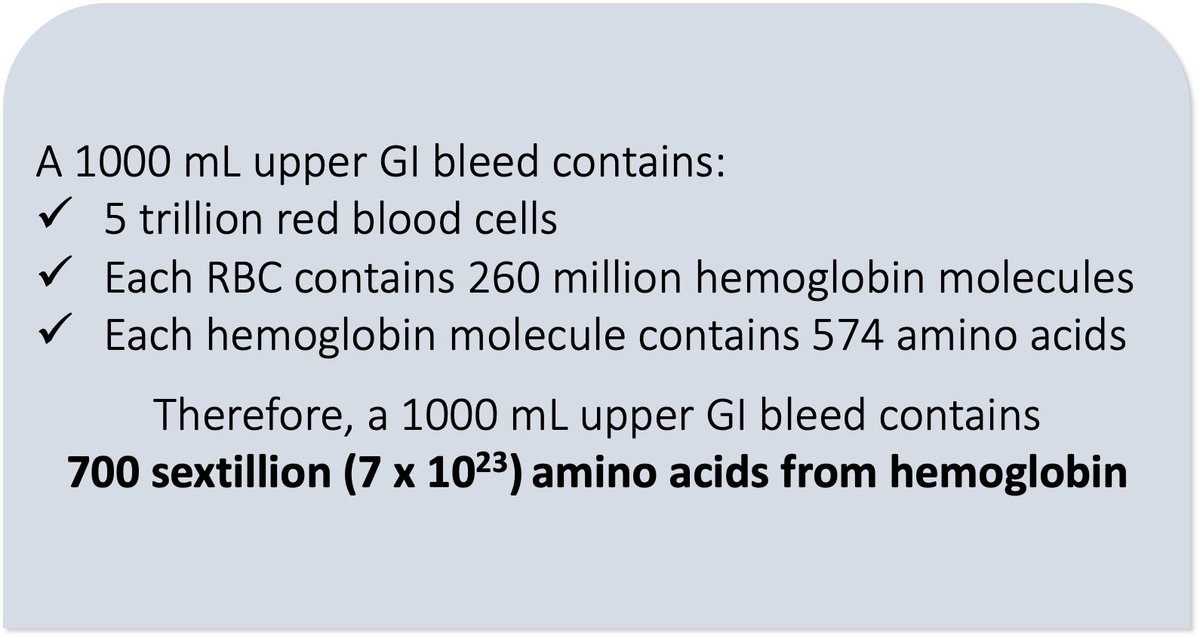
The most plentiful protein in the blood, and therefore the greatest source of amino acids in upper GI bleeding, is hemoglobin.
Assuming a hemoglobin of 15 g/dL, a 1 liter GI bleed contains...
💥7²³ (700 sextillion) amino acids!
The most plentiful protein in the blood, and therefore the greatest source of amino acids in upper GI bleeding, is hemoglobin.
Assuming a hemoglobin of 15 g/dL, a 1 liter GI bleed contains...
💥7²³ (700 sextillion) amino acids!
@AdamRodmanMD @WilliamAird4 13/
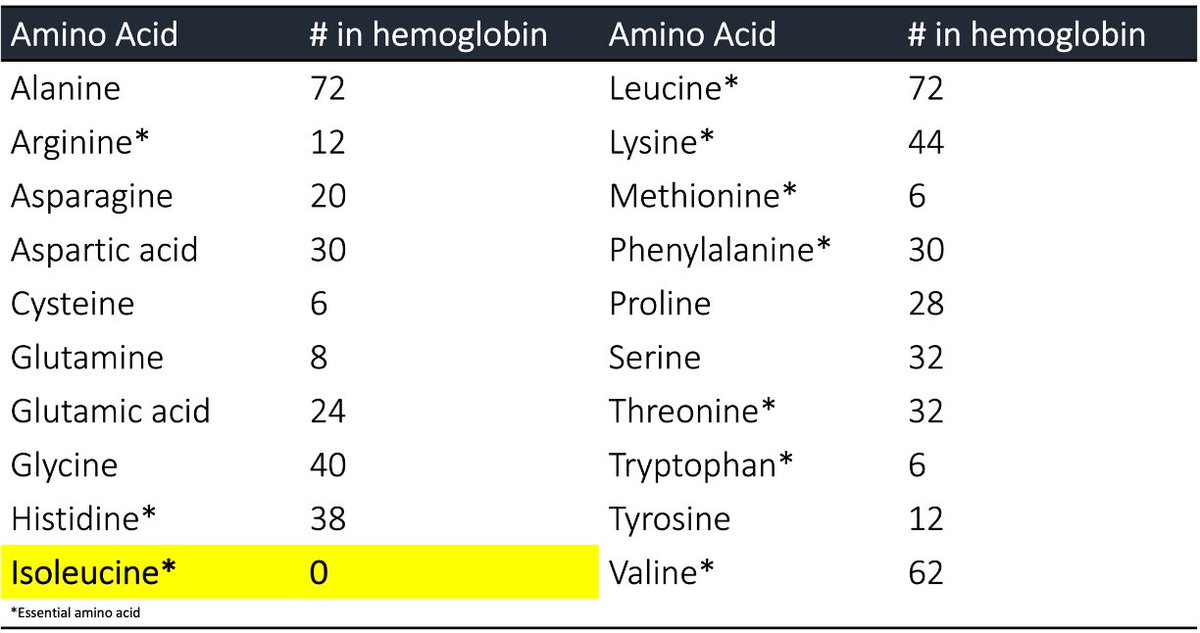
Here's the key. Among hemoglobin's...
700,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 amino acids...
...0 are isoleucine moieties!
Some have argued that this results in an inability for the body to use metabolized hemoglobin to make other proteins, as most will require isoleucine.
Here's the key. Among hemoglobin's...
700,000,000,000,000,000,000,000 amino acids...
...0 are isoleucine moieties!
Some have argued that this results in an inability for the body to use metabolized hemoglobin to make other proteins, as most will require isoleucine.
@AdamRodmanMD @WilliamAird4 14/
Stated another way, hemoglobin is an example of a protein with low biologic value.
Proteins lacking an essential amino acid have low biological value, meaning that a paucity of absorbed amino acids are incorporated into other proteins.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Stated another way, hemoglobin is an example of a protein with low biologic value.
Proteins lacking an essential amino acid have low biological value, meaning that a paucity of absorbed amino acids are incorporated into other proteins.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
@AdamRodmanMD @WilliamAird4 15/
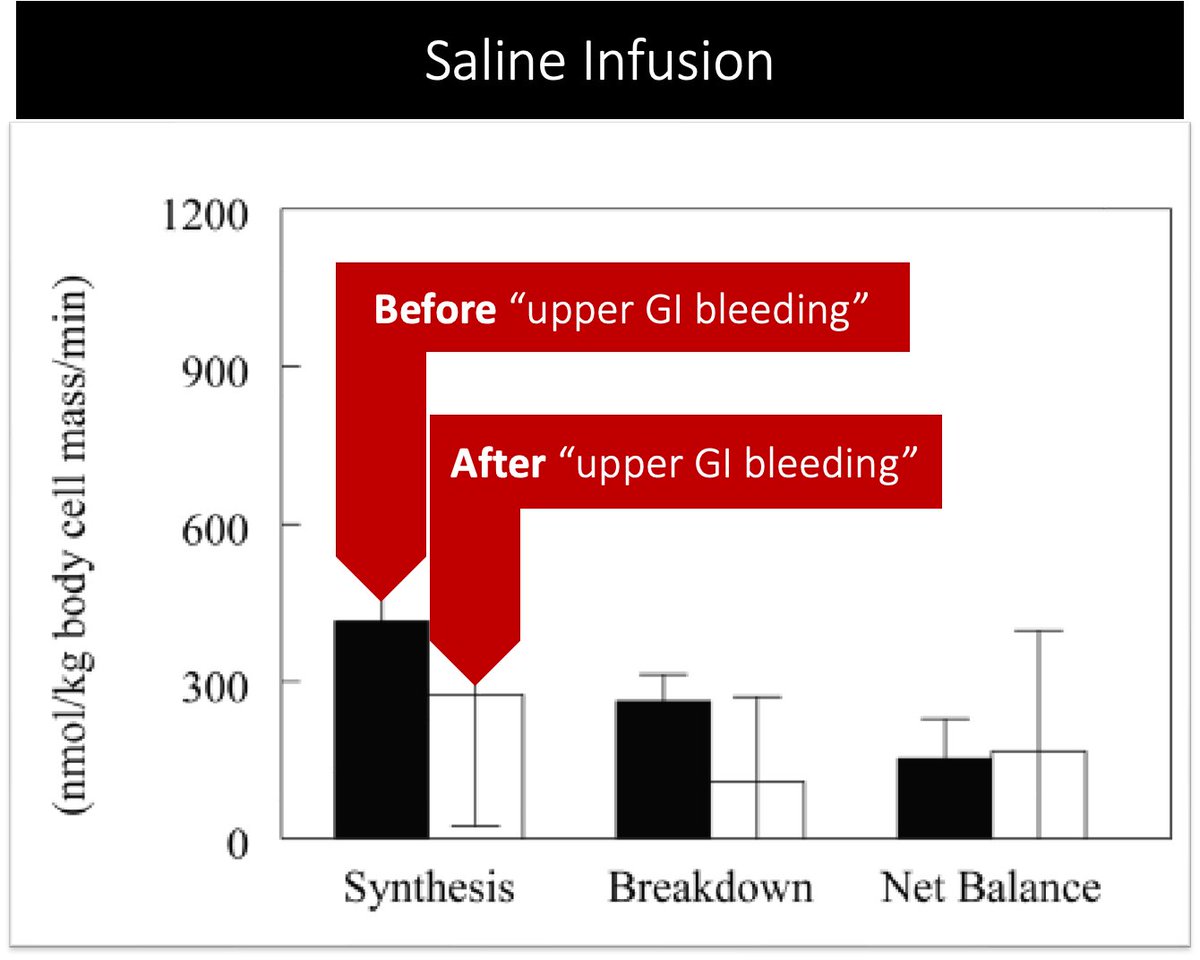
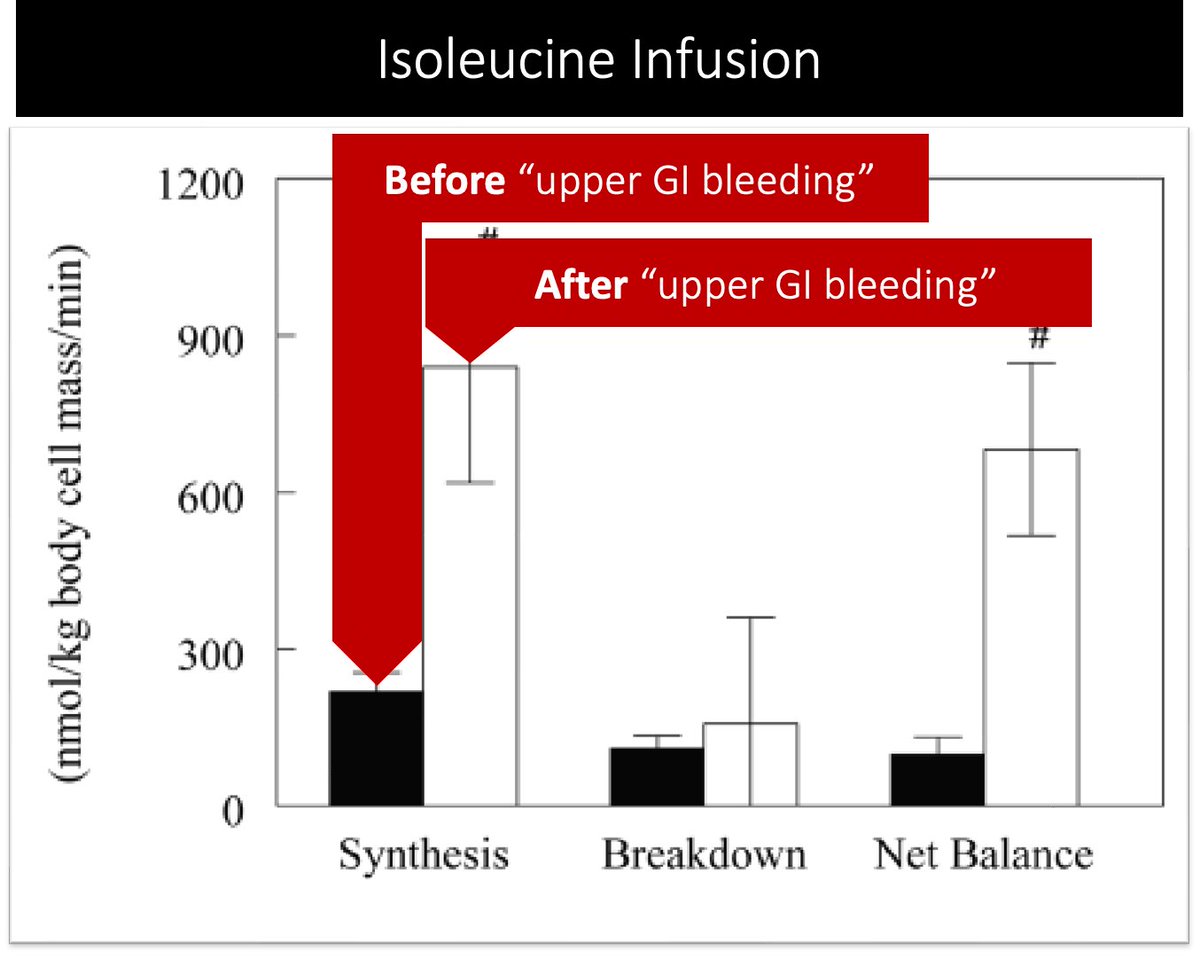
This means that hemoglobin is more likely to generate urea.
There is even data showing that protein synthesis DECREASES after a simulated GI bleed. And even cooler, you can mitigate the reduction in protein synthesis if you infuse isoleucine.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
This means that hemoglobin is more likely to generate urea.
There is even data showing that protein synthesis DECREASES after a simulated GI bleed. And even cooler, you can mitigate the reduction in protein synthesis if you infuse isoleucine.
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
@AdamRodmanMD @WilliamAird4 16/
The above shows that BUN increases in upper GI bleeding and that absorption of the isoleucine pour hemoglobin contributes.
Because creatinine is generated exclusively from the metabolism of muscle protein, ingestion of blood protein has no effect.
The above shows that BUN increases in upper GI bleeding and that absorption of the isoleucine pour hemoglobin contributes.
Because creatinine is generated exclusively from the metabolism of muscle protein, ingestion of blood protein has no effect.
@AdamRodmanMD @WilliamAird4 17/
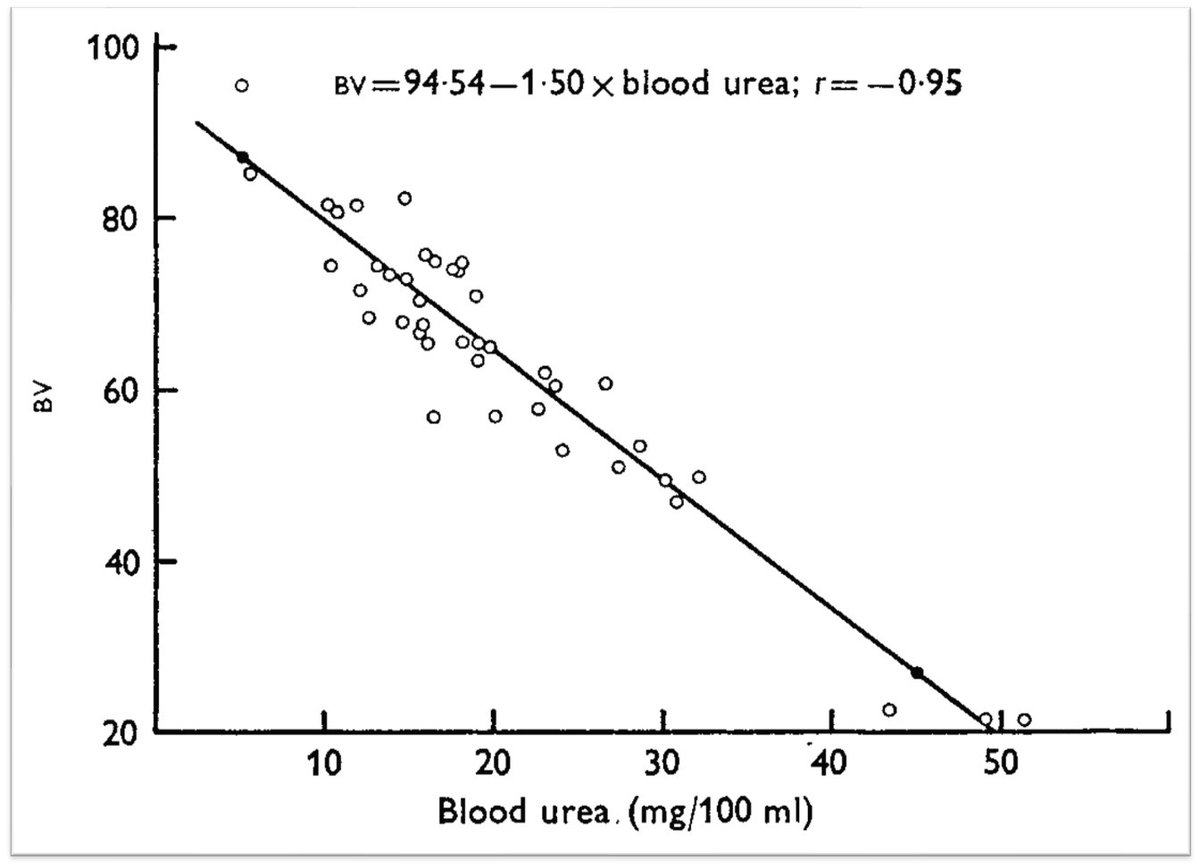
So you see a rise in BUN without a concomitant rise in creatinine.
Thus the rise in the BUN/Cr ratio!
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
So you see a rise in BUN without a concomitant rise in creatinine.
Thus the rise in the BUN/Cr ratio!
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
@AdamRodmanMD @WilliamAird4 18/18
💥In upper GI bleeding, hemoglobin's amino acids are absorbed and metabolized to urea
💥Because hemoglobin lacks isoleucine, a net catabolic state occurs in upper GI bleeding
💥Because creatinine is not similarly affected, the BUN/Cr rises
💥In upper GI bleeding, hemoglobin's amino acids are absorbed and metabolized to urea
💥Because hemoglobin lacks isoleucine, a net catabolic state occurs in upper GI bleeding
💥Because creatinine is not similarly affected, the BUN/Cr rises
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...