To fully understand Flexbox, make sure to read Part 1 if you haven't already.
Recap: In Part 1, we covered the introduction to Flexbox, including its main entities, the `flex-container`, and `flex-item`, as well as the display property. We also discussed the flex-direction property.
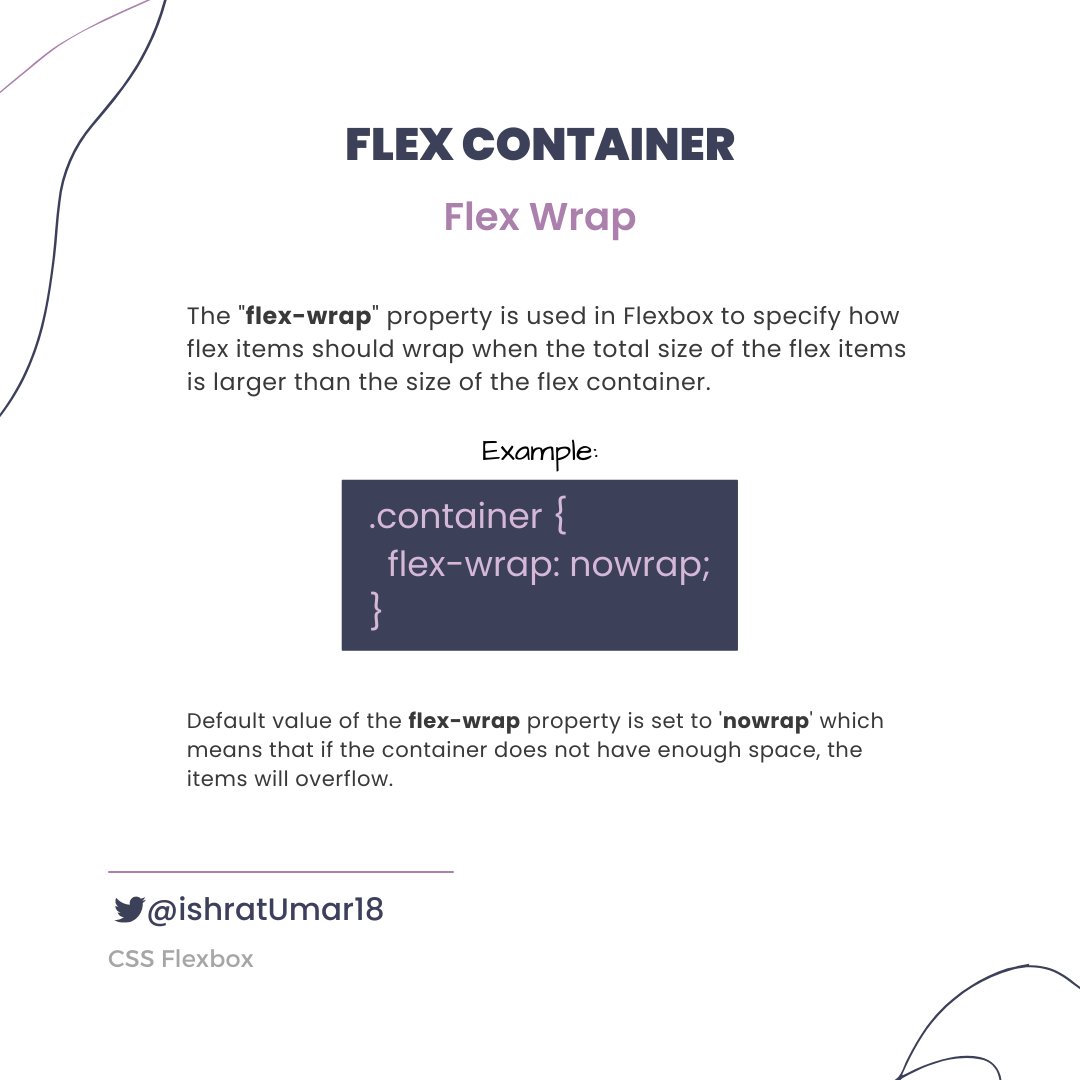
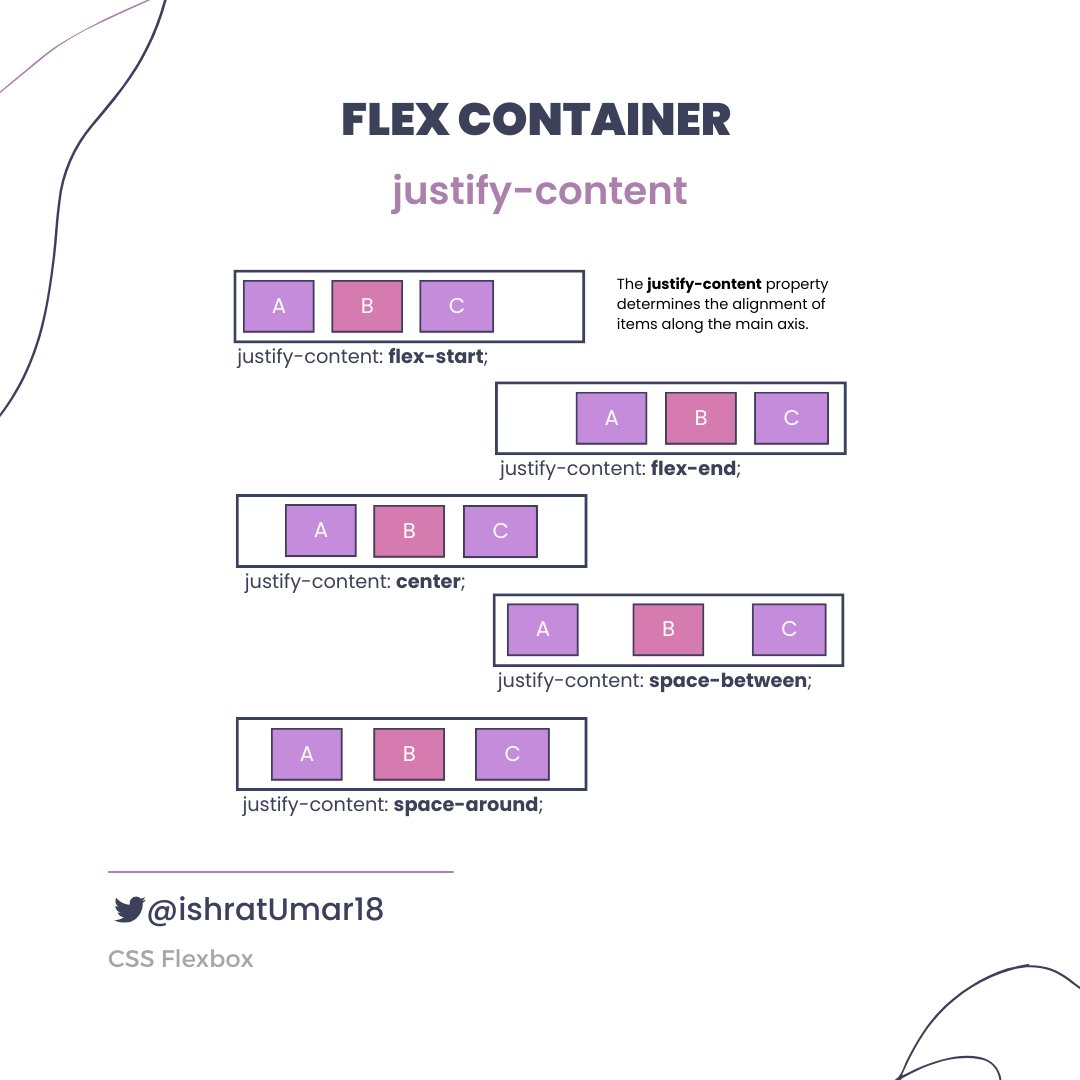
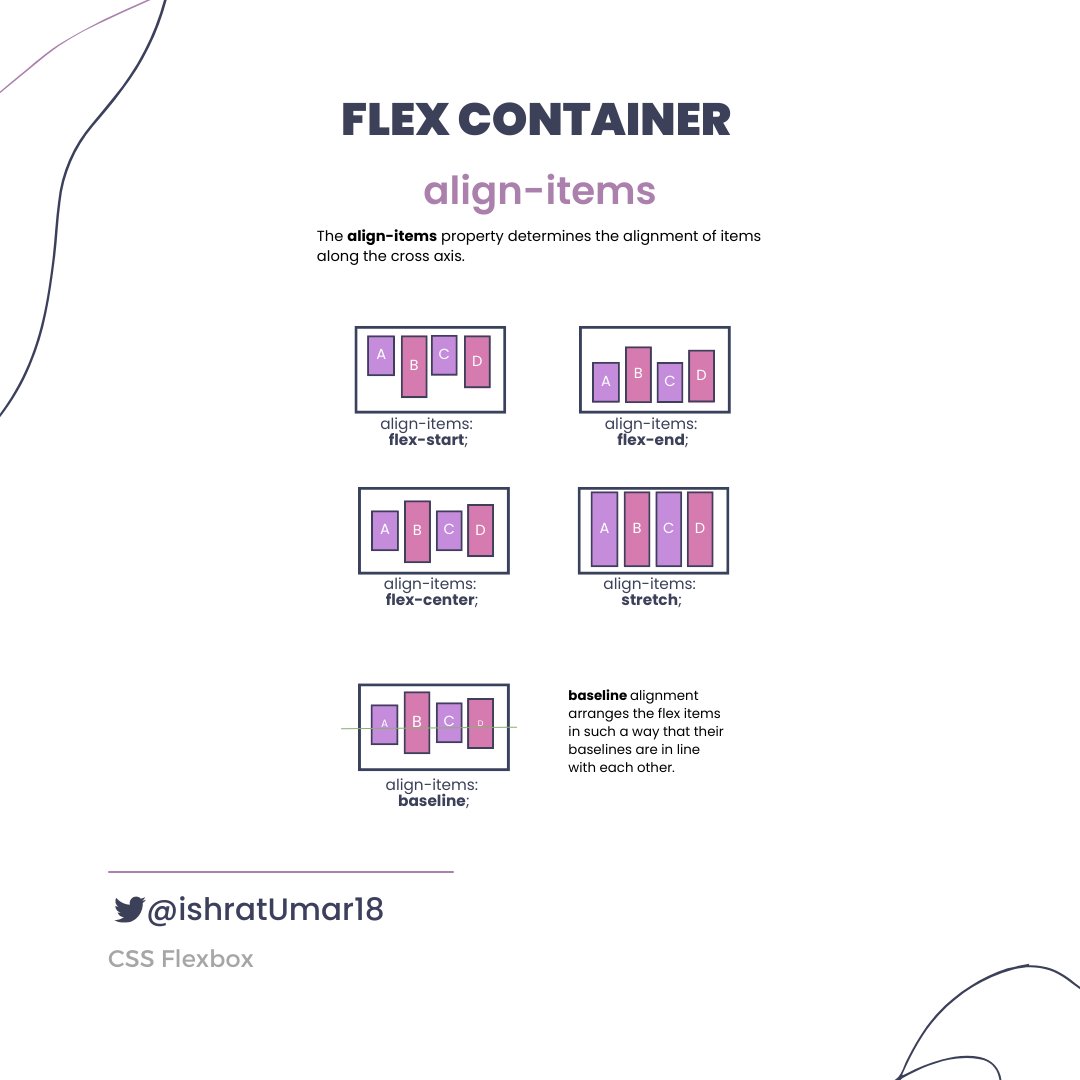
Next, we will learn about advanced Flexbox topics such as flex-wrap, align-items, justify-content, and responsive design.
That's a wrap. Thank you so much for reading!
If you found it helpful, like and retweet the first tweet and follow @ishratUmar18 for more awesome content.
If you found it helpful, like and retweet the first tweet and follow @ishratUmar18 for more awesome content.
Loading suggestions...