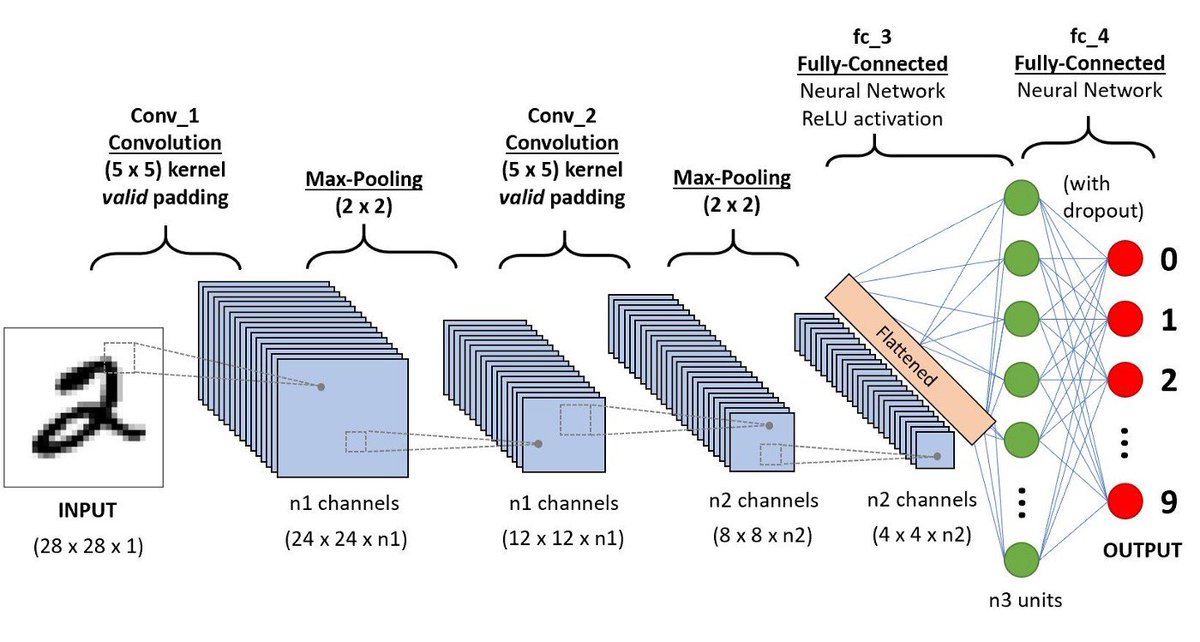
CNNs are composed of multiple layers, each of which performs a specific function. The first layer, known as the input layer, receives the raw data.
The next layer, known as the convolutional layer, applies a set of filters to the data. These filters extract features from the data, such as edges, corners, and shapes.
The output of the convolutional layer is then passed through a non-linear activation function, which introduces non-linearity to the model.
The next layer, known as the pooling layer, reduces the dimensionality of the data by applying a down-sampling operation. This helps to reduce the computational complexity of the model.
The final layer, known as the fully-connected layer, maps the output of the pooling layer to the desired output. This layer is responsible for making the final prediction.
CNNs have been highly successful in a wide range of tasks, including image classification, object detection, and facial recognition. They have also been applied to other areas, such as natural language processing and speech recognition.
CNNs have become the go-to choice for many tasks due to their ability to learn features automatically and their strong performance on a wide range of tasks.
Loading suggestions...