In 2021, Polygon brought together multiple teams to build the holy grail of ZK technology - @0xPolygonZK
One year later, that dream seems to be coming true as their solution marches towards a mainnet launch
Everything you need to know 🧵
One year later, that dream seems to be coming true as their solution marches towards a mainnet launch
Everything you need to know 🧵
@0xPolygonZK is a zkEVM solution being designed to scale the Ethereum blockchain
Specifically, zkEVMs are general-purpose virtual computers that replicate the Ethereum environment in a zk rollup
Specifically, zkEVMs are general-purpose virtual computers that replicate the Ethereum environment in a zk rollup
Depending on how closely they are able to replicate the Ethereum environment, there are various types of zkEVMs
Polygon is building towards a type-2 zkEVM
Polygon is building towards a type-2 zkEVM
Type-2 means that devs can copy-paste their Ethereum apps, codes, dev tools, etc. to the Polygon zkEVM without making any changes
Users can then use these apps at extremely low tx costs & much faster speeds
All while inheriting near proximal security to Ethereum's L1
Users can then use these apps at extremely low tx costs & much faster speeds
All while inheriting near proximal security to Ethereum's L1
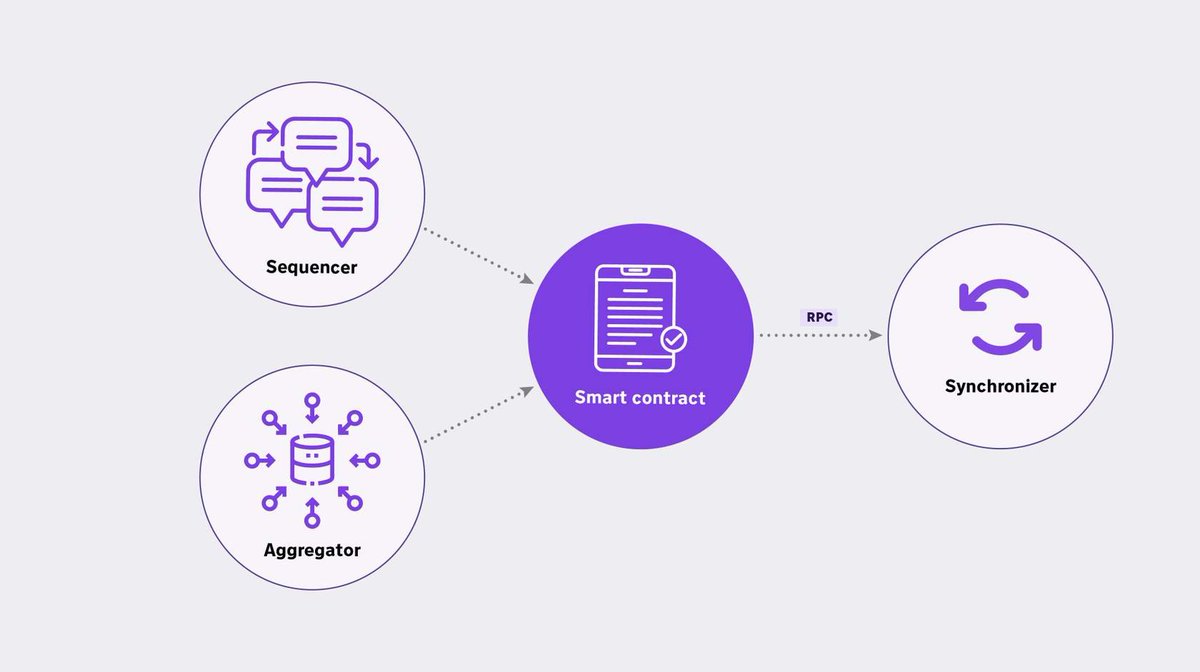
The zkEVM batches all the tx data & state changes and sends it to the L1, along with proof of the validity of these txs
Anyone can sign up to create these batches (sequencers) & proofs (aggregators) in a permissionless way
Anyone can sign up to create these batches (sequencers) & proofs (aggregators) in a permissionless way
To decide the next batch/proof creator, Polygon uses a Proof-of-Efficiency consensus model
PoE ensures that the network is:
• permissionless,
• decentralized,
• secure, and
• efficient, with verifiable block data
PoE ensures that the network is:
• permissionless,
• decentralized,
• secure, and
• efficient, with verifiable block data
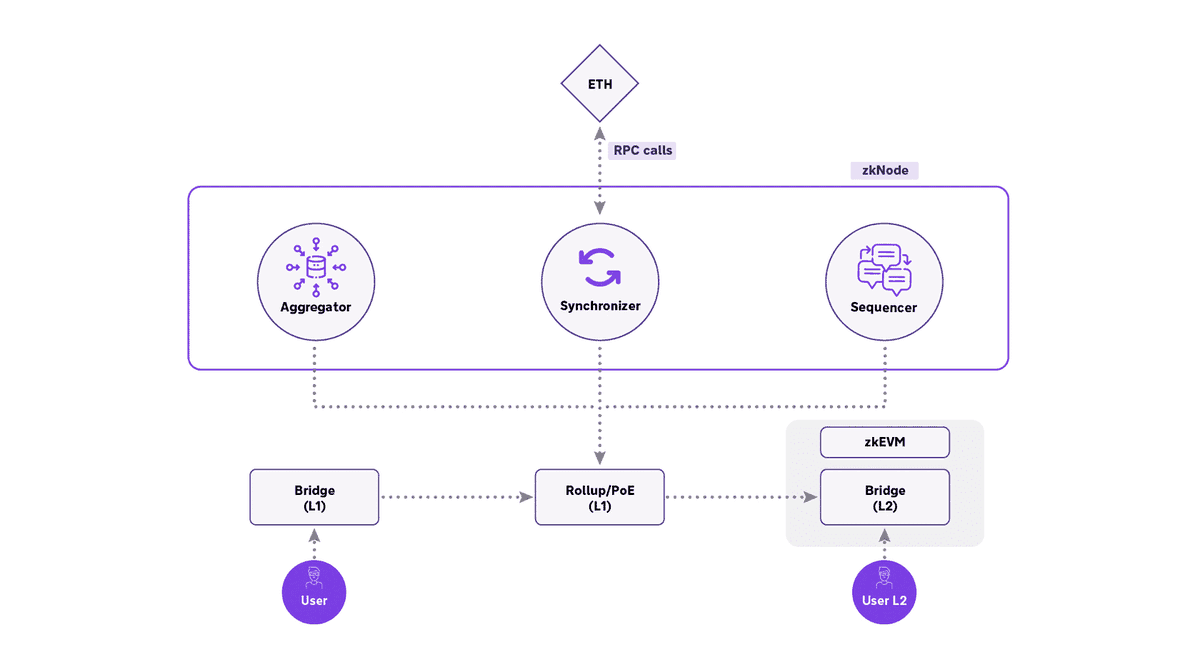
Other than the PoE consensus mechanism, there are 4 major components of the Polygon zkEVM architecture:
• zkNode
• zkProver
• LX-to-LY bridge
• Active users of the zkEVM network who create transactions
• zkNode
• zkProver
• LX-to-LY bridge
• Active users of the zkEVM network who create transactions
• zkNode
zkNode is the software needed to run a zkEVM node
Anyone can participate in the zkEVM network by running a zkEVM node in one of the 3 ways:
- Node: Know/verify the state of the network
- Sequencers: Create batches
- Aggregators: Create validity proofs
zkNode is the software needed to run a zkEVM node
Anyone can participate in the zkEVM network by running a zkEVM node in one of the 3 ways:
- Node: Know/verify the state of the network
- Sequencers: Create batches
- Aggregators: Create validity proofs
• zkProver
To create the validity proofs, Aggregators use a zero-knowledge Prover
The prover uses 2 specially developed languages:
- zero-knowledge Assembly language (or zkASM)
- Polynomial Identity Language (or PIL)
Why do we need these languages?
To create the validity proofs, Aggregators use a zero-knowledge Prover
The prover uses 2 specially developed languages:
- zero-knowledge Assembly language (or zkASM)
- Polynomial Identity Language (or PIL)
Why do we need these languages?
The basic purpose of these languages is to make the tx data machine-readable
Machines can't understand words, so the data needs to be converted to 0s & 1s
This is done with the help of the two languages
Machines can't understand words, so the data needs to be converted to 0s & 1s
This is done with the help of the two languages
• LX-to-LY bridge
Just like any other bridge, the zkEVM bridge helps users transfer assets from Ethereum L1 to the zkEVM L2
The Polygon zkEVM Bridge is more flexible and allows bridging between any two arbitrary L2 chains as well
Just like any other bridge, the zkEVM bridge helps users transfer assets from Ethereum L1 to the zkEVM L2
The Polygon zkEVM Bridge is more flexible and allows bridging between any two arbitrary L2 chains as well
Characteristic of the fantastic work of the Polygon BD team, the zkEVM effort has been put together by acquiring multiple teams:
- @0xPolygonZK (previously Hermez)
- @0xPolygonZero
- @0xPolygonMiden
@MihailoBjelic explained why this strategy makes sense:
- @0xPolygonZK (previously Hermez)
- @0xPolygonZero
- @0xPolygonMiden
@MihailoBjelic explained why this strategy makes sense:
The development of zkEVM is a massive step forward toward Ethereum's end-state
I will be watching Polygon's solution closely as they build toward the mainnet launch
Exciting times ahead!
You can try the testnet here:
public.zkevm-test.net
I will be watching Polygon's solution closely as they build toward the mainnet launch
Exciting times ahead!
You can try the testnet here:
public.zkevm-test.net
I hope you enjoyed reading this
Follow me @ShivanshuMadan for more learning and alpha!
Retweet the first tweet (linked below) to spread the word:
Follow me @ShivanshuMadan for more learning and alpha!
Retweet the first tweet (linked below) to spread the word:
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...