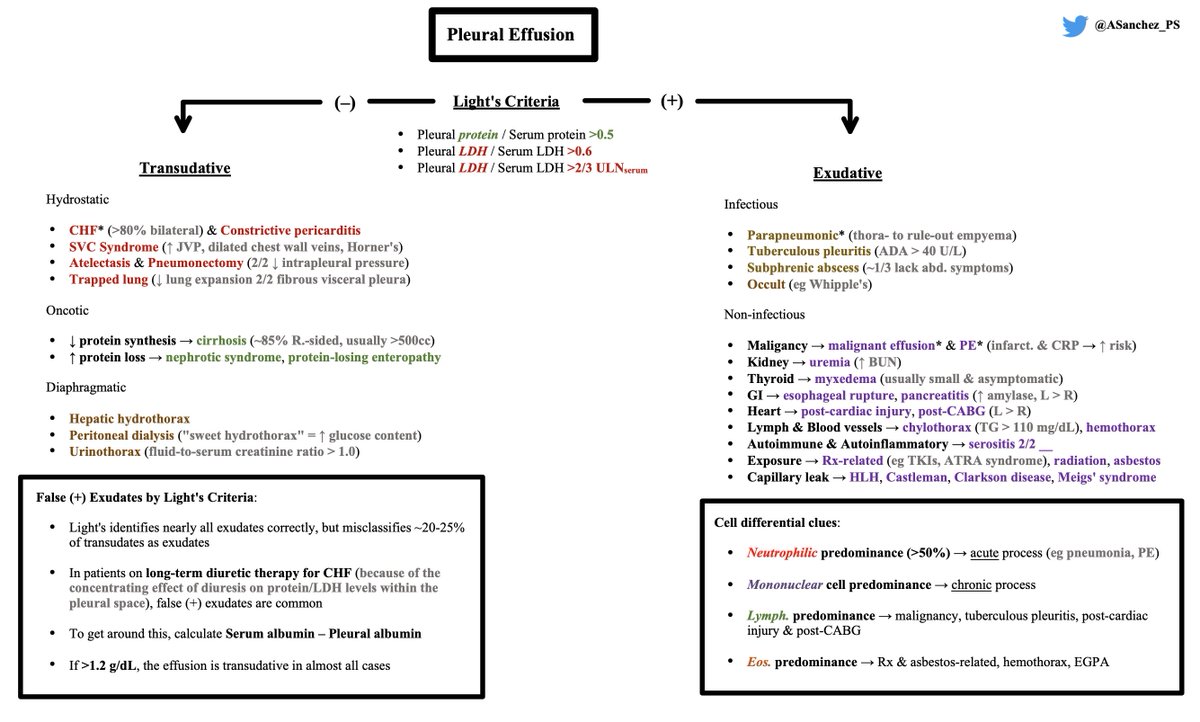
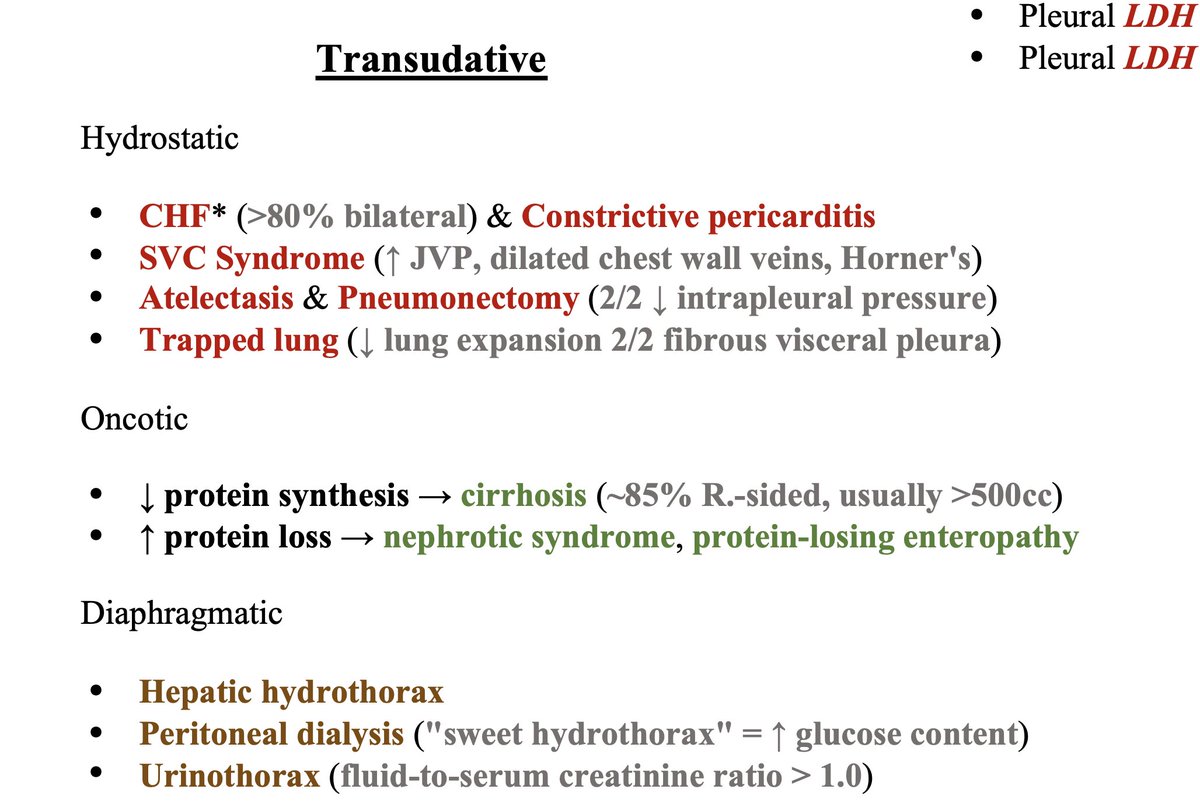
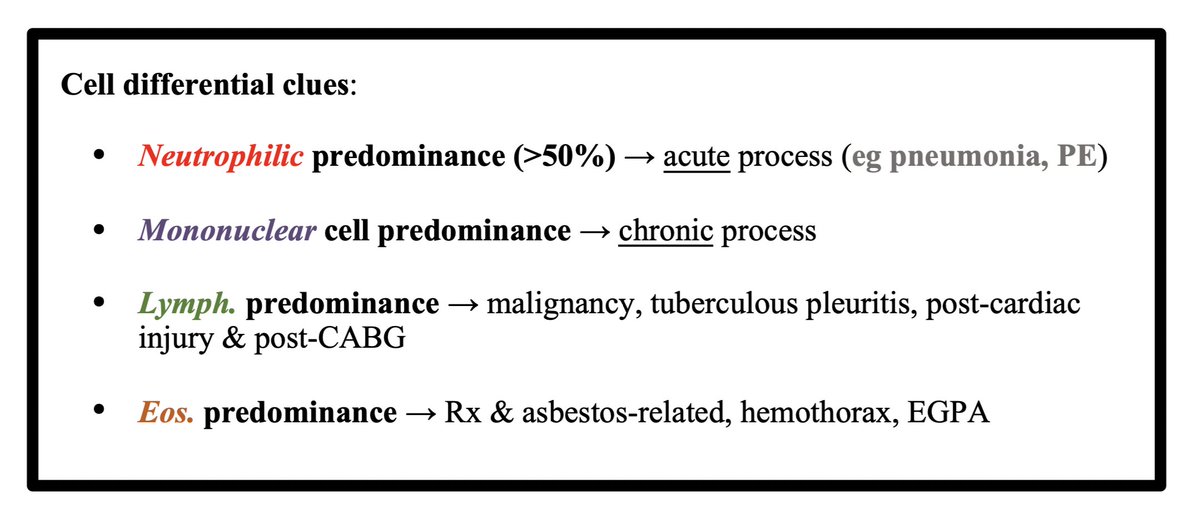
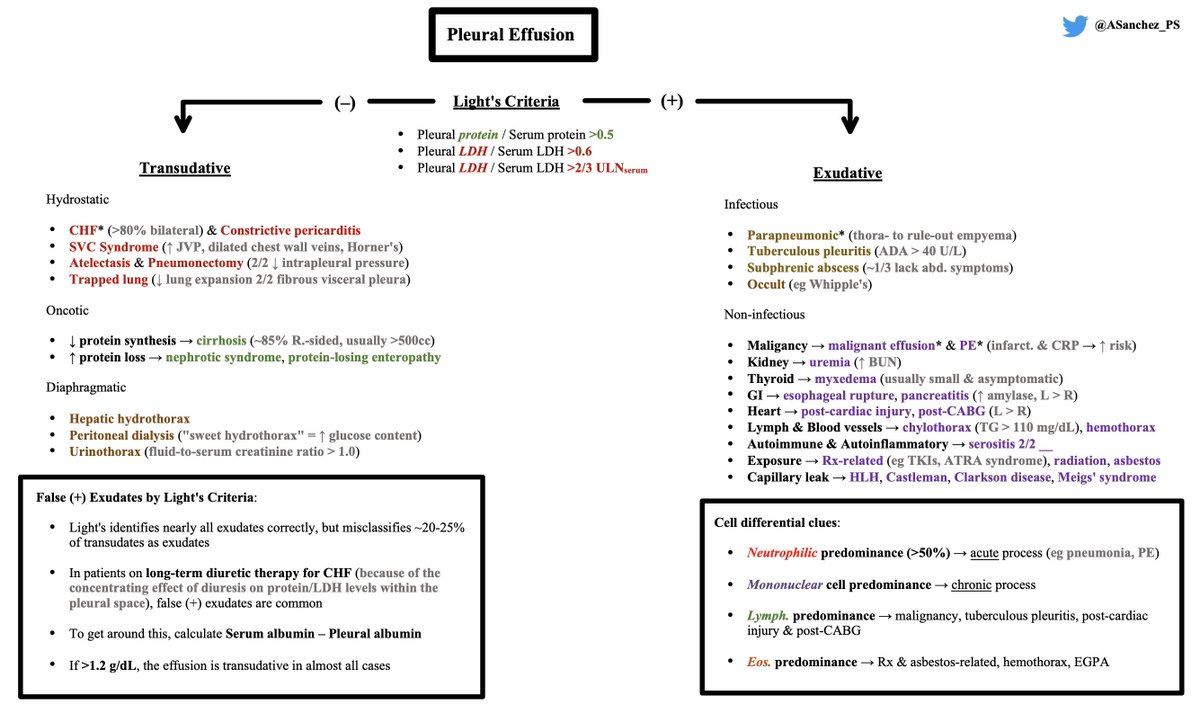
Exudative effusions = infectious vs. non-infectious
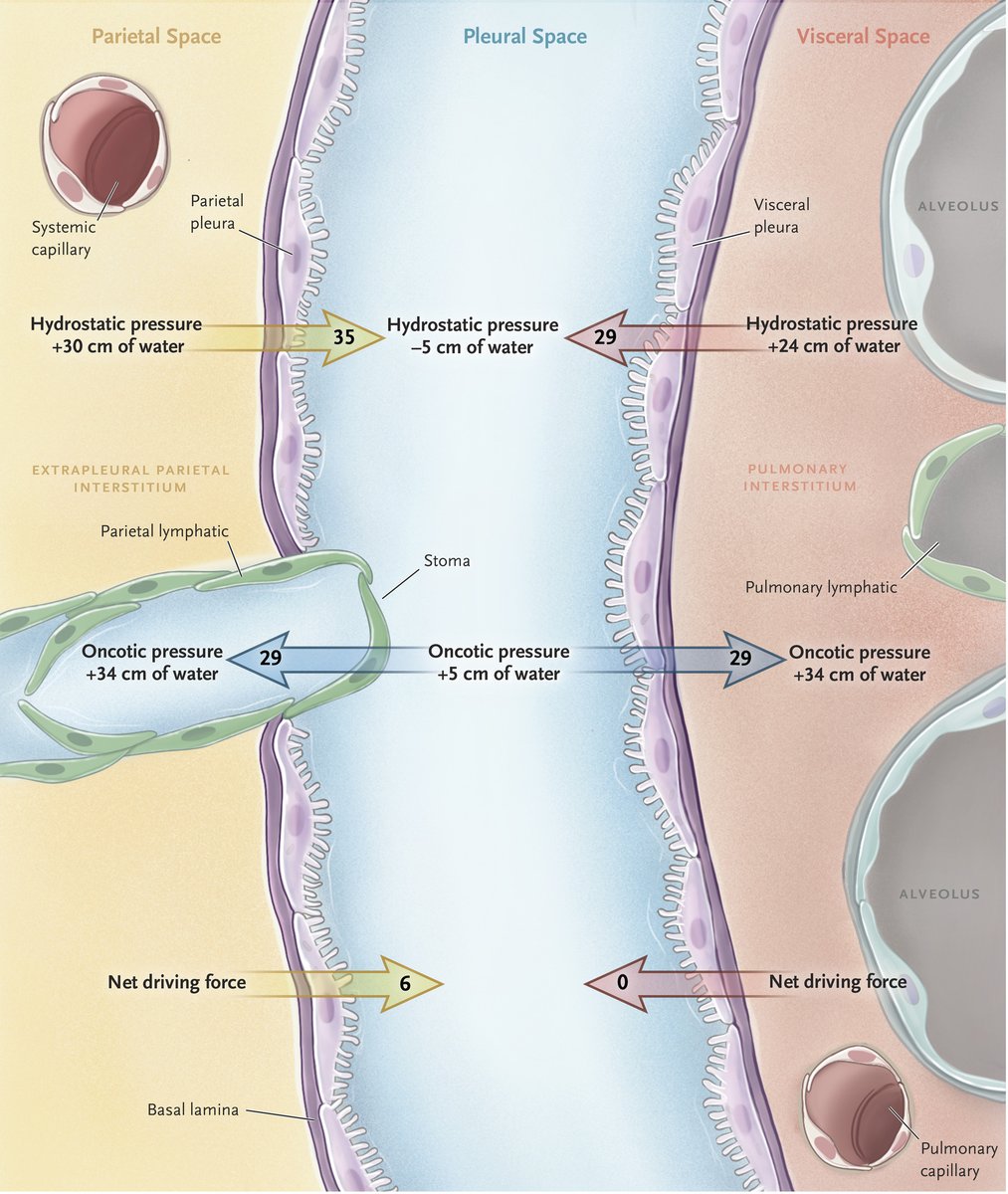
- Mechanism #1: ↑ capillary permeability
- Mechanism #2: Lymphatic obstruction
- Mechanism #1: ↑ capillary permeability
- Mechanism #2: Lymphatic obstruction
Infectious exudates:
🦠 If pneumonia, must perform thora- to rule-out complicated parapneumonic effusion. The following findings can be seen:
- Frank pus
- (+) Gram stain/culture
- pH < 7.2
- Glucose < 60 mg/dL
- Loculated, thick parietal pleura
🦠 If pneumonia, must perform thora- to rule-out complicated parapneumonic effusion. The following findings can be seen:
- Frank pus
- (+) Gram stain/culture
- pH < 7.2
- Glucose < 60 mg/dL
- Loculated, thick parietal pleura
References:
1) @AndreMansoor (Whose pleural effusion DDx is available in the book Frameworks for IM. This schema is heavily adapted from that DDx.)
2) nejm.org
3) #c8" target="_blank" rel="noopener" onclick="event.stopPropagation()">emedicine.medscape.com
4) sciencedirect.com
1) @AndreMansoor (Whose pleural effusion DDx is available in the book Frameworks for IM. This schema is heavily adapted from that DDx.)
2) nejm.org
3) #c8" target="_blank" rel="noopener" onclick="event.stopPropagation()">emedicine.medscape.com
4) sciencedirect.com
Awesome summary of helpful fluid results:
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...