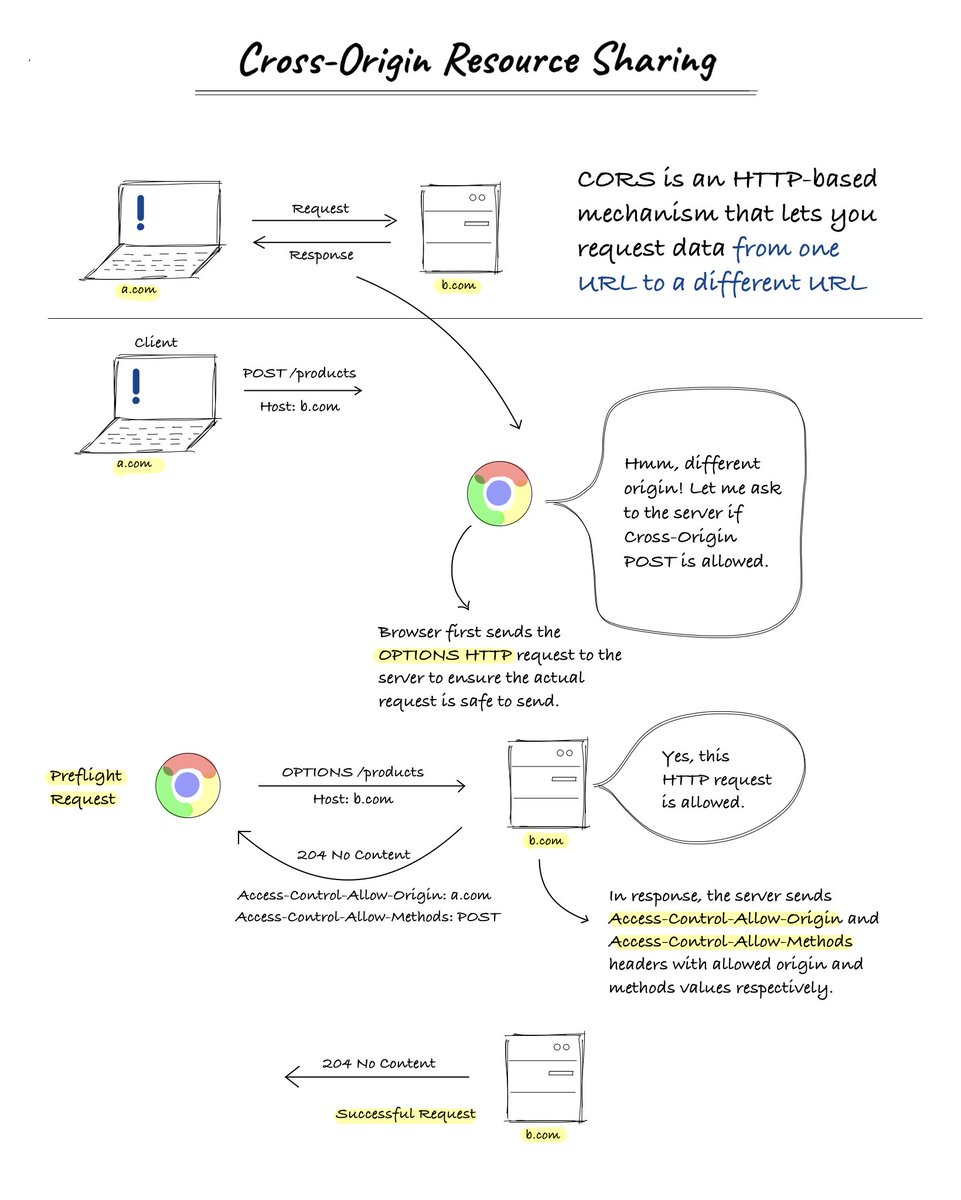
25 API-related terms every web developer should be aware of 🧵:
1. Endpoint
An endpoint is nothing but the location(URL) where the actual resource is present.
An endpoint is nothing but the location(URL) where the actual resource is present.
2. Origin Server
The origin server is the actual server that contains the data and servers on the client's request.
There may or may not be other intermediate servers included in the path.
The origin server is the actual server that contains the data and servers on the client's request.
There may or may not be other intermediate servers included in the path.
3. Proxy Server
Servers have the ability to further pass your request to the other server.
These types of intermediate servers are known as proxy servers.
Servers have the ability to further pass your request to the other server.
These types of intermediate servers are known as proxy servers.
4. DNS Server
DNS stands for Domain Name System.
As computer devices are interacted using IP addresses, the DNS server provides the IP address of the requested URL.
DNS stands for Domain Name System.
As computer devices are interacted using IP addresses, the DNS server provides the IP address of the requested URL.
5. API key
An API key is a unique code for every user which lets you call an API.
The length of an API key could be anything.
The only rule is that these keys must be unique and not easy to guess.
Generally, API keys contain lower case and upper case letters with numbers.
An API key is a unique code for every user which lets you call an API.
The length of an API key could be anything.
The only rule is that these keys must be unique and not easy to guess.
Generally, API keys contain lower case and upper case letters with numbers.
6. API Token
The API token is a unique identifier of an application requesting access to your API.
An API token is a form of authentication similar to a username/password.
The API token is a unique identifier of an application requesting access to your API.
An API token is a form of authentication similar to a username/password.
7. Access token
An access token is used for authentication.
Applications use an access token to authenticate themselves so that they can make an API call.
An access token is used for authentication.
Applications use an access token to authenticate themselves so that they can make an API call.
8. SDK
SDK stands for Software Development Kit.
It is a set of development tools that allows the creation of software or an application for a particular platform.
SDK provides you with the whole package from compilers to debuggers to even a software development framework.
SDK stands for Software Development Kit.
It is a set of development tools that allows the creation of software or an application for a particular platform.
SDK provides you with the whole package from compilers to debuggers to even a software development framework.
9. RPC
Remote Procedure Call (RPC) is the oldest client-server communication method in use today. Instead of the traditional HTTP call, RPC uses a function call.
It means that on the client-side, you invoke a function that is written on the server-side code.
Remote Procedure Call (RPC) is the oldest client-server communication method in use today. Instead of the traditional HTTP call, RPC uses a function call.
It means that on the client-side, you invoke a function that is written on the server-side code.
11. Async API
AsyncAPI is an open-source project aimed at improving the current state of Event-Driven Architecture.
These APIs allow relatively time-consuming requests to be processed in the background while other requests are made.
AsyncAPI is an open-source project aimed at improving the current state of Event-Driven Architecture.
These APIs allow relatively time-consuming requests to be processed in the background while other requests are made.
12. Internal API
Internal API, also known as Private API is only accessible to the developers within an organization.
Internal API, also known as Private API is only accessible to the developers within an organization.
13. API Caching
API Caching is the ability to store copies of frequently accessed data in several places along the request-response path.
API Caching is the ability to store copies of frequently accessed data in several places along the request-response path.
14. External API
External API, also known as Public API is accessible to all the developers outside the enterprise or organization.
External API, also known as Public API is accessible to all the developers outside the enterprise or organization.
15. HTTP cookies
An HTTP cookie is a small piece of data created by the web server inside your browser.
The data inside a cookie has an ID that is unique to you and your computer. This ID helps the server know who the user is to send the data accordingly.
An HTTP cookie is a small piece of data created by the web server inside your browser.
The data inside a cookie has an ID that is unique to you and your computer. This ID helps the server know who the user is to send the data accordingly.
16. Authorization
Authorization always comes after authentication. It is the process of permitting users to access different resources from the server, and it’s not visible and changeable by the user.
Authorization always comes after authentication. It is the process of permitting users to access different resources from the server, and it’s not visible and changeable by the user.
17. Microservices
A microservice is an application design that breaks up a monolithic architecture into small, self-containing services.
A microservice is an application design that breaks up a monolithic architecture into small, self-containing services.
18. OpenAPI spec
It is a format to define structure and syntax for REST APIs. It provides a standard that allows both humans and computers to discover and understand the service's capabilities without access to source code, documentation, or traffic inspection.
It is a format to define structure and syntax for REST APIs. It provides a standard that allows both humans and computers to discover and understand the service's capabilities without access to source code, documentation, or traffic inspection.
19. Composite API
Composite API is a design approach in which we bundle multiple API requests into a single API call.
Composite API is a design approach in which we bundle multiple API requests into a single API call.
20. API Versioning
API versioning is the practice of managing changes in your API.
You should version your API if you are introducing any breaking changes. Clients can still access the old version, and their products will not break as soon as you launch a new release.
API versioning is the practice of managing changes in your API.
You should version your API if you are introducing any breaking changes. Clients can still access the old version, and their products will not break as soon as you launch a new release.
21. Authentication
Authentication and authorization are the two most confusing terms.
Authentication is validating the user to identify if they are who they claim to be.
Authentication and authorization are the two most confusing terms.
Authentication is validating the user to identify if they are who they claim to be.
22. API Lifecycle
API lifecycle is the entire lifespan of any particular API from its planning phase to when it gets stale.
API lifecycle is the entire lifespan of any particular API from its planning phase to when it gets stale.
23. API-first approach
The API-first approach ensures that all the functionality of an application is accessed through APIs.
This approach involves designing every API around a contract written in an API description language. For example, OpenAPI Specification.
The API-first approach ensures that all the functionality of an application is accessed through APIs.
This approach involves designing every API around a contract written in an API description language. For example, OpenAPI Specification.
24. API Gateway
An API gateway is a component or tool of an API management approach.
Gateways are used as the entry point for client requests.
This allows them to facilitate requests, combine results, and handle things like authentication.
An API gateway is a component or tool of an API management approach.
Gateways are used as the entry point for client requests.
This allows them to facilitate requests, combine results, and handle things like authentication.
25. HATEOAS
HATEOAS stands for Hypermedia As The Engine Of Application State.
HATEOAS defines that clients should be provided with hypermedia, in response to a particular request, which help them to use or explore further points of an API.
HATEOAS stands for Hypermedia As The Engine Of Application State.
HATEOAS defines that clients should be provided with hypermedia, in response to a particular request, which help them to use or explore further points of an API.
That's pretty much it for this thread.
Follow @Rapid_API for more exclusive content.
Visit RapidAPI Hub and get access to more than 40,000 APIs.
RapidAPI.com
Follow @Rapid_API for more exclusive content.
Visit RapidAPI Hub and get access to more than 40,000 APIs.
RapidAPI.com
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...