SQL: DELETE, TRUNCATE and DROP commands
🧵👇
🧵👇
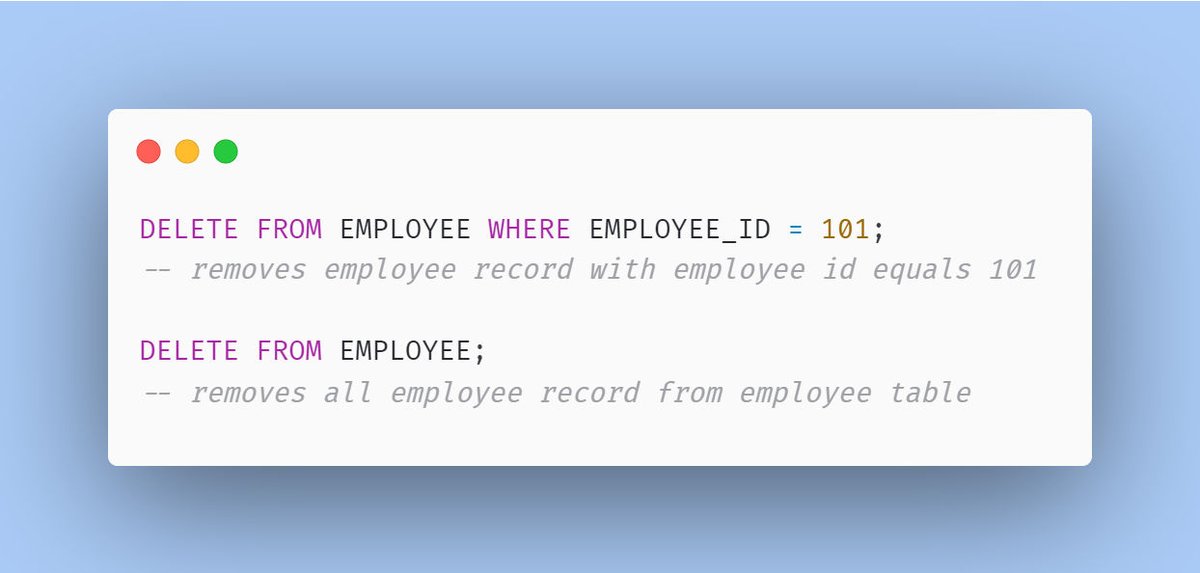
1. DELETE
- It supports the where clause in the query, so conditionally we can remove selected rows from a table.
- When not using the where clause it removes all rows from the table.
- Auto increment values of the primary key start from the previous number.
- It supports the where clause in the query, so conditionally we can remove selected rows from a table.
- When not using the where clause it removes all rows from the table.
- Auto increment values of the primary key start from the previous number.
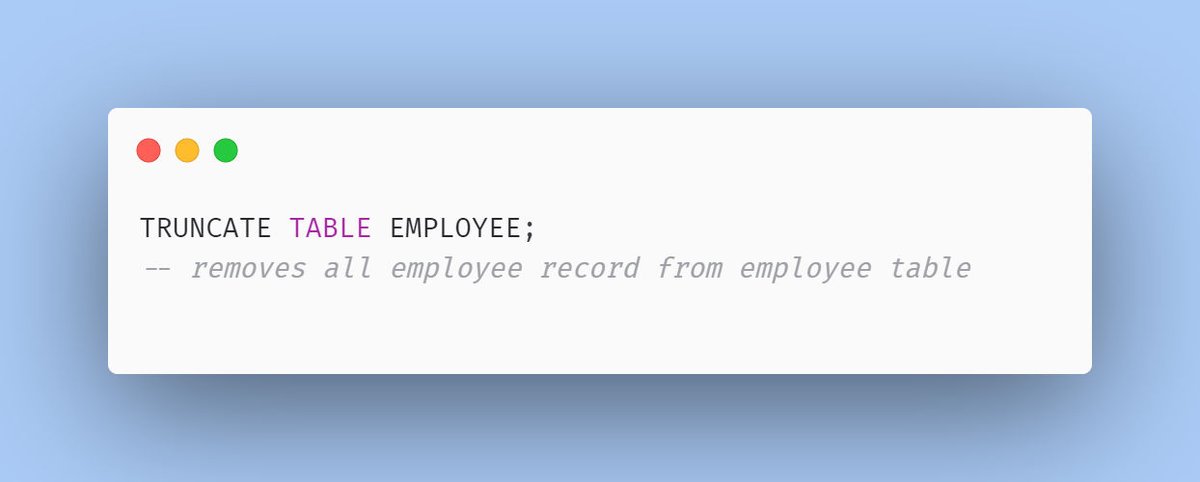
2. TRUNCATE
- In TRUNCATE, we've no option to use the where clause due to which it will remove all the rows from the table.
- After TRUNCATE, if we insert a new record in the table then AUTO INCREMENT primary key values normally start from the beginning.
- In TRUNCATE, we've no option to use the where clause due to which it will remove all the rows from the table.
- After TRUNCATE, if we insert a new record in the table then AUTO INCREMENT primary key values normally start from the beginning.
3. DROP
- The DROP query, removes the whole object in the database.
- It can be used to remove the entire table structure along with its data.
- Similarly, it can be used to remove Stored procedures, Functions, Triggers, Index, Constraints, etc.
- The DROP query, removes the whole object in the database.
- It can be used to remove the entire table structure along with its data.
- Similarly, it can be used to remove Stored procedures, Functions, Triggers, Index, Constraints, etc.
That's a wrap!
If you loved reading this thread, you might enjoy reading my previous thread on SQL:
If you loved reading this thread, you might enjoy reading my previous thread on SQL:
Namaste, I'm Vikas!
Trying to diversify tech twitter with Backend content.
Every Mon, Wed & Fri - I write a thread,
follow @vikasrajputin to read all my future threads.
Trying to diversify tech twitter with Backend content.
Every Mon, Wed & Fri - I write a thread,
follow @vikasrajputin to read all my future threads.
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...