What exactly is a JSON Web Token.
Thread 🧵
Thread 🧵
JSON Web Token (JWT) is a secure way to transmit information between parties as a JSON object.
This information is trustworthy because it is digitally signed.
This information is trustworthy because it is digitally signed.
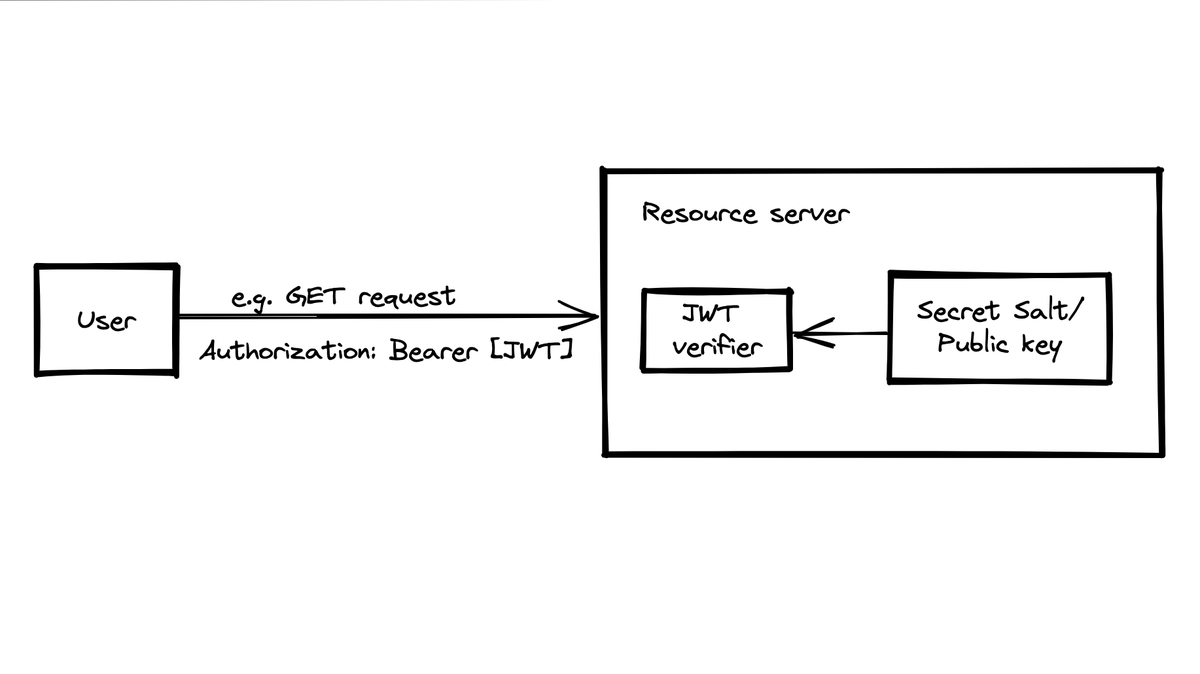
JWTs can be signed using a secret or public key to ensure that only the intended recipient can read the token's contents.
The Header contains the information about the token type and the hash algorithm that was used for signing and encoding.
In our example, you can see we're using an HS256 hash.
In our example, you can see we're using an HS256 hash.
The Payload contains session data we want to send between the client and server.
Standard data:
- Issuer(iss)
- Subject (sub)
- Audience (aud)
- Expiration time (exp) - in unix timestampt format
- Issued at (iat) - in unix timestampt format
Standard data:
- Issuer(iss)
- Subject (sub)
- Audience (aud)
- Expiration time (exp) - in unix timestampt format
- Issued at (iat) - in unix timestampt format
You can also include custom session data into the payload you want to exchange with the server.
In our example, we're sending the role information and user_id.
The additional information you're sending in the payload should be short in size.
In our example, we're sending the role information and user_id.
The additional information you're sending in the payload should be short in size.
Also, keep in mind that payload can be easily decoded so you mustn't be sending any critical or sensitive data.
Signature is the last and most important part of JWT.
Base64url encoding is used to calculate signature by encoding the header and payload and then concatenating them with a period separator.
Base64url encoding is used to calculate signature by encoding the header and payload and then concatenating them with a period separator.
The result is then used as an argument for the cryptographic function defined in the Header of the JWT.
As you can see, if you change either the header or payload, the signature has to be re-calculated.
As you can see, if you change either the header or payload, the signature has to be re-calculated.
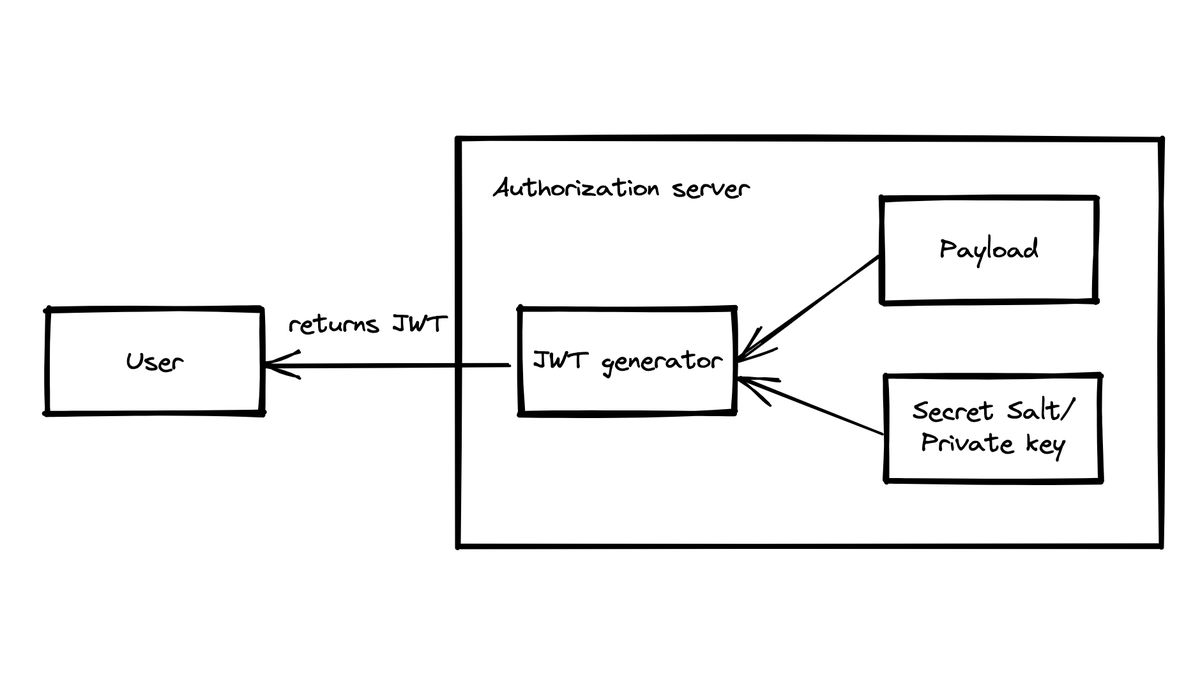
The private key used for calculation is stored on the auth server and is not accessible/visible to third parties.
Let's discuss a bit about how JWT works. 👇🏻
The JWT is usually stored on the client in the session data.
For this, cookies or databases can be used.
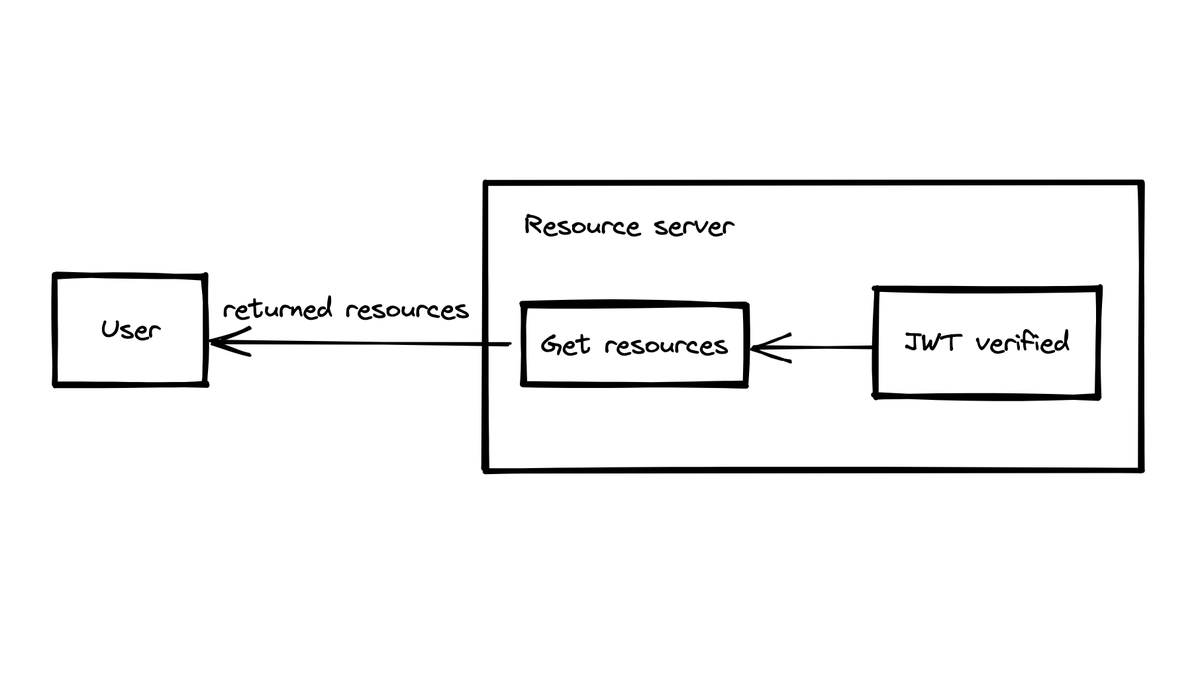
In the following, let's use a GET request as an example.
For this, cookies or databases can be used.
In the following, let's use a GET request as an example.
With that said, this is pretty much it for this thread.
Follow @Rapid_API for more exclusive content.
Visit RapidAPI Hub (RapidAPI.com) and get access to over 40,000 APIs. 🐙💙
Follow @Rapid_API for more exclusive content.
Visit RapidAPI Hub (RapidAPI.com) and get access to over 40,000 APIs. 🐙💙
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...