Blockchain, it's the technology behind cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum which hold ~$1,700,000,000,000 in value.
Changing the way we do finance and also shaping the next generation of the internet, web3.
Let's see how it works. This is the anatomy of a blockchain 🧵
Changing the way we do finance and also shaping the next generation of the internet, web3.
Let's see how it works. This is the anatomy of a blockchain 🧵
What is a blockchain? 🤔
The blockchain is a (A) decentralised, (B) immutable, (C) verfiable and (D) public ledger(list) of transactions.
Let's break this down.
The blockchain is a (A) decentralised, (B) immutable, (C) verfiable and (D) public ledger(list) of transactions.
Let's break this down.
The blockchain is basically a list of transactions that is...
(A) Distributed 🌐: Not owned or controlled by a central authority and is distrubuted amongst several nodes.
(B) Immutable 🔐: Transactions on the blockchain cannot be changed once they've gone through.
(A) Distributed 🌐: Not owned or controlled by a central authority and is distrubuted amongst several nodes.
(B) Immutable 🔐: Transactions on the blockchain cannot be changed once they've gone through.
(C) Verifiable ✅: Each and every transaction on the blockchain can be verified by anyone.
(D) Public 👪: The transactions on the blockchain can viewed by anyone.
(D) Public 👪: The transactions on the blockchain can viewed by anyone.
In more simple terms, a blockchain keeps track of transactions that take place on a network in an open and secure manner.
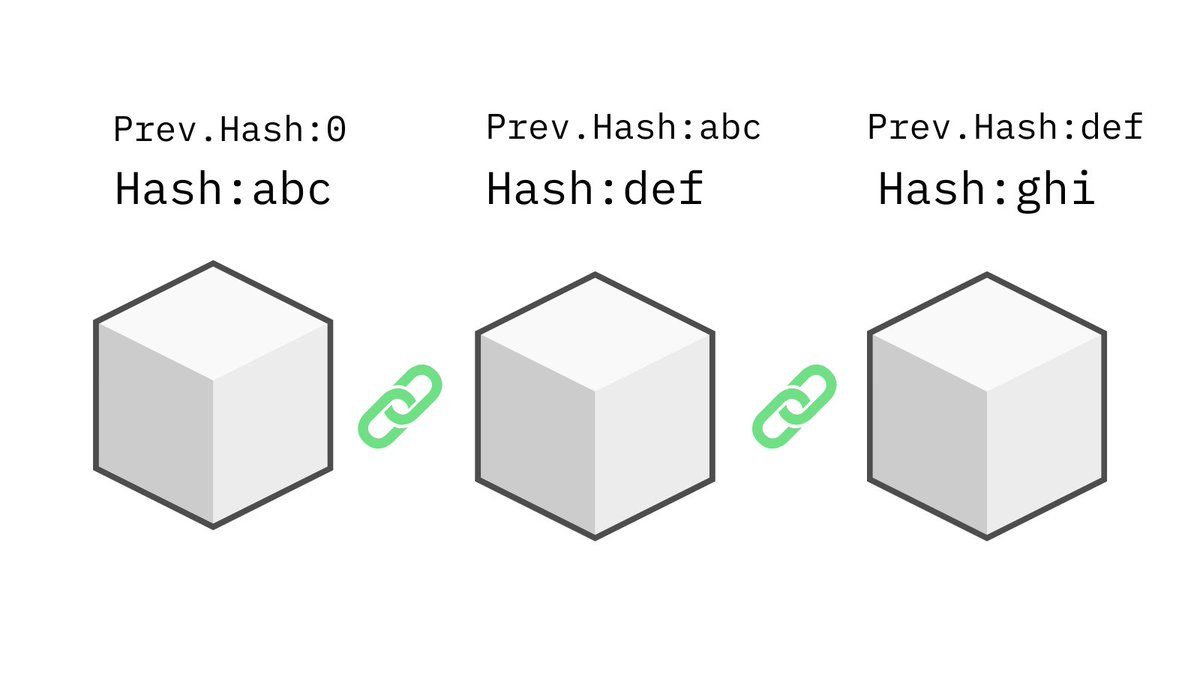
As the name suggests, the blockchain is a chain of 'blocks' connected to each other.
The blocks are individual transactions that place on the network.
As the name suggests, the blockchain is a chain of 'blocks' connected to each other.
The blocks are individual transactions that place on the network.
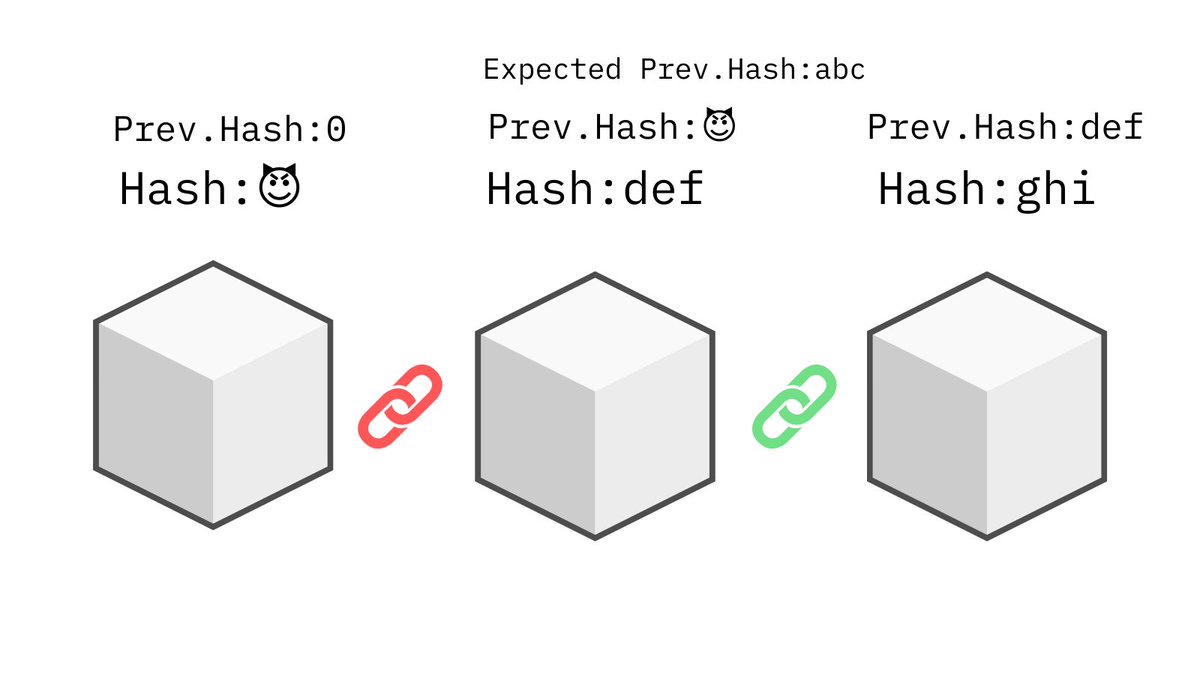
In order to change one transaction, you'd have to recalculate and make sure the hashes of all the other blocks match on the chain.
This is computationally intensive, however not impossible to achieve.
This is computationally intensive, however not impossible to achieve.
A modern computer could change the hash of a block and then figure out the corresponding hashes of the other blocks, making the blockchain valid and sucessfully tampering with a transaction.
This is obviously is a problem.
This is obviously is a problem.
It ensures all nodes are in agreement that the transactions that have taken place.
Different blockchains use different consensus protocols, bitcoin uses something called "Proof of Work", Solana operates on "Proof of History" and so on.
Different blockchains use different consensus protocols, bitcoin uses something called "Proof of Work", Solana operates on "Proof of History" and so on.
It is because of this consensus protocol that if you were trying to create a fradulent transaction on the blockchain, you'd have to have to control a huge number of the nodes which is (mostly) impossible.
This makes the blockchain secure and immutable.
This makes the blockchain secure and immutable.
In this thread we mainly learnt about:
• Some of the important properties of a blockchain
• What is a blockchain made up of?
• How does a blockchain validate transactions?
All this information gives us a good fundamental understanding of how a blockchain works.
• Some of the important properties of a blockchain
• What is a blockchain made up of?
• How does a blockchain validate transactions?
All this information gives us a good fundamental understanding of how a blockchain works.
In a future thread we will look at exactly how these hashes in the blocks work, consenus protocols along with the reason why do so many different blockchains exist and the problems they are trying to solve.
Make sure you retweet this thread and follow @PrasoonPratham for more!
Make sure you retweet this thread and follow @PrasoonPratham for more!
Loading suggestions...