#ثريد
راح نتكلم اليوم عن
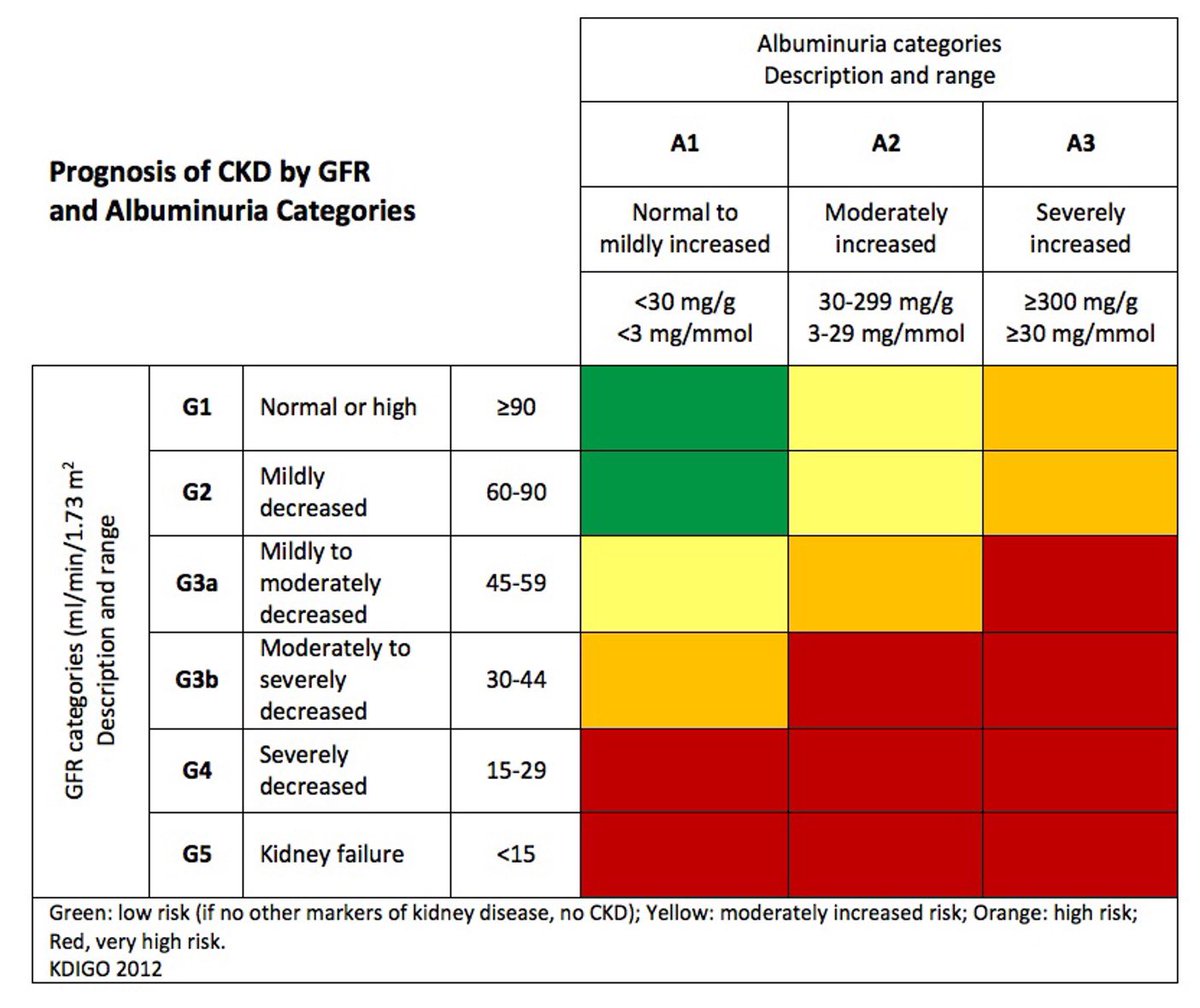
Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
للمختصين في المجال الصحي
كوب القهوة معاك ☕️ واستمتع ❤️
راح نتكلم اليوم عن
Chronic kidney disease (CKD)
للمختصين في المجال الصحي
كوب القهوة معاك ☕️ واستمتع ❤️
2- Diabetes mellitus
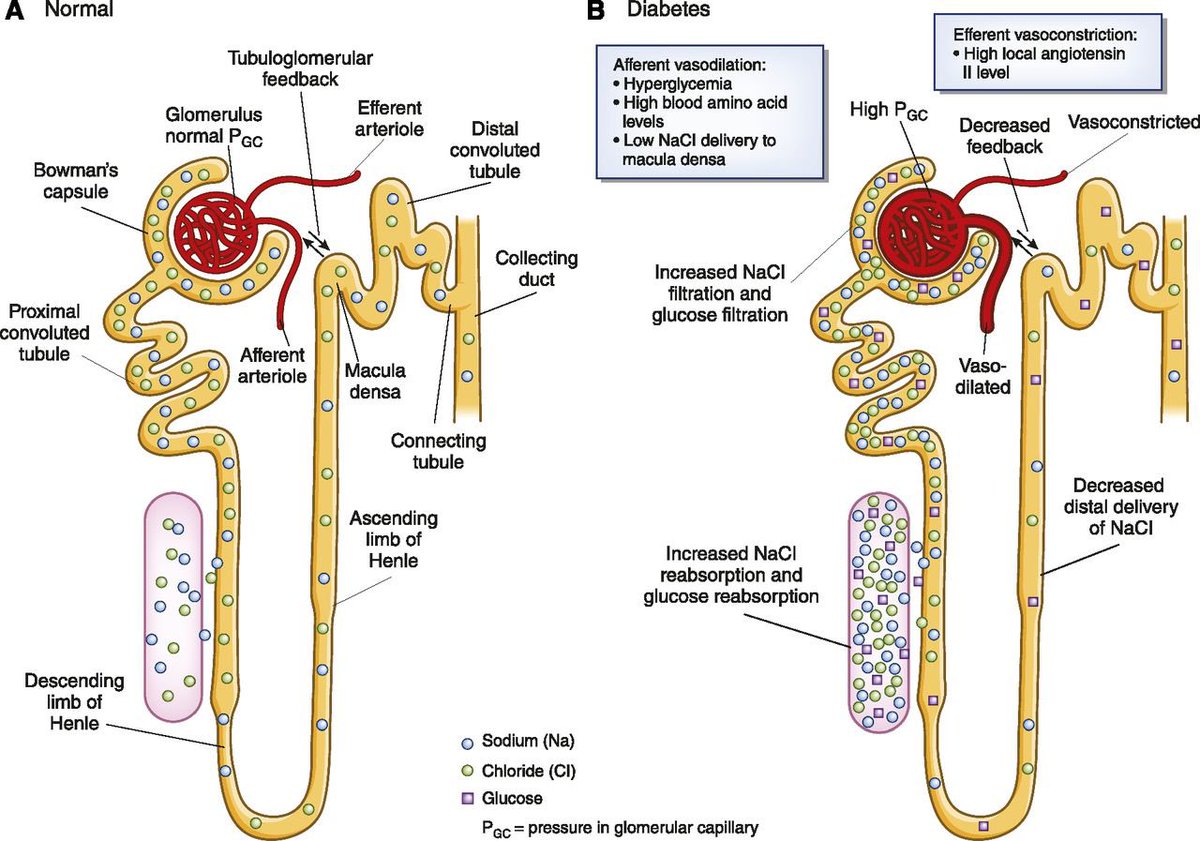
High glucose by (non-enzymatic glycosylation) ➡️ attach to protein and lipid ➡️ pre inflammatory molecules ➡️ arteriosclerosis /atherosclerosis – in E.A lead to:
>>>>>>
High glucose by (non-enzymatic glycosylation) ➡️ attach to protein and lipid ➡️ pre inflammatory molecules ➡️ arteriosclerosis /atherosclerosis – in E.A lead to:
>>>>>>
Signs and symptoms:
1- Electrolytes abnormalities
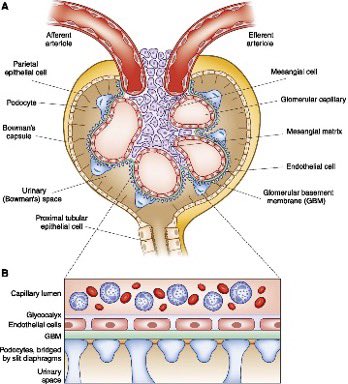
⁃Decrease GFR lead to hyperkalemia and hyperphosphatemia.
⁃Decrease alpha 1 hydroxylase that located in proximal tubular lead to decrease vitamin D which lead to hypocalcemia.
1- Electrolytes abnormalities
⁃Decrease GFR lead to hyperkalemia and hyperphosphatemia.
⁃Decrease alpha 1 hydroxylase that located in proximal tubular lead to decrease vitamin D which lead to hypocalcemia.
2- Fluid overload
⁃⬇️ GFR lead to ⬆️ H2O retention (fluid overload).
⁃⬆️ albuminuria (albumin is protein made by liver keep fluid in the blood stream so it doesn’t leak into tissues) so decrease albumin lead to fluid overload (pulmonary edema, HTN, peripheral edema).
⁃⬇️ GFR lead to ⬆️ H2O retention (fluid overload).
⁃⬆️ albuminuria (albumin is protein made by liver keep fluid in the blood stream so it doesn’t leak into tissues) so decrease albumin lead to fluid overload (pulmonary edema, HTN, peripheral edema).
3- Uremia and Azotemia
Kidney starts to damage ➡️ urea build up in blood (uremia) also (azotemia) is the buildup of nitrogen waste products in the blood (BUN and creatinine).
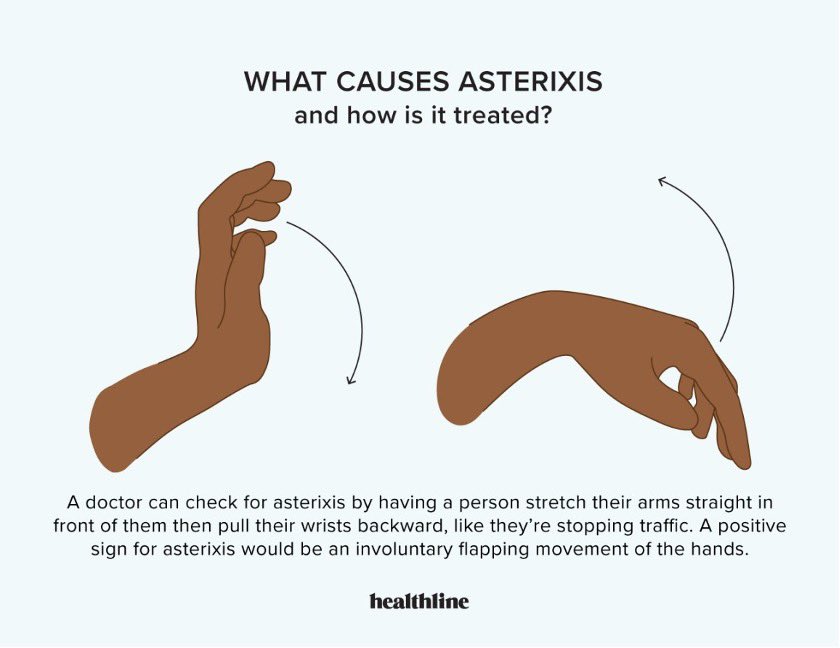
Uremia can cause (uremic pericarditis, uremic frost in skin, platelet dysfunction)
>>>>>
Kidney starts to damage ➡️ urea build up in blood (uremia) also (azotemia) is the buildup of nitrogen waste products in the blood (BUN and creatinine).
Uremia can cause (uremic pericarditis, uremic frost in skin, platelet dysfunction)
>>>>>
4- Hormone imbalance
⁃In proximal tubular, decrease Erythroprotien (EPO) lead to decease bone marrow function – decrease red blood cells (anemia).
⁃Decrease alpha 1 hydroxylase mean hypocalcemia, so parathyroid starts to produce parathyroid hormone (PTH), >>>>>>>
⁃In proximal tubular, decrease Erythroprotien (EPO) lead to decease bone marrow function – decrease red blood cells (anemia).
⁃Decrease alpha 1 hydroxylase mean hypocalcemia, so parathyroid starts to produce parathyroid hormone (PTH), >>>>>>>
5- Metabolic acidosis
Decrease alpha intercalated cells (located in distal convoluted tubule) lead to:
⁃⬇️ proton excretion
⁃⬇️ HCO3 reabsorption
6- Albumin regulation
⬇️ albumin in blood makes liver to produce lipoproteins (triglycerides and LDL) = hyperlipidemia
Decrease alpha intercalated cells (located in distal convoluted tubule) lead to:
⁃⬇️ proton excretion
⁃⬇️ HCO3 reabsorption
6- Albumin regulation
⬇️ albumin in blood makes liver to produce lipoproteins (triglycerides and LDL) = hyperlipidemia
3- Renal U/S
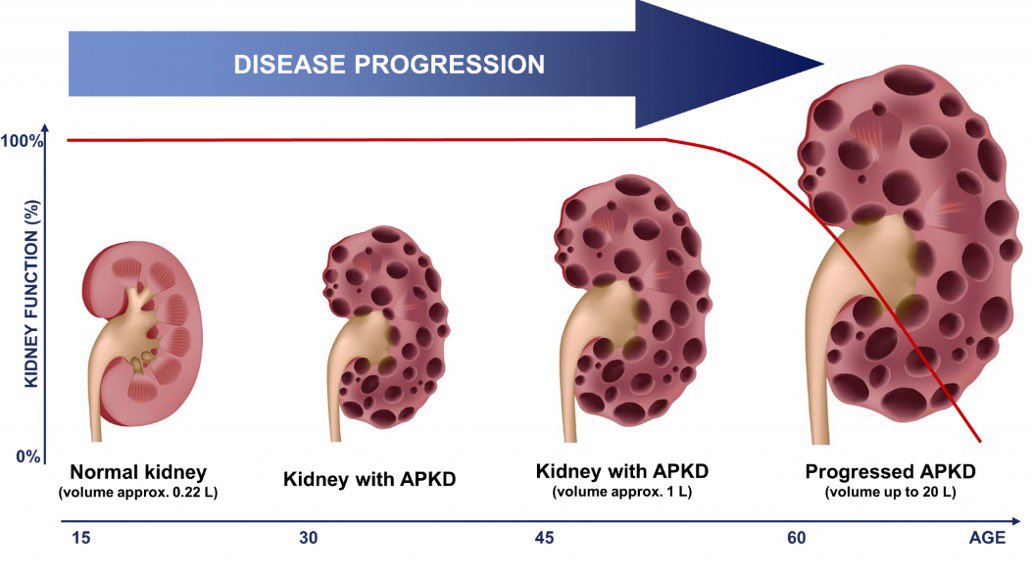
If we saw Cysts (PCKD)
If we saw kidney small (atrophic)
4- Renal biopsy + serology
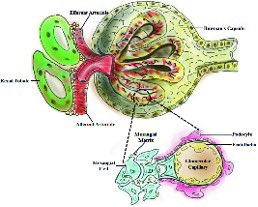
⁃Study on actual tissue to determine (glomerular nephritis)
⁃Serology of:
Anti-nuclear antibodies ANA (autoimmune disorder)
Rheumatoid factors RF (rheumatoid arthritis)
If we saw Cysts (PCKD)
If we saw kidney small (atrophic)
4- Renal biopsy + serology
⁃Study on actual tissue to determine (glomerular nephritis)
⁃Serology of:
Anti-nuclear antibodies ANA (autoimmune disorder)
Rheumatoid factors RF (rheumatoid arthritis)
5- Additional labs
BMP
⁃K+ high, ca++ low, Na+ variable
⁃Add phosphate (low), CBC (RBC’S low) anemia normotic (normal mcv).
ABG
H+ high, HCO3 low
Lipid panel
TG and LDL high
PTH high
BMP
⁃K+ high, ca++ low, Na+ variable
⁃Add phosphate (low), CBC (RBC’S low) anemia normotic (normal mcv).
ABG
H+ high, HCO3 low
Lipid panel
TG and LDL high
PTH high
Treatment
Treat underlying causes:
⁃HTN (ACE-I, ARBS, K+ sparing like Spirolactone, diuretics)
⁃DM (for type 1 - insulin, antidiabetics like metformin, weight loss)
⁃Glomerulonephritis (steroid, DMARD’S)
⁃PCKD (renal transplant)
Treat underlying causes:
⁃HTN (ACE-I, ARBS, K+ sparing like Spirolactone, diuretics)
⁃DM (for type 1 - insulin, antidiabetics like metformin, weight loss)
⁃Glomerulonephritis (steroid, DMARD’S)
⁃PCKD (renal transplant)
Treat complications:
⁃Hyperkalemia (insulin, SABA, HCO3, diuretics and Na+ polystyrene sulfonate)
⁃Hyperphosphatemia (sevelamer hydrochloride by binding phosphate in the gastrointestinal tract and decreasing absorption.
⁃Hypocalcemia (give calcium, may give vitamin D)
>>
⁃Hyperkalemia (insulin, SABA, HCO3, diuretics and Na+ polystyrene sulfonate)
⁃Hyperphosphatemia (sevelamer hydrochloride by binding phosphate in the gastrointestinal tract and decreasing absorption.
⁃Hypocalcemia (give calcium, may give vitamin D)
>>
⁃hyperparathyroidism (Cinacalcet is used to treat secondary hyperparathyroidism) if failed (parathyroidectomy)
⁃⬇️ Erythropoietin (EPO) lead to decrease RBC’s (aim to keep Hgb 8-10) give EPO synthetic.
⁃Metabolic acidosis (NaHCO₃ push or infusion)
>>>>
⁃⬇️ Erythropoietin (EPO) lead to decrease RBC’s (aim to keep Hgb 8-10) give EPO synthetic.
⁃Metabolic acidosis (NaHCO₃ push or infusion)
>>>>
⁃⬆️ albumnuria (ACE-I or ARB’s)
⁃⬆️ T.G and LDL (statins) also it’s risk of bleeding give DDAVP(1-desamino-8-d-arginine vasopressin) to increase platelets activities
⁃CKD worsen ⬇️ GFR until stage IV or V (dialysis)
⁃⬆️ T.G and LDL (statins) also it’s risk of bleeding give DDAVP(1-desamino-8-d-arginine vasopressin) to increase platelets activities
⁃CKD worsen ⬇️ GFR until stage IV or V (dialysis)
جاري تحميل الاقتراحات...