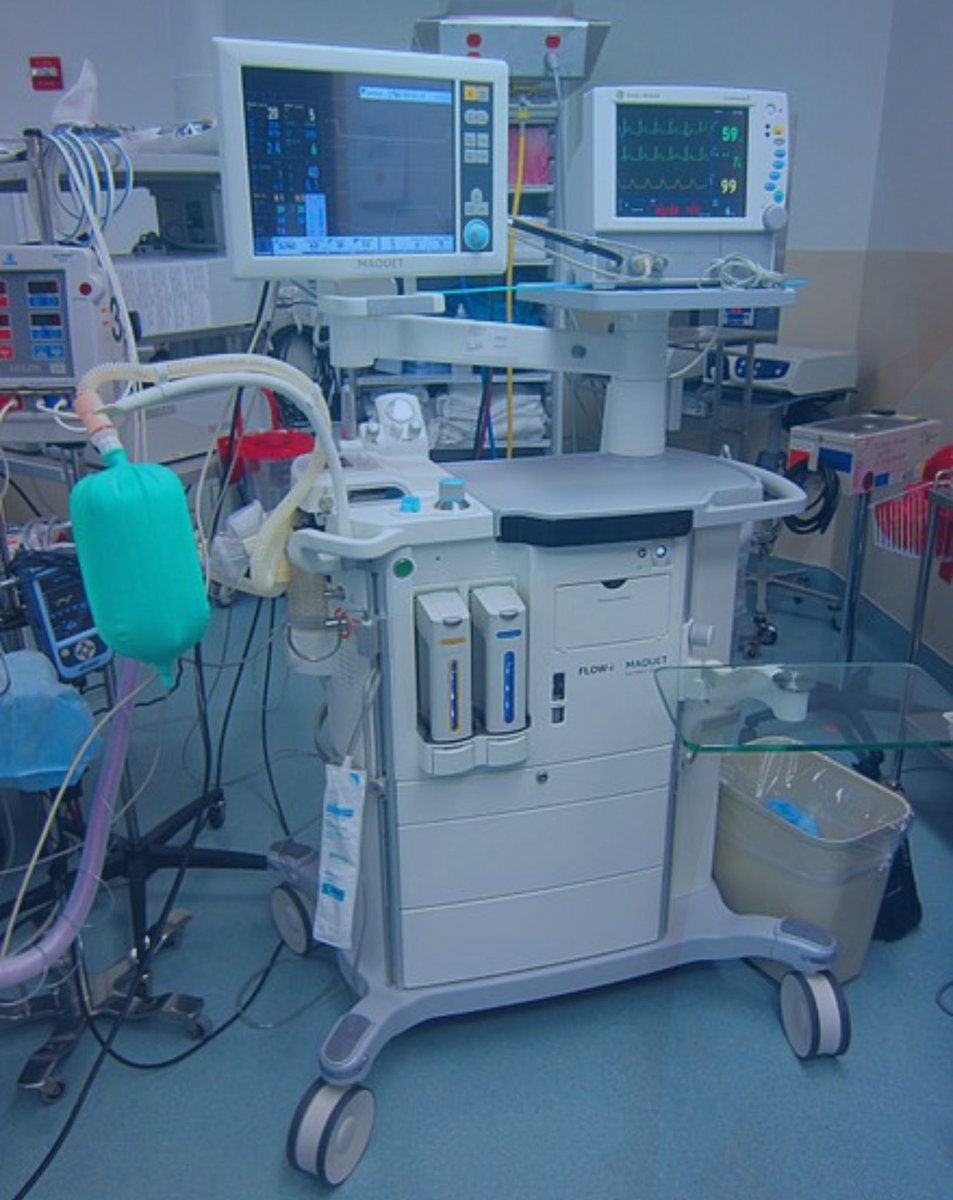
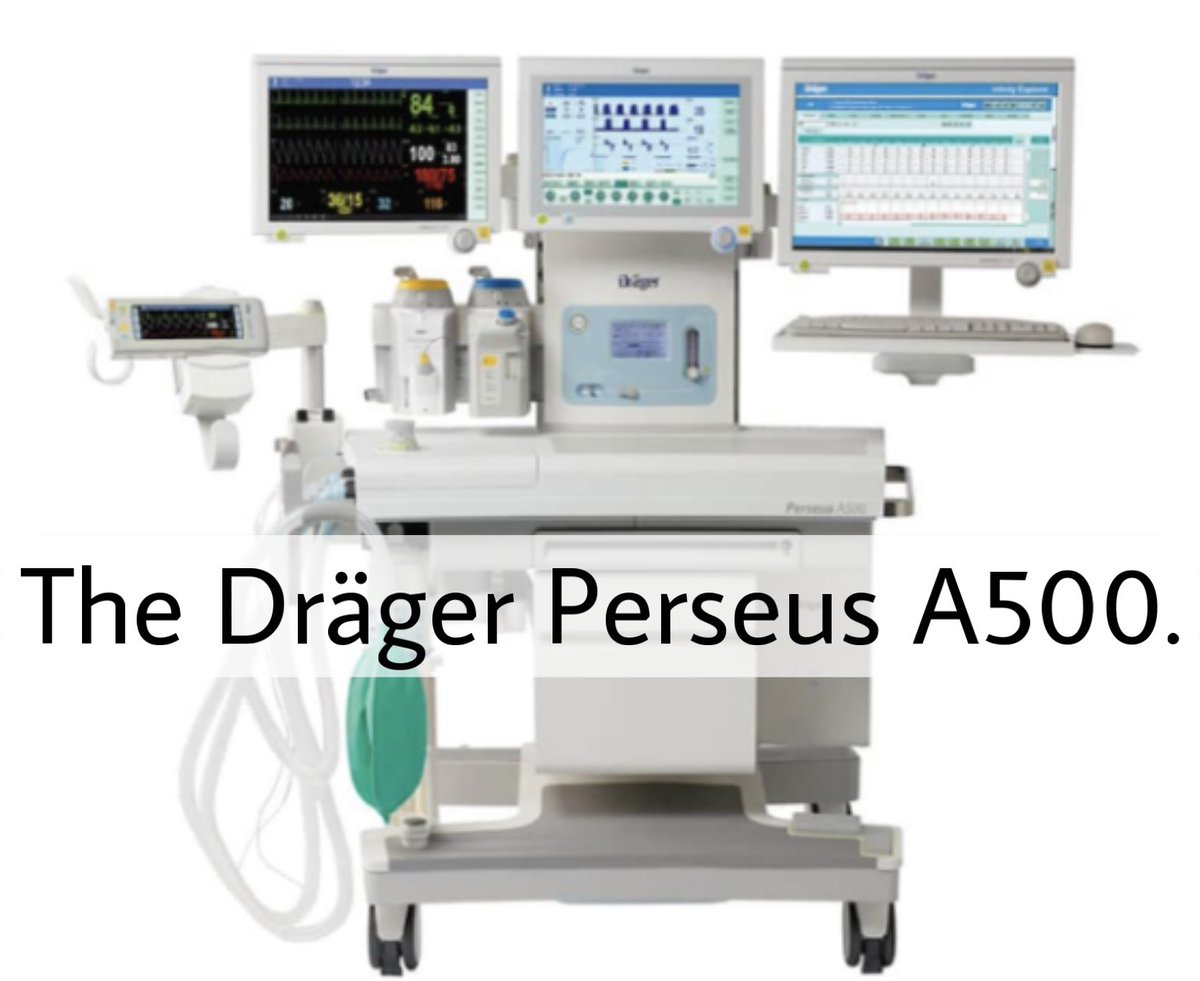
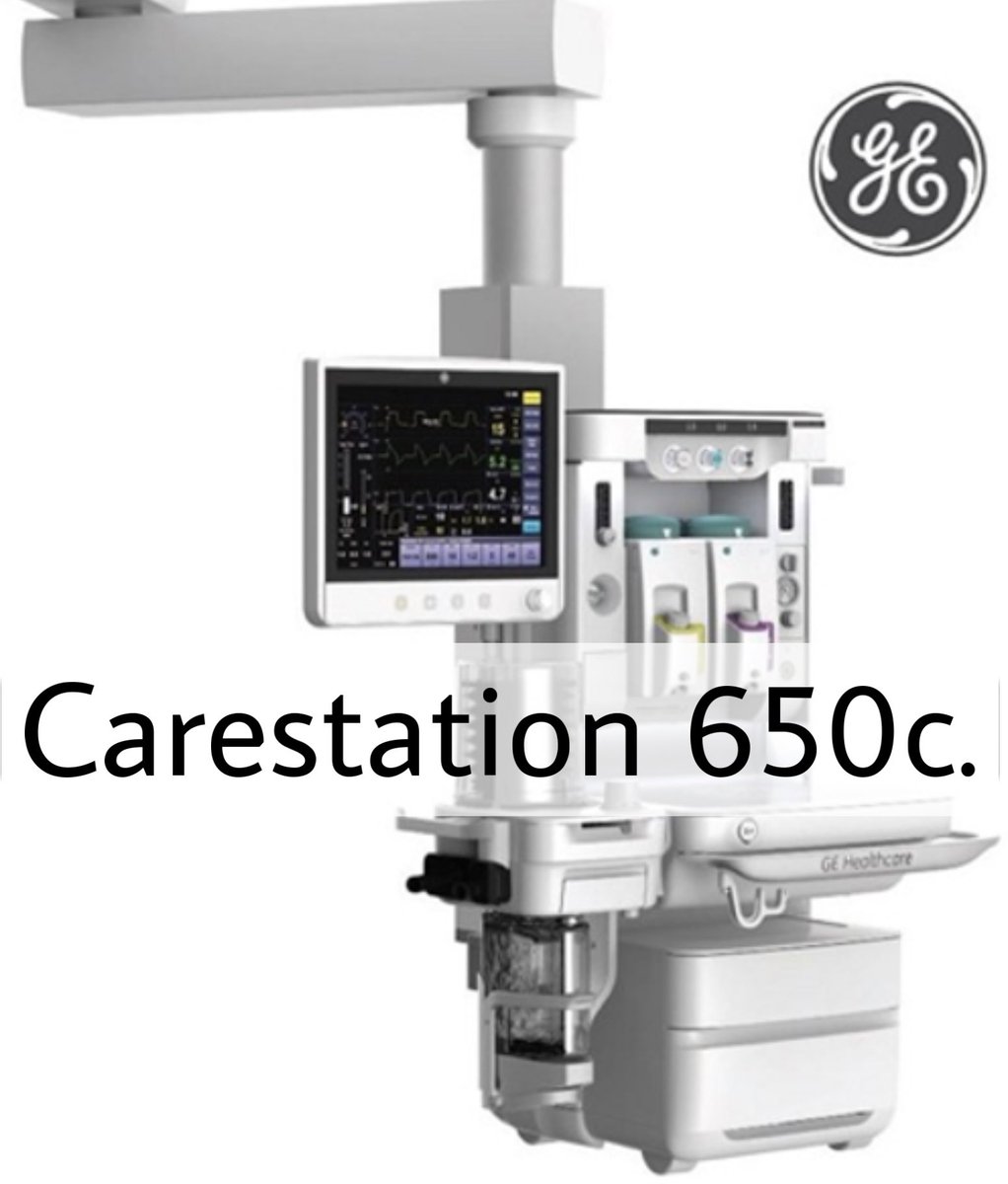
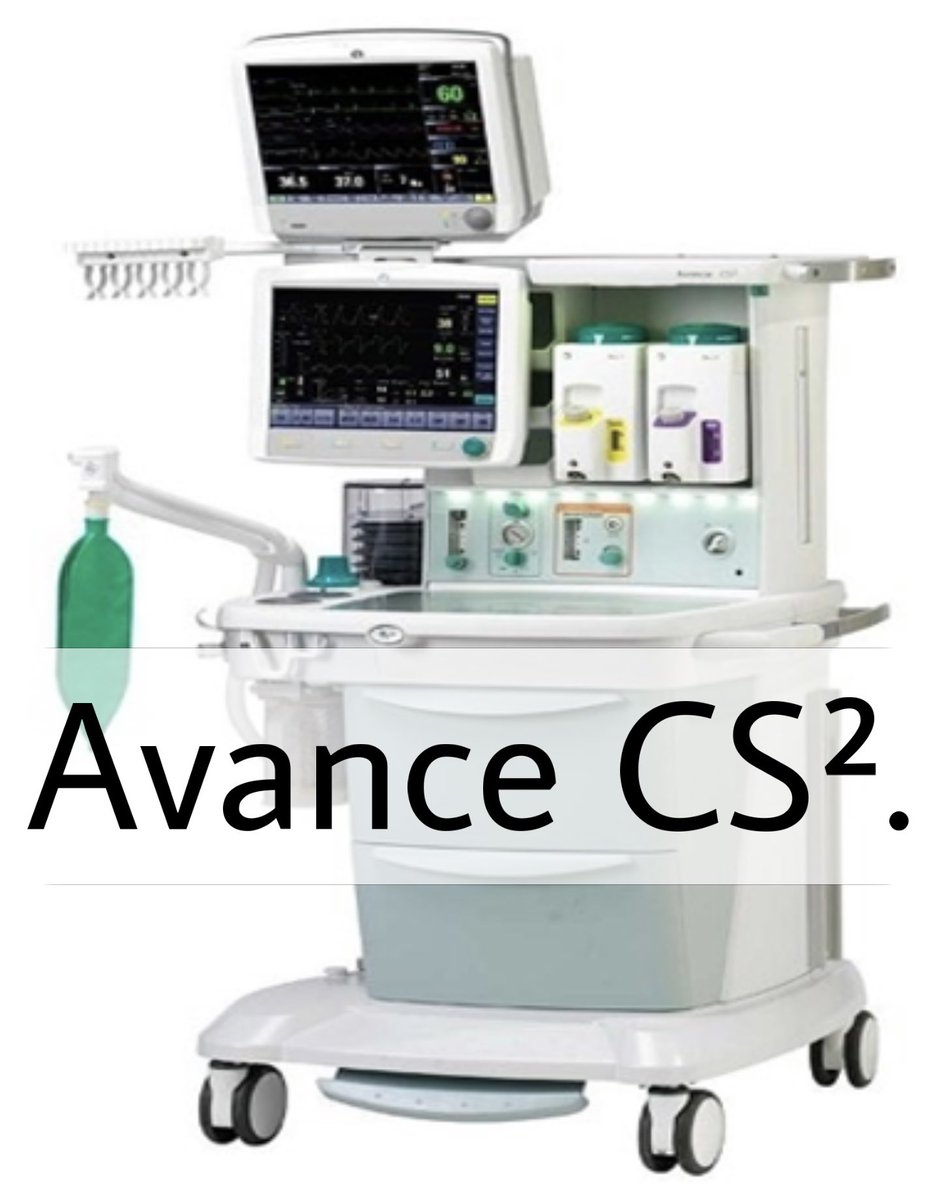
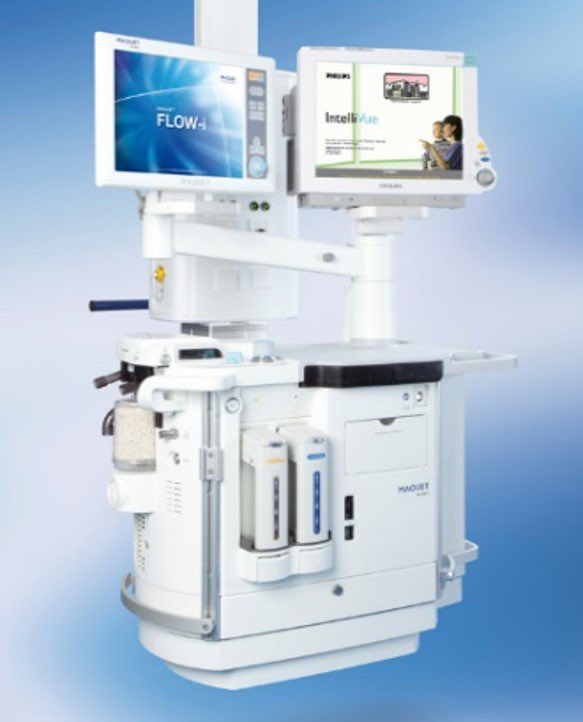
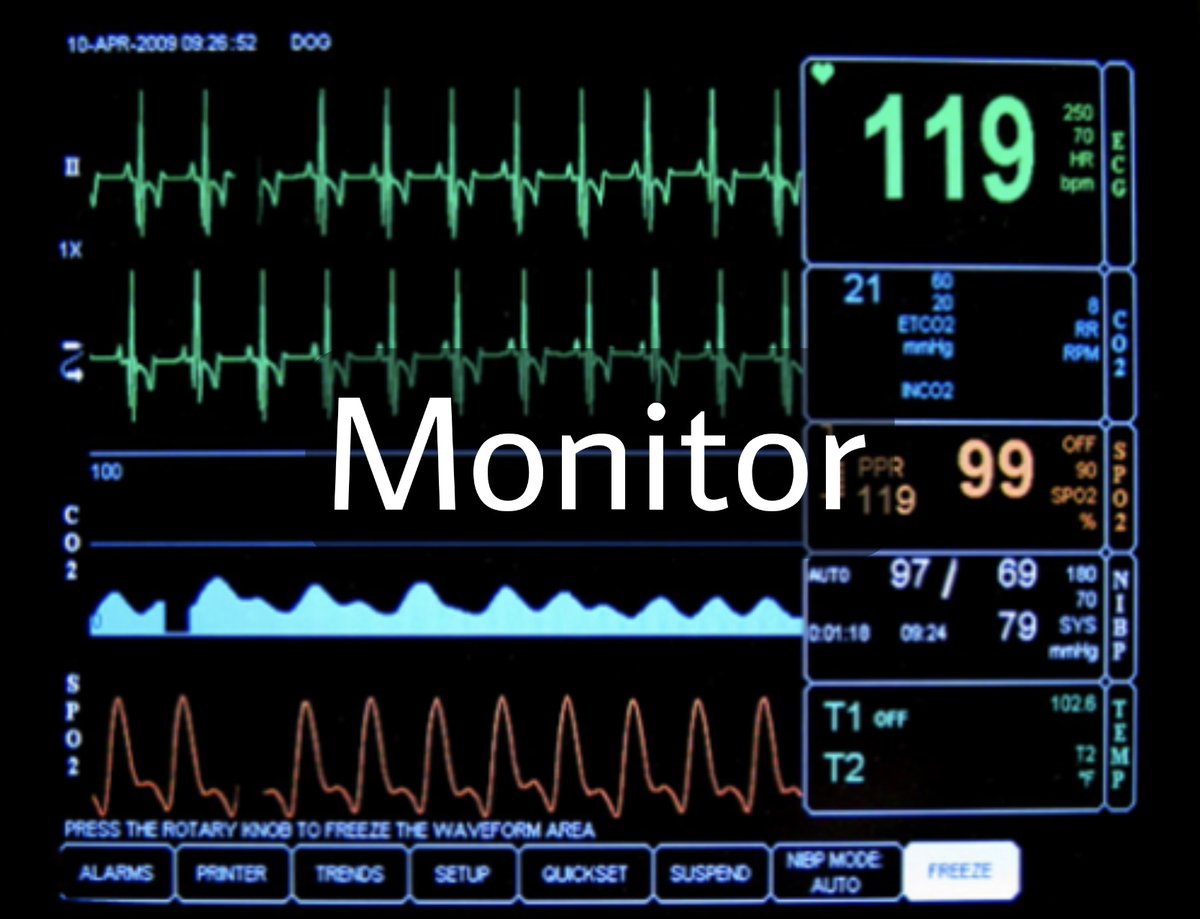
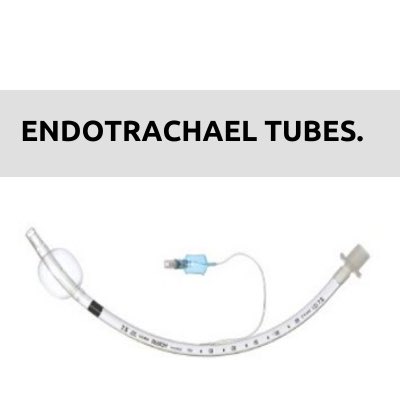
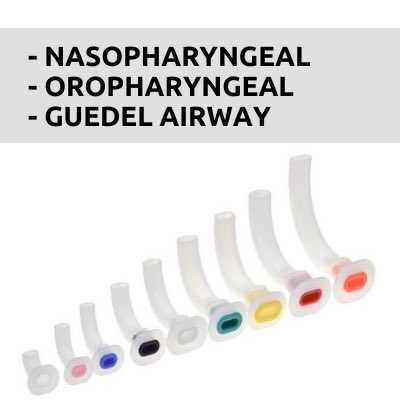
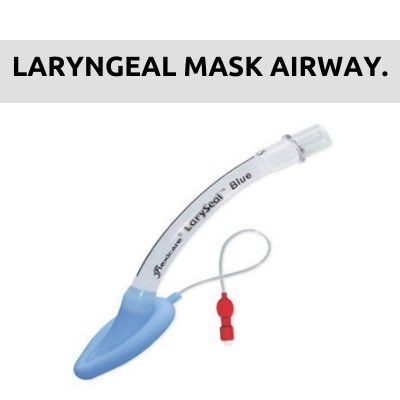
The main purpose of anesthesia machine is to prevent patients from pain during surgery. It also delivers gases to them.
ECRI NO. for Anesthesia unit is 10134.
ECRI NO. for Anesthesia unit is 10134.
Specialized doctors called anesthetists are the users of anesthesia, usually supported by a specialist team of nurses and technicians. anesthesia devices are located in hospitals: operating rooms, and some clinics such as the dental clinic, the eye clinic.
Due to the high risk on the patient, anesthesia machine is classified as a class IIb device. It also classified as a type BF as it has medium term contact with patient.
An anesthesia machine is a portable device in which it can operates by portable compressed nitrous oxide, oxygen cylinders and other additions to the circuit. It also can be operated when it connected to a medical gases system that is present inside the operation room (OR).
During the installation process of anesthesia machine, The following test equipment are used:
1. Gas analyzer, to check:
flow rate, pressure, Oxygen concentration, Nitrous Oxide concentration.
2. Patient simulator.
1. Gas analyzer, to check:
flow rate, pressure, Oxygen concentration, Nitrous Oxide concentration.
2. Patient simulator.
The Principle of Operation:
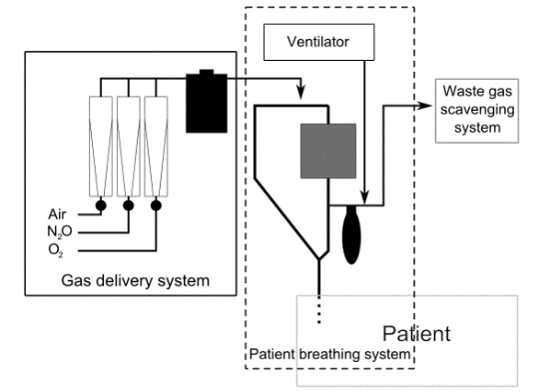
1.The anesthesia machine receives the gases from the gas delivery system.
2. IT controls the flow and reduces the pressure of these gases to a safe level by the gas flowmeter.
1.The anesthesia machine receives the gases from the gas delivery system.
2. IT controls the flow and reduces the pressure of these gases to a safe level by the gas flowmeter.
Test Equipment and PPM:
• PPM for anesthesia machine is done annually, There is a self-check by the anesthesia
machine and it is done every time it is turned on.
• The following systems will be checked once the machine is turned on:
• PPM for anesthesia machine is done annually, There is a self-check by the anesthesia
machine and it is done every time it is turned on.
• The following systems will be checked once the machine is turned on:
1) High pressure system.
a. O2 cylinder: contents.
b. pipelines: connections.
2) Low pressure system.
a. control valves/flow meters.
b. Vaporizers.
c. breathing system.
d. O2 failure device.
e. O2 flush.
a. O2 cylinder: contents.
b. pipelines: connections.
2) Low pressure system.
a. control valves/flow meters.
b. Vaporizers.
c. breathing system.
d. O2 failure device.
e. O2 flush.
3) Ventilator.
a. Function.
b. Leaks.
c. low pressure alarm.
4) Scavenging system.
a. Connections.
b. Suction on
a. Function.
b. Leaks.
c. low pressure alarm.
4) Scavenging system.
a. Connections.
b. Suction on
Common problems:
1. low pressure due to a leakage or sensors are not positioned correctly.
2. Flowmeter problems due to gas leak.
3. Vaporizer's failure while changing the anesthetic liquid into vapour.
1. low pressure due to a leakage or sensors are not positioned correctly.
2. Flowmeter problems due to gas leak.
3. Vaporizer's failure while changing the anesthetic liquid into vapour.
Fault and Solutions:
1. Equipment is not running: Check main power socket, refer to electrician for repair.
2. No gas output: Restore gas supply, replace O2cylinder and/or N2O cylinder.
3. O2 alarm failure: Contact the manufacturer or a technician.
1. Equipment is not running: Check main power socket, refer to electrician for repair.
2. No gas output: Restore gas supply, replace O2cylinder and/or N2O cylinder.
3. O2 alarm failure: Contact the manufacturer or a technician.
4. Machine has leaks: Clean leaking seal or gasket, replace if broken, contact the manufacturer.
5. Flowmeter fault: Refer to biomedical technician.
6. Electrical shocks: Refer to electrician immediately.
5. Flowmeter fault: Refer to biomedical technician.
6. Electrical shocks: Refer to electrician immediately.
Loading suggestions...