What is chemotherapy?
Also called “chemo,” it’s a way to treat cancer that uses drugs to kill cancer cells.
Also called “chemo,” it’s a way to treat cancer that uses drugs to kill cancer cells.
How does chemotherapy work?
It targets cells that grow and divide quickly, as cancer cells do. Unlike radiation or surgery, which target specific areas
It targets cells that grow and divide quickly, as cancer cells do. Unlike radiation or surgery, which target specific areas
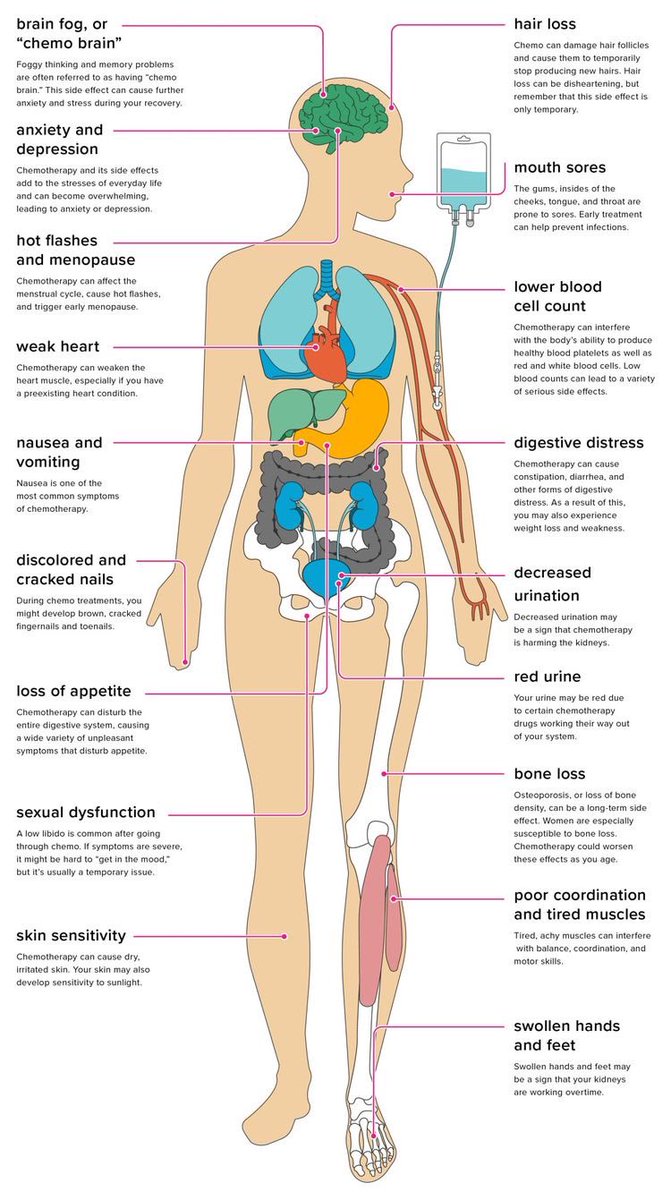
chemo can work throughout the body. But it can also affect some fast-growing healthy cells, like those of the skin, hair, intestines, and bone marrow.
What does chemotherapy do?
It depends on the kind of cancer and how far along it is.
* Cure: destruction of cancer cells to the point that they can’t be detected anymore in the body.
It depends on the kind of cancer and how far along it is.
* Cure: destruction of cancer cells to the point that they can’t be detected anymore in the body.
* Control: only to keep cancer from spreading to other parts of your body or slow the growth of cancer tumors.
* Ease symptoms: In some cases, chemotherapy can’t cure or control the spread of cancer and is simply used to shrink tumors that cause pain or pressure. These tumors often continue to grow back.
Administrations of chemotherapeutic drugs requires skills in addition to those used when giving other drugs. only specially trained nurses and physicians should administer chemotherapeutic drugs.
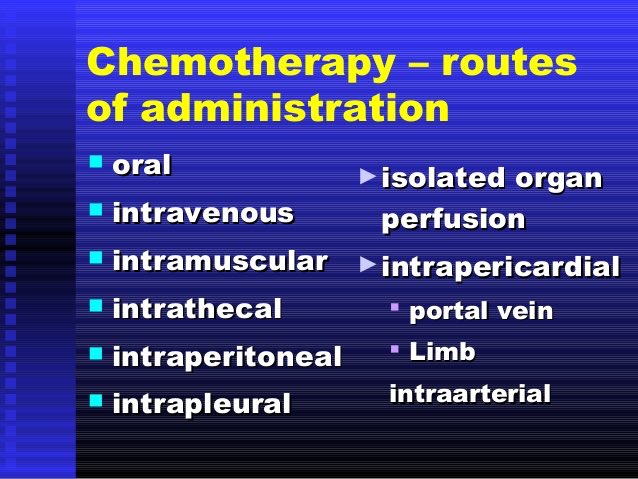
The administration route depends on the drugs pharmacodynamic and the tumors characteristics
for example : malignant tumor is confined to one area
for example : malignant tumor is confined to one area
Drug may be administered through a localized or regional method
It will allow to deliver of a drug dose directly to the tumor this is advantageous, because many solid tumors don’t respond to drug levels that are save for systemic administrations.
It will allow to deliver of a drug dose directly to the tumor this is advantageous, because many solid tumors don’t respond to drug levels that are save for systemic administrations.
• IV administration of chemotherapeutic drugs may lead to extra-vasation , which can cause blistering , peeling and tissue necrosis ,functional and sensory impairment of the effected area , damage to tendons , nerves and joints
Special considerations
• If some of the drugs come in contact with the skin wash the area with soap not with germicidal agent . If I contact a course flood the eye with water or saline solution for at least 15minutes while holding the eye lid open
• If some of the drugs come in contact with the skin wash the area with soap not with germicidal agent . If I contact a course flood the eye with water or saline solution for at least 15minutes while holding the eye lid open
•If a spill occurs use chemotherapeutic spill kit to clean the area
•Don’t place any food or drinks in the same refrigerator as chemotherapeutic drugs
•Provide male patients with a urinal with a tight fitting lid
•Wear disposable latix surgical gloves when handling body fluid
•Don’t place any food or drinks in the same refrigerator as chemotherapeutic drugs
•Provide male patients with a urinal with a tight fitting lid
•Wear disposable latix surgical gloves when handling body fluid
• Women who are pregnant trying conceive or breast feeding should exercise caution when handling chemotherapeutic drugs
• During infusion some drugs need protection from direct sunlight in this
case cover the container with brown paper bag or aluminum foil
• During infusion some drugs need protection from direct sunlight in this
case cover the container with brown paper bag or aluminum foil
• Scalp veins shouldn’t be used to administer vesicant drugs to neonate or
pediatric patient
• monitor the patient vital signs through out the infusion
pediatric patient
• monitor the patient vital signs through out the infusion
• monitor the patient cumulative chemotherapy dose to make sure that the drug is discontinued if the maximum life time dose is achieved
• During IV administration closely monitor the patient for signs of hypersensitivity reaction (agitation chest tightness , shortness of breath ,hypotenstion , rash , itching , facial edema , light headache , dizzyness , and abdominal cramping) or extravasation .
• When administering vesicant drug by short term infusion using peripheral vein stay with the patient during the infusion monitor the site for extravasation and verify blood return every 5 to 10 minutes
تم بواسطة @NursesCap شكرًا ل إثرائك المحتوى العلمي في منظومة My way nursing
Loading suggestions...